
Continuation of: The Literary Finder: A Multi-Agent System for Deep Literary Discovery
This publication demonstrates the production-ready implementation of The Literary Finder multi-agent system, showcasing the transformation from research prototype to enterprise-grade deployment. Building on the foundational multi-agent architecture established in our previous publication, this work focuses on production engineering excellence, comprehensive testing strategies, user interface design, and operational reliability with specific emphasis on:
Production Achievements:
The transition from research prototype to production deployment presents unique challenges for multi-agent AI systems, particularly regarding infrastructure complexity, user accessibility, and operational overhead. Traditional deployment approaches often require significant DevOps expertise, server management, and ongoing maintenance costs that can limit the accessibility and adoption of agentic AI applications. HuggingFace Spaces emerges as an optimal solution for democratizing AI deployment by providing managed infrastructure, automatic scaling, and built-in sharing capabilities that eliminate traditional deployment barriers.
For this project, deployment strategy prioritizes user accessibility and operational simplicity while maintaining production-grade reliability. HuggingFace Spaces offers several critical advantages for multi-agent systems: zero infrastructure management eliminates server provisioning and maintenance overhead; automatic scaling handles variable user loads without manual intervention; built-in security features provide HTTPS encryption and environment isolation; and the community-driven platform facilitates easy discovery and collaboration. The platform's native Gradio integration allows for sophisticated user interfaces while maintaining deployment simplicity, making advanced AI capabilities accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
The architectural decision to optimize specifically for HuggingFace Spaces, while maintaining compatibility with Docker-based deployments, reflects a strategic balance between accessibility and flexibility. This approach enables rapid deployment and iteration cycles essential for production AI systems, while providing fallback options for enterprise environments requiring custom infrastructure. The following sections detail the technical implementation of this cloud-native deployment strategy, demonstrating how modern platform-as-a-service solutions can effectively support sophisticated multi-agent AI applications.
HuggingFace Spaces Configuration:
The Literary Finder is specifically optimized for HuggingFace Spaces deployment, leveraging the platform's managed infrastructure and seamless sharing capabilities:
# README.md - HuggingFace Spaces Metadata --- title: The Literary Finder emoji: 📚 colorFrom: blue colorTo: purple sdk: gradio sdk_version: "5.39.0" app_file: app.py pinned: false ---
The production environment cab be found at: https://poacosta-literary-finder.hf.space/
HuggingFace Spaces Benefits:
This application runs on the CPU-basic hardware plan (2vCPU + 16GB RAM) with all required environment variables configured.
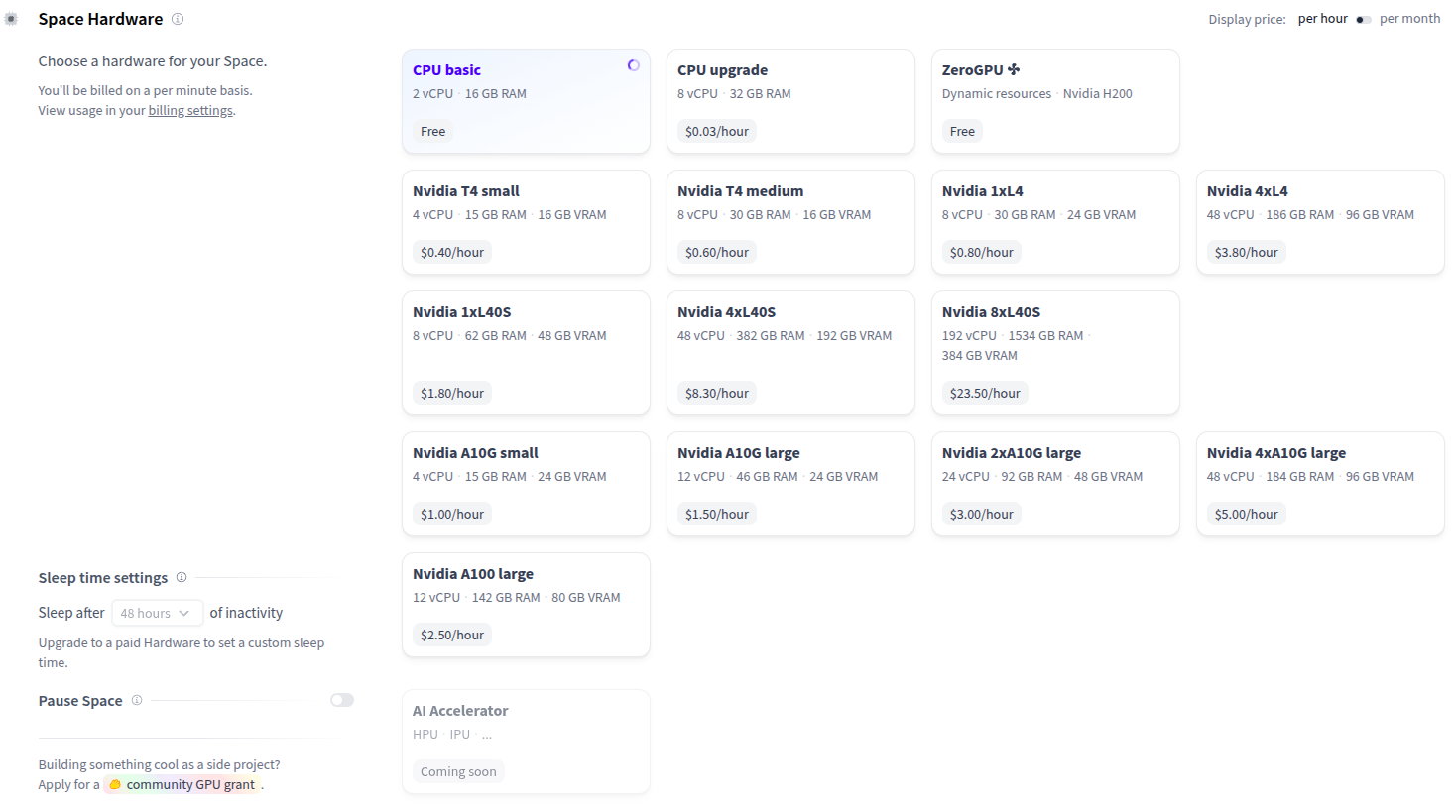
If your Space runs on the default cpu-basic hardware, it will go to sleep if inactive for more than a set time (currently, 48 hours). Anyone visiting the Space will restart it automatically.
If you want your Space to remain continuously active or if you want to set a custom sleep time, you need to upgrade to paid hardware. For the demonstration purposes of this app, the default plan fits well.
While optimized for HuggingFace Spaces, the system supports a containerized deployment strategy using Docker to ensure consistent, reproducible deployments across different environments. The system leverages a multi-layered containerization approach optimized for production AI applications.
FROM python:3.11-slim WORKDIR /app COPY . . RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \ pip install --no-cache-dir -e .[dev] EXPOSE 7860 CMD ["literary-finder", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "7860"]
The container architecture utilizes:
-e .[dev]) enabling development-time code modificationsThe deployment implements a hierarchical configuration system:
OPENAI_API_KEY, GOOGLE_API_KEYLANGCHAIN_API_KEY, LANGCHAIN_PROJECTLOG_LEVEL, REQUEST_TIMEOUT, MAX_CONCURRENT_REQUESTSIn order to fulfill:
MAX_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS=3)REQUEST_TIMEOUT=180)This deployment alternative offers several advantages:
Previously mentioned options cover the application needs, with mostly common specs. However, it may be useful to clarify the application prerequisites and requirements for all on-premise or cloud deployments.
All Python dependencies are automatically installed. See requirements.txt for complete list:
Quality assurance for multi-agent AI systems presents fundamentally different challenges compared to traditional software applications. The non-deterministic nature of AI agents, combined with complex inter-agent dependencies and external API integrations, creates a testing landscape where conventional approaches often fall short. Traditional unit testing methodologies, while necessary, are insufficient for validating emergent behaviors that arise from agent coordination, handling of partial failures across distributed AI components, and ensuring consistent quality of generated content under varying operational conditions.
In this project, testing strategy addresses these challenges through a three-tier testing pyramid specifically designed for agentic AI systems. The foundation layer focuses on deterministic component behavior, ensuring individual agents respond predictably to known inputs and handle error conditions gracefully. The integration layer validates multi-agent coordination patterns, testing how agents share information, handle dependencies, and maintain system coherence when individual components fail. The end-to-end layer validates complete user workflows under production conditions, including API rate limiting, network interruptions, and real-world usage patterns that cannot be simulated in isolation.
This comprehensive approach recognizes that multi-agent systems exhibit emergent properties that cannot be validated through component testing alone. Agent coordination behaviors, quality assessment algorithms, and user experience patterns only manifest when the complete system operates under realistic conditions. The testing strategy therefore emphasizes not just code coverage, but behavioral coverage that validates the system's ability to deliver consistent, high-quality results across the full spectrum of operational scenarios. The following sections detail how this testing philosophy translates into concrete validation techniques that ensure production reliability for complex AI systems.
The Literary Finder implements a robust three-tier testing pyramid ensuring comprehensive coverage and reliable production deployment:
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Test Pyramid │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ╭─────────────╮ │
│ ╱ E2E Tests ╲ │
│ ╱_________________╲ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ ╱ API & Interface ╲ │
│ ╱ Tests ╲ │
│ ╱_________________________╲ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ ╱ Unit Tests ╲ │
│ ╱ (Agent Behavior & ╲ │
│ ╱ Component Logic) ╲ │
│╱___________________________________╲│
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
This testing strategy addresses three fundamental challenges in multi-agent AI systems:
Scope: Individual agent behavior and core component logic
Agent Behavior Validation:
# literary_finder/tests/unit/test_contextual_historian.py class TestContextualHistorian: def test_biographical_parsing_accuracy(self): """Test biographical data extraction accuracy.""" agent = ContextualHistorian() test_output = "Born 1928, died 2014, American author and civil rights activist" result = agent._parse_research_results(test_output, "Maya Angelou") assert isinstance(result, AuthorContext) assert result.birth_year == 1928 assert result.death_year == 2014 assert result.nationality == "American" def test_error_handling_resilience(self): """Test agent resilience to API failures.""" agent = ContextualHistorian() # Simulate API failure with patch.object(agent.search_api, 'search_author_biography', side_effect=ConnectionError("API unavailable")): result = agent.process("Test Author") assert result["success"] is False assert "error" in result assert "API unavailable" in result["error"]
Component Validation Tests:
# literary_finder/tests/unit/test_models.py def test_full_state_flow(): """Test creating a full LiteraryFinderState with all nested models.""" # Test complete workflow state management entry = ReadingMapEntry(title="Book", year=2001) reading_map = ReadingMap(start_here=[entry], chronological=[entry]) author_ctx = AuthorContext(birth_year=1950, nationality="Test") state = LiteraryFinderState( author_name="Test Author", results=AgentResults( contextual_historian=author_ctx, literary_cartographer=reading_map ) ) # Validate state transitions state.agent_statuses["contextual_historian"] = AgentStatus.COMPLETED assert state.agent_statuses["contextual_historian"] == AgentStatus.COMPLETED assert state.results.contextual_historian.birth_year == 1950
Scope: Agent coordination, API interfaces, and cross-component workflows
Multi-Agent Coordination Tests:
# literary_finder/tests/integration/test_models_integration.py def test_complete_workflow_integration(): """Test end-to-end multi-agent coordination.""" # Test agent coordination workflow state = LiteraryFinderState(author_name="Virginia Woolf") # Simulate agent completion sequence state.agent_statuses["contextual_historian"] = AgentStatus.COMPLETED state.agent_statuses["literary_cartographer"] = AgentStatus.COMPLETED state.agent_statuses["legacy_connector"] = AgentStatus.COMPLETED # Verify system integrity assert len(state.agent_statuses) == 3 assert all(status == AgentStatus.COMPLETED for status in state.agent_statuses.values()) def test_partial_failure_handling(): """Test graceful degradation with partial agent failures.""" graph = LiteraryFinderGraph() # Simulate partial failure scenario with patch.object(graph.historian, 'process', return_value={"success": False, "error": "API timeout"}): result = graph.process_author("Test Author") # System should continue with other agents assert "errors" in result assert len(result["errors"]) == 1
API Integration Tests:
# literary_finder/tests/integration/test_api_interface.py def test_api_analyze_performance(): """Test production API endpoint with performance validation.""" response = client.post("/analyze", json={ "author_name": "Maya Angelou", "enable_parallel": True }) assert response.status_code == 200 data = response.json() assert data["success"] is True assert len(data["final_report"]) > 10000 # Comprehensive content assert data["processing_time_seconds"] < 120 # Performance requirement
Scope: Complete user workflows under production conditions
Production Interface Testing:
# test_gradio.py - HuggingFace Spaces Compatibility def test_gradio_interface_creation(): """Test Gradio 5.x interface compatibility for HF Spaces.""" # Test Gradio version compatibility import gradio as gr print(f"✅ Gradio version: {gr.__version__}") # Test interface creation app = create_gradio_app() assert app is not None # Test HF Spaces specific features with gr.Blocks() as demo: gr.Markdown("# Test Interface") text_input = gr.Textbox(label="Input") btn = gr.Button("Test") btn.click(fn=lambda x: x, inputs=[text_input], outputs=[text_input]) print("✅ HuggingFace Spaces interface validated")
To measure testing effectiveness quantitatively, Literary Finder implements test coverage metrics.
Test coverage provides a quantitative measure of software reliability by tracking the percentage of code executed during testing. This identifies untested paths that might contain bugs, regressions, or unexpected behaviors in production. High coverage builds confidence that critical business logic has been validated, allows safer refactoring by detecting breaking changes, and minimizes runtime failures reaching users.
However, coverage alone is insufficient for ensuring software quality—especially in AI systems where deterministic testing cannot capture emergent behaviors, non-deterministic outputs, or complex interactions between components. The real value isn't in reaching arbitrary coverage percentages, but in thoroughly testing high-impact code paths, error conditions, and user-critical workflows. This makes coverage more useful as a diagnostic tool for identifying testing gaps rather than a direct measure of system reliability.
Strategic coverage directs testing resources where they deliver maximum risk reduction and debugging capability. Often, 60% coverage of critical paths provides better production confidence than 95% coverage that neglects testing complex, failure-prone components that determine the user experience.
Coverage Analysis:
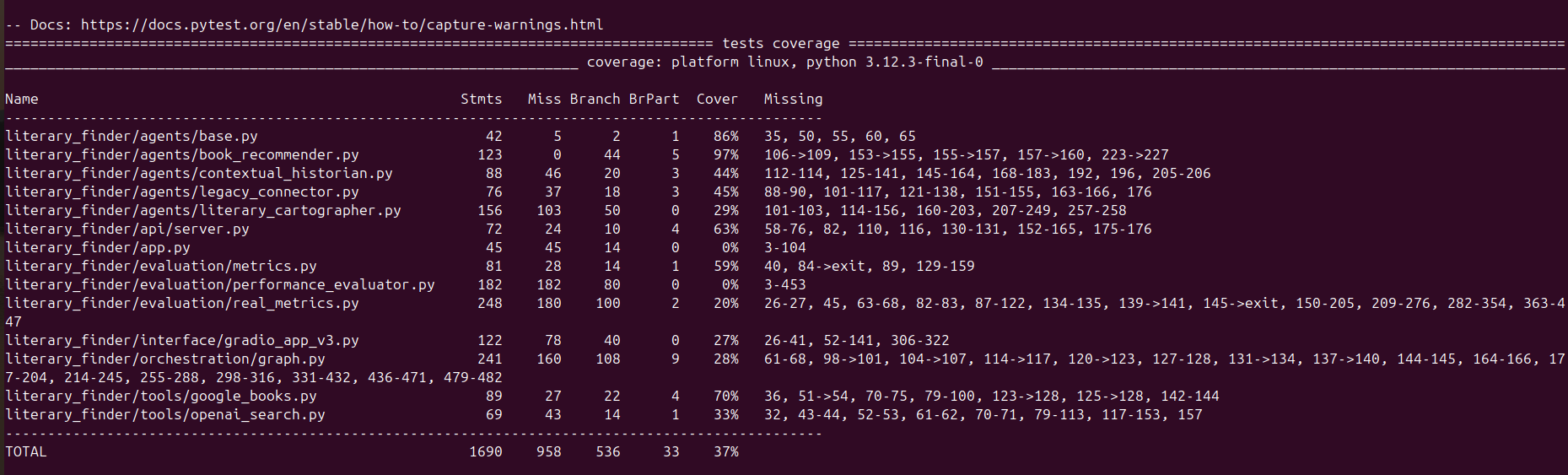
This project achieves an overall 37% test coverage, strategically focusing on essential and reliable test cases. Rather than pursuing blanket coverage, the testing strategy prioritizes deterministic components (with up to 97% coverage on core logic), critical integration scenarios for multi-agent coordination, and end-to-end user experience validation. This approach recognizes the unique challenges of testing AI systems with non-deterministic outputs, external API dependencies, and emergent behaviors, providing stronger production confidence than systems with higher percentage coverage that haven't addressed these complex realities.
Observability in multi-agent AI systems represents a critical yet often overlooked aspect of production deployment. Unlike traditional applications where execution paths are deterministic and debuggable through conventional logging, multi-agent systems exhibit complex, non-linear behaviors where emergent intelligence arises from the interaction of autonomous components. Traditional monitoring approaches fail to capture the nuanced performance characteristics of AI agents, including reasoning quality, inter-agent communication effectiveness, and the correlation between system performance and output quality. This observability gap creates significant challenges for production deployment, debugging, and continuous improvement of agentic AI systems.
LangSmith addresses these challenges by providing specialized observability infrastructure designed specifically for language model applications and multi-agent workflows. The platform offers distributed tracing capabilities that track requests across multiple AI agents and external APIs, performance analytics that correlate execution time with output quality, and debugging tools that provide visibility into agent decision-making processes. For multi-agent systems, these capabilities are essential for understanding system behavior, identifying performance bottlenecks, and ensuring consistent quality delivery under production loads.
The integration of LangSmith into the Literary Finder architecture serves dual purposes: operational excellence and continuous improvement. From an operational perspective, LangSmith provides real-time monitoring, automated alerting, and comprehensive debugging capabilities that enable proactive issue resolution and system optimization. From a development perspective, the platform facilitates data-driven iteration by providing detailed analytics on user interactions, agent performance patterns, and quality metrics that inform architectural decisions and optimization strategies. This comprehensive observability foundation is essential for maintaining production-grade reliability while enabling continuous enhancement of AI system capabilities.
The following sections detail how LangSmith integration provides this essential observability layer for production multi-agent systems.
LangSmith provides critical observability capabilities essential for production multi-agent systems:
Environment-Aware Configuration:
# literary_finder/config.py class LangSmithConfig: """Configuration for LangSmith tracing.""" @classmethod def setup_tracing(cls, project_name: Optional[str] = None) -> None: """Setup LangSmith tracing with environment variables.""" os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true" api_key = os.getenv("LANGCHAIN_API_KEY") if api_key: os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = api_key if project_name: os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = project_name elif not os.getenv("LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"): # Environment-specific project naming env = os.getenv("ENVIRONMENT", "dev") os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = f"literary-finder-{env}" @classmethod def is_enabled(cls) -> bool: """Check if LangSmith tracing is enabled.""" return ( os.getenv("LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2", "").lower() == "true" and bool(os.getenv("LANGCHAIN_API_KEY")) )
Multi-Environment Project Organization:
# Automatic project naming by environment ENVIRONMENT=dev → literary-finder-dev ENVIRONMENT=staging → literary-finder-staging ENVIRONMENT=production → literary-finder-prod ENVIRONMENT=hf-spaces → literary-finder-hf
LangSmith provides comprehensive system-level tracing and agent-level tracing capabilities that enable deep observability across the entire LLM application stack.
System-Level Tracing:
At the system level, LangSmith captures end-to-end execution flows, tracking how data moves through complex multi-agent architectures, monitoring cross-service dependencies, and providing holistic performance metrics that reveal bottlenecks and optimization opportunities across the entire system topology.
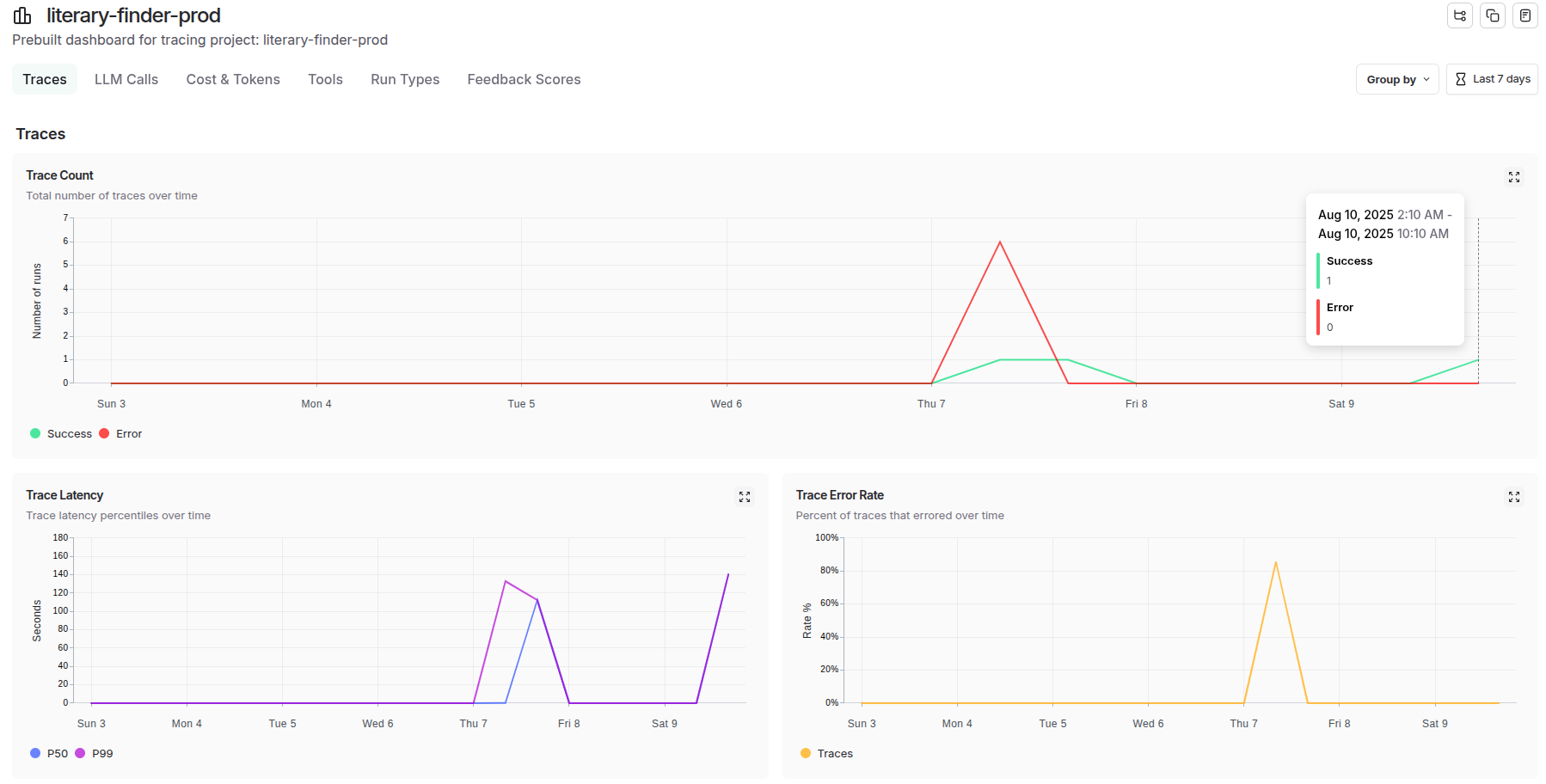
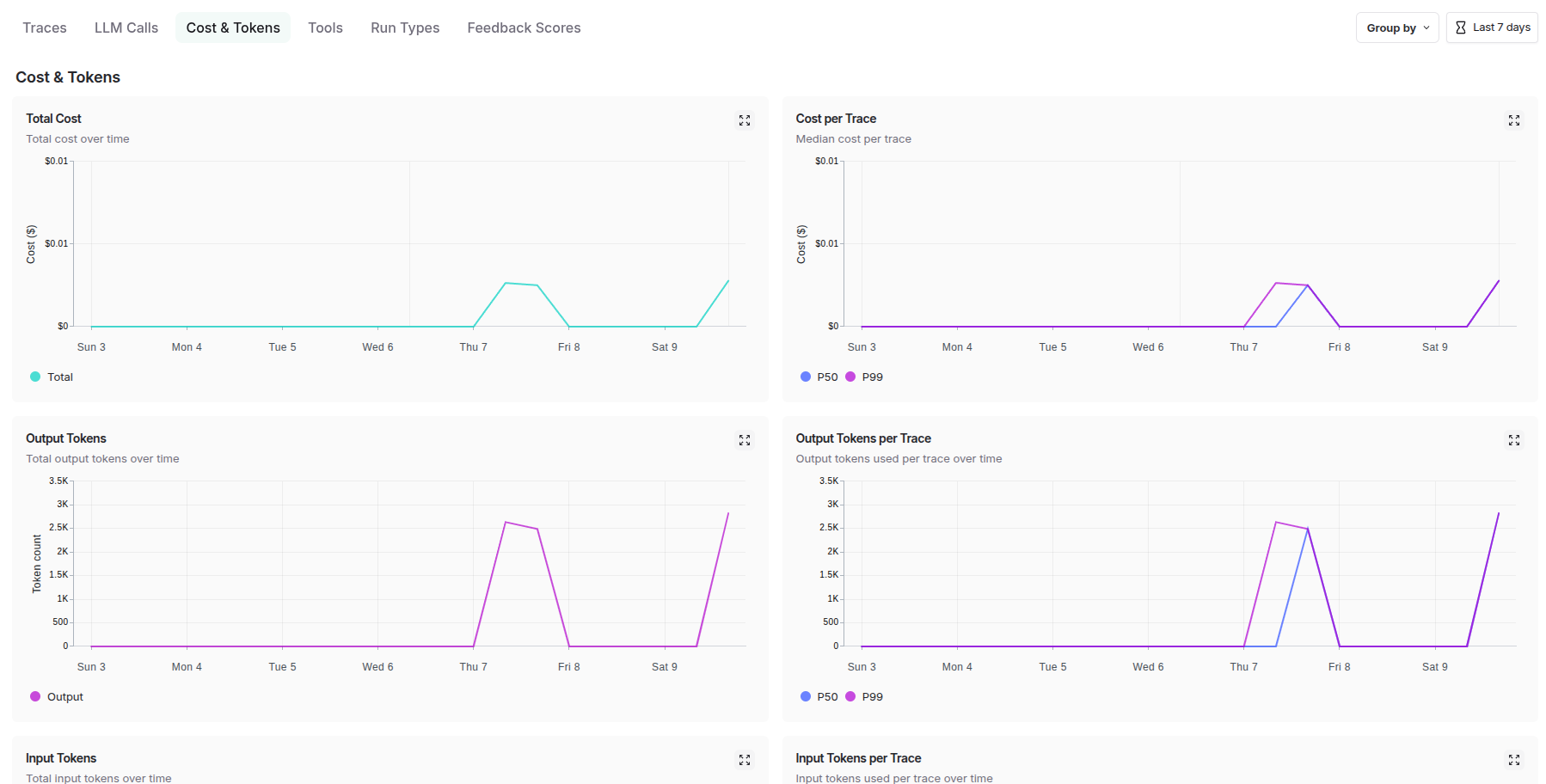
Agent-Level Tracing:
The agent-level tracing functionality delivers granular visibility into individual agent behaviors, decision-making processes, and internal state transitions. This includes detailed logging of prompt engineering iterations, model inference patterns, tool usage sequences, and memory state changes. Each agent's reasoning chain becomes transparent, allowing developers to understand not just what decisions were made, but why they were made, enabling sophisticated debugging of emergent behaviors in autonomous systems.
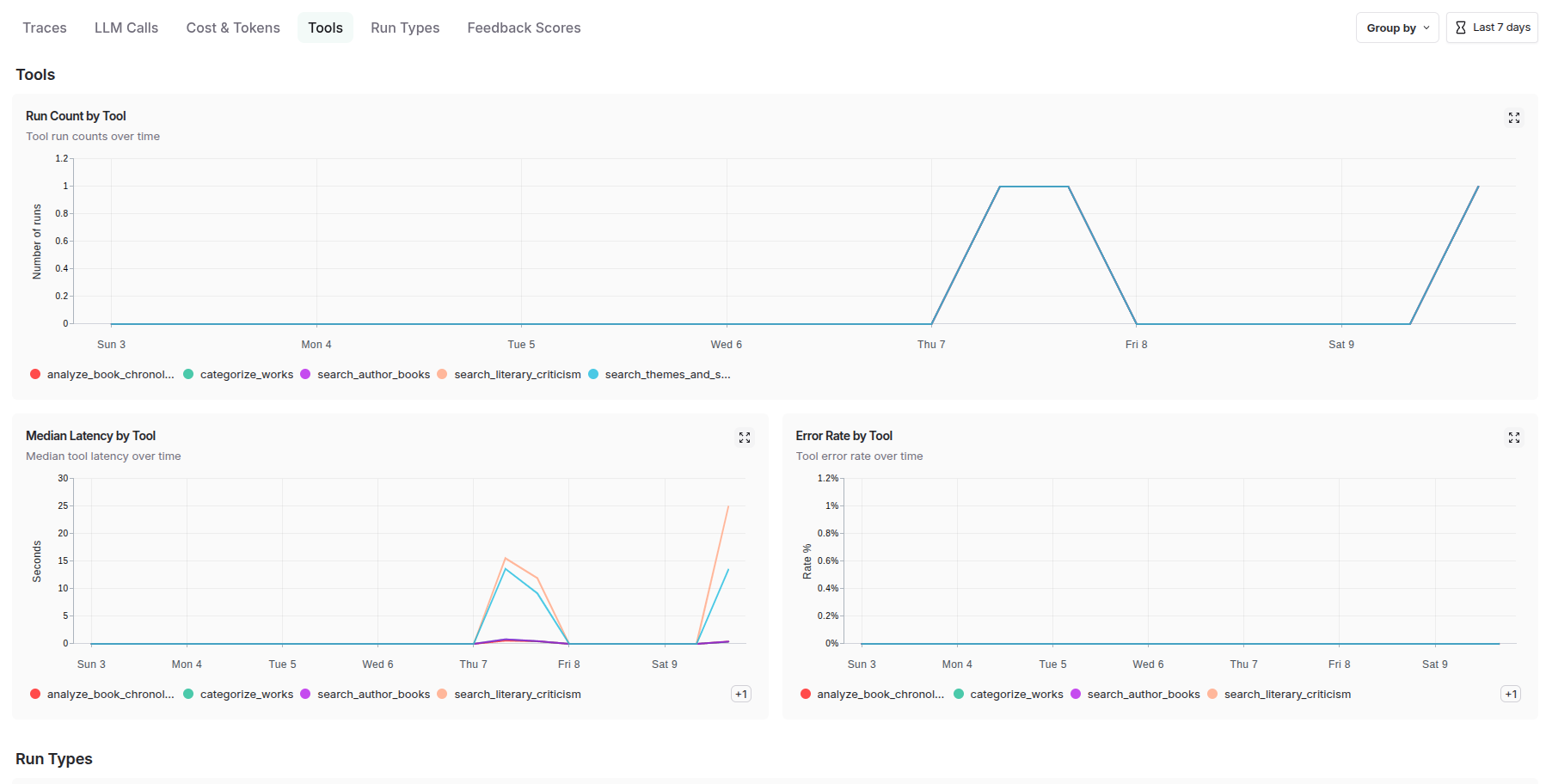
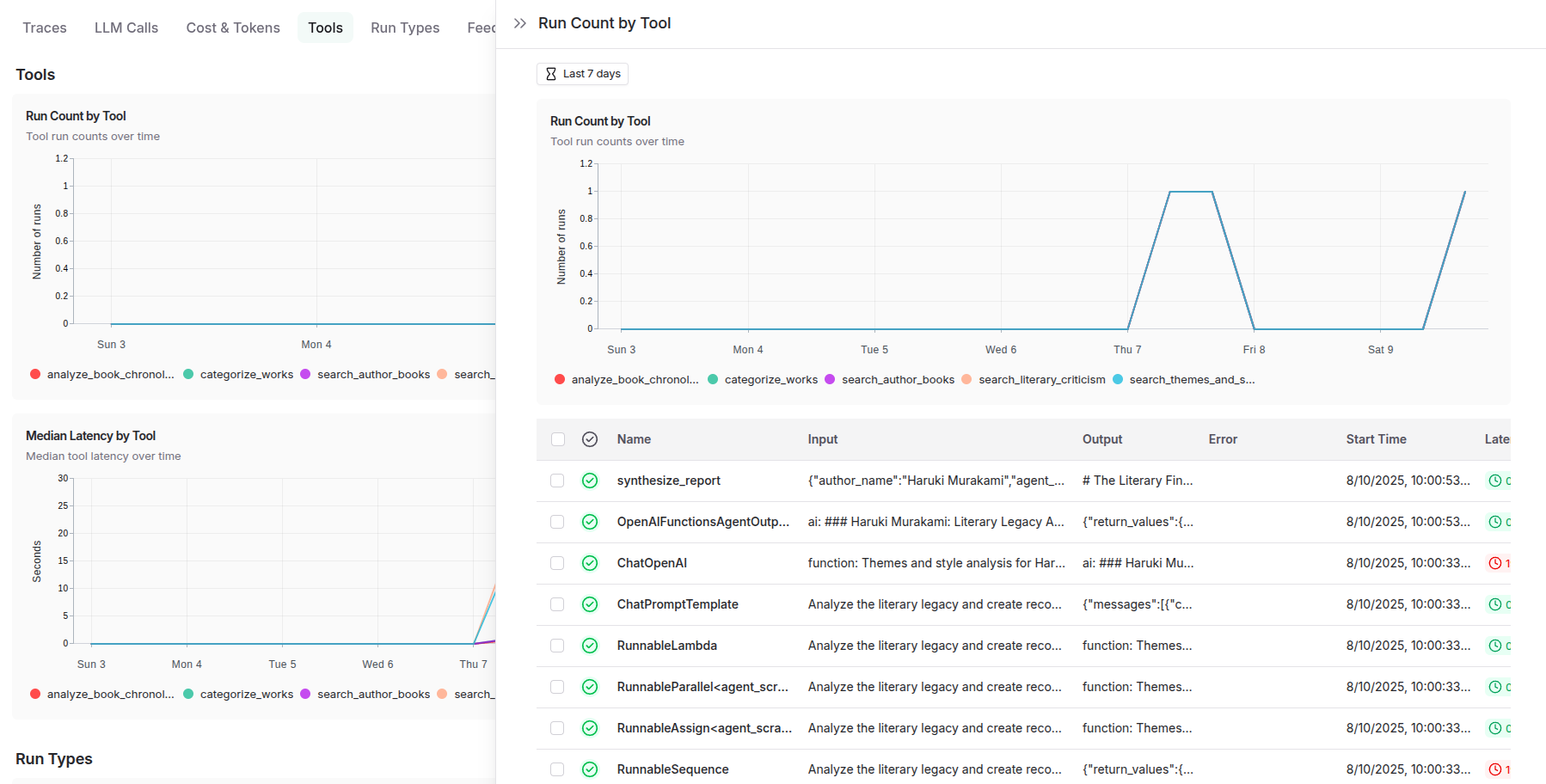
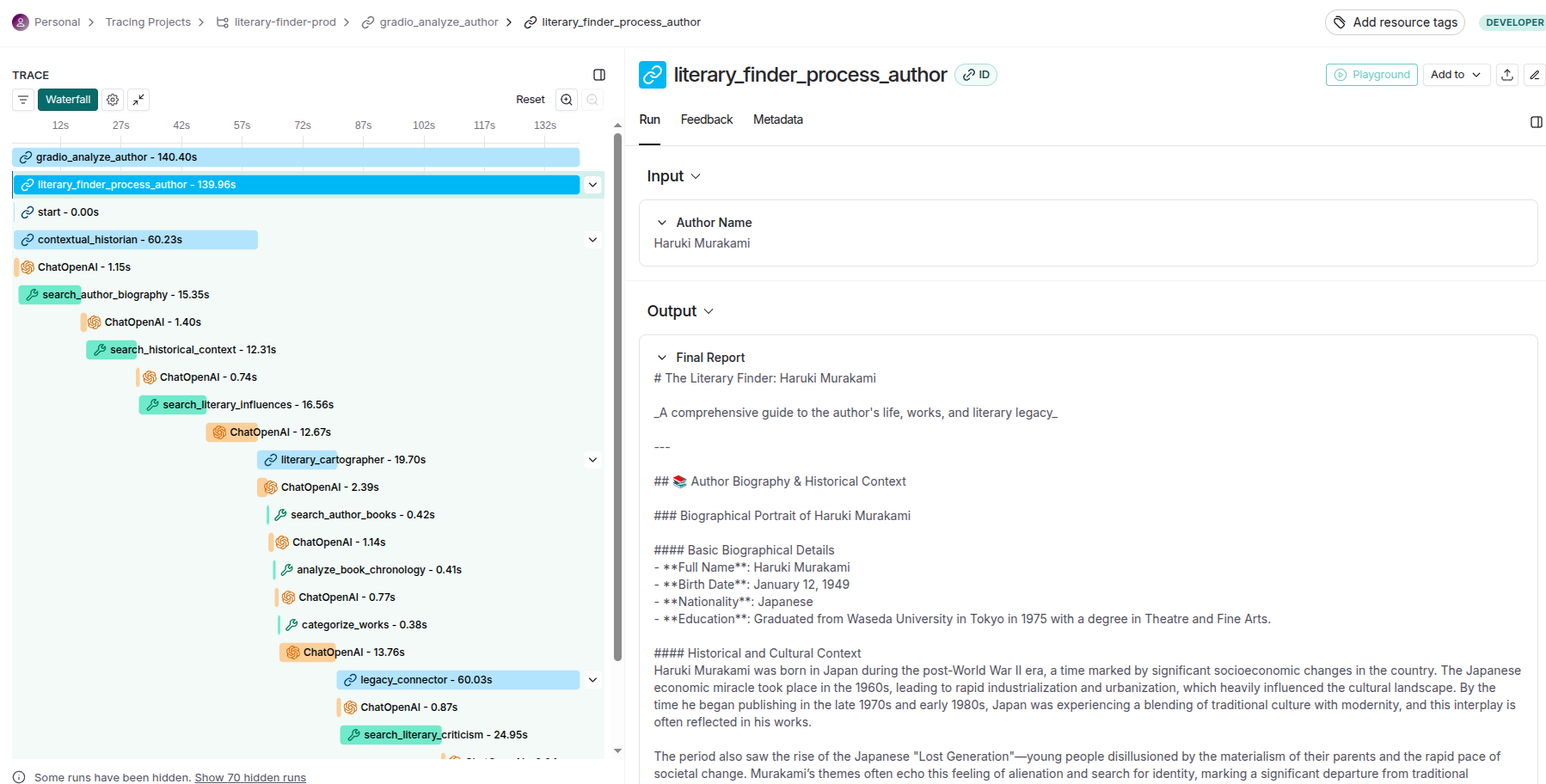
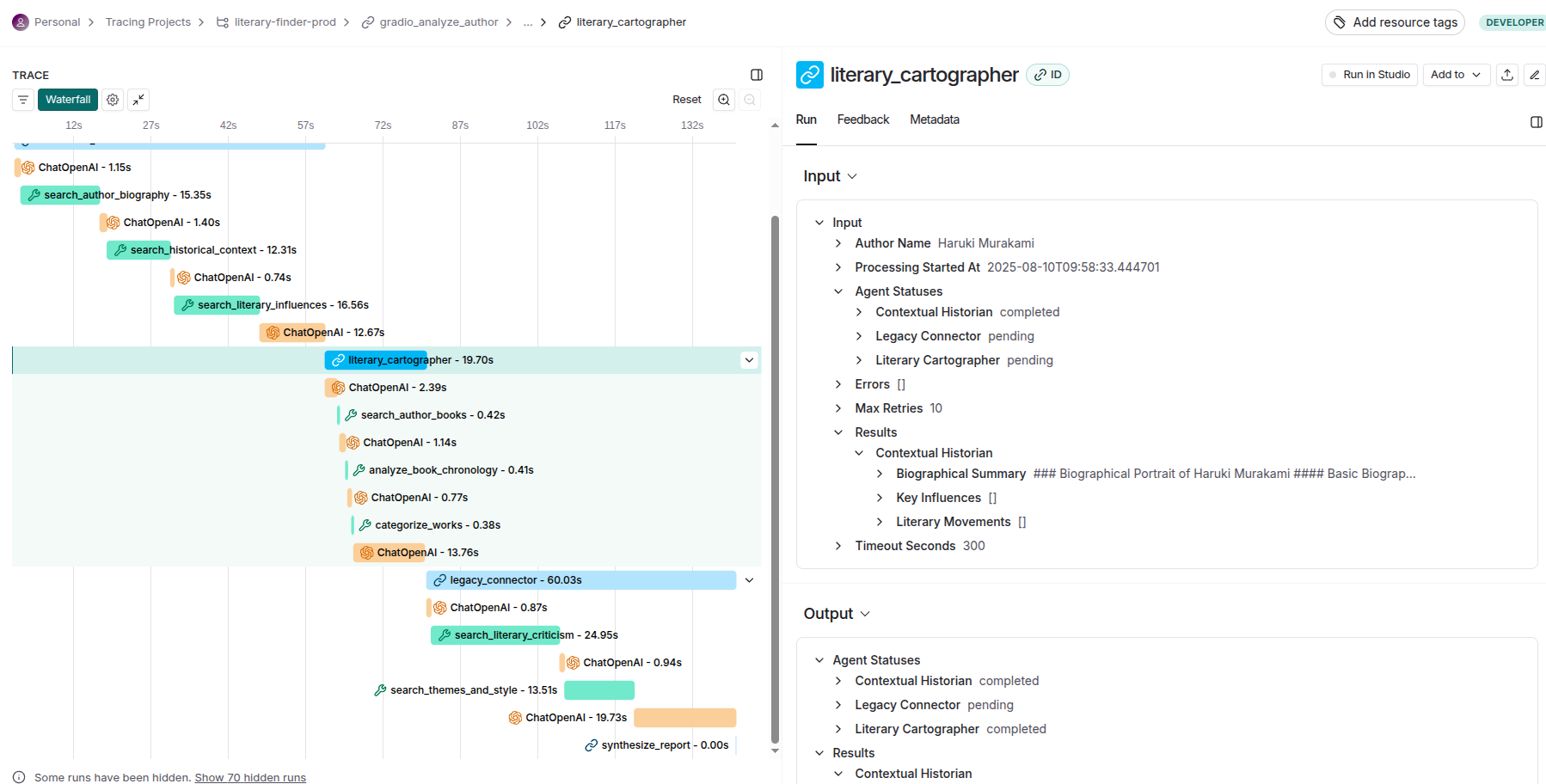
To summarize, LangSmith delivers comprehensive production analytics including:
Offering benefits like:
1. Proactive Issue Detection
2. Optimization Insights:
3. Production Debugging:
For information regarding the usage of the application or code, please refer to the licensing and rights section below. This segment provides essential details about the terms of use.
Literary Finder is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
You CAN:
You MUST:
Limitations:
API Terms of Service
Usage Responsibilities
Allowed Commercial Uses
Commercial Deployment Recommendations
Generated Content Rights
Content Responsibility
As LICENSE said:
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
When using or redistributing this software, please include:
The Literary Finder - A Multi-Agent System for Deep Literary Discovery
Copyright (c) 2025 Pedro Orlando Acosta Pereira
Licensed under the MIT License
https://github.com/poacosta/literary-finder
For academic use, cite as:
@software{literary_finder_2025, title={The Literary Finder: A Multi-Agent System for Deep Literary Discovery}, author={Acosta Pereira, Pedro Orlando}, year={2025}, url={https://github.com/poacosta/literary-finder}, license={MIT} }
The Literary Finder at this stage exemplifies the successful transformation of a research prototype into a production-ready multi-agent AI system, demonstrating that sophisticated agentic architectures can achieve enterprise-grade reliability while maintaining accessibility through modern cloud-native deployment strategies. This implementation showcases how thoughtful engineering practices—comprehensive testing, specialized observability, and platform-optimized deployment—enable complex AI systems to operate reliably in production environments.
The transition from prototype to production required addressing fundamental challenges inherent to multi-agent systems: non-deterministic behaviors, emergent properties from agent interactions, and complex dependency management across external APIs. The three-tier testing pyramid strategically addresses these challenges by focusing on deterministic component validation, multi-agent coordination patterns, and complete workflow validation under production conditions. While achieving 37% test coverage, the strategic focus on critical paths and error conditions provides stronger production confidence than blanket coverage approaches that fail to address the unique complexities of agentic AI systems.
The HuggingFace Spaces deployment strategy demonstrates how platform-as-a-service (PaaS) solutions can democratize AI deployment without sacrificing operational capabilities. By optimizing for zero-infrastructure management while maintaining Docker-based deployment flexibility, the system achieves rapid iteration cycles essential for AI development while providing enterprise-compatible fallback options. This architectural approach reduces deployment barriers that traditionally limit AI application adoption and accessibility.
LangSmith integration represents a critical advancement in multi-agent system observability, providing specialized monitoring capabilities that traditional application monitoring cannot deliver. The platform's distributed tracing across autonomous agents, quality monitoring for AI-generated content, and debugging visibility into agent decision-making processes address observability gaps that often prevent AI systems from achieving production reliability. This comprehensive observability foundation enables proactive issue resolution, performance optimization, and data-driven system improvement—capabilities essential for maintaining AI system quality at scale.
This implementation contributes to the broader evolution of AI engineering practices, demonstrating that multi-agent systems can achieve the reliability, observability, and operational characteristics required for production deployment. The successful integration of modern development practices—cloud-native deployment, comprehensive testing, specialized monitoring—with complex AI capabilities establishes a foundation for wider adoption of agentic AI architectures in enterprise environments.
As multi-agent AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the engineering practices demonstrated in The Literary Finder—particularly the focus on observability, testing strategies adapted for non-deterministic systems, and cloud-native deployment optimization—will become essential competencies for AI engineering teams. This work provides a practical reference for those seeking to bridge the gap between AI research capabilities and production deployment realities, advancing the state of practice in production AI system engineering.
Project Repository: https://github.com/poacosta/literary-finder
Huggingface Spaces App: https://huggingface.co/spaces/poacosta/literary-finder
Demo Video: https://www.loom.com/share/85732b4b3bf8426d9e9d0ee7e1944e4d?sid=f9f525e5-7360-48e2-8918-738af589b617
Author: Pedro Orlando Acosta Pereira
Certification Program: Agentic AI Developer Certification 2025 (AAIDC2025) - AAIDC-M3
Project Classification: Multi-Agent System Implementation - Production Ready Stage