Retrieval-Augmented AI Assistant
Introduction
This publication presents a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant tailored for answering questions over technical documentation and internal knowledge base materials. The system combines: document ingestion, semantic chunking, vector embedding storage, similarity retrieval, and controlled generation. It targets scenarios where accurate, source-grounded answers are preferred over purely generative responses.
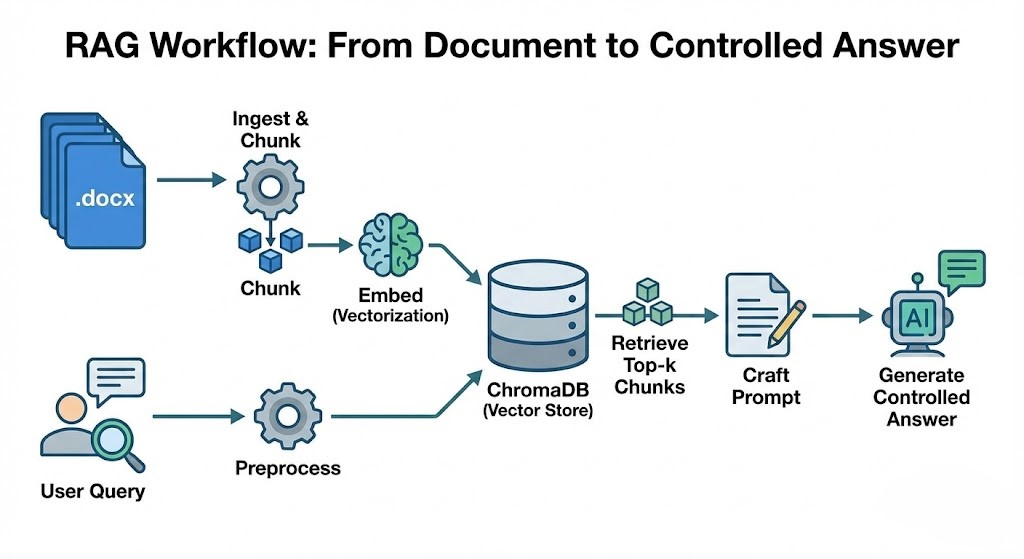
Built in the context of the Ready Tensor Agentic AI Developer Certification, the project emphasizes clarity, reproducibility, safety (prompt injection defenses), and evaluation of retrieval quality.
Domain Scope
"Domain" simply means the general type of documents the assistant focuses on. Here we choose: Technical & Project Documentation (design notes, API descriptions, architecture summaries). You can switch to another domain (policies, medical guidelines (non-diagnostic), legal briefs) by replacing the documents in data/.
System Architecture Diagram
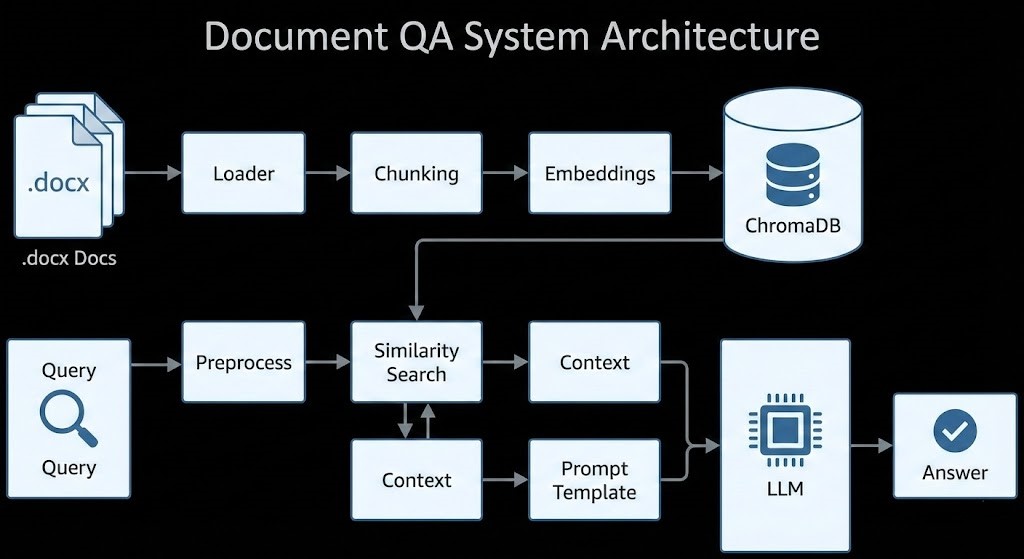
Component Walkthrough
- Loader: Reads
.docx files and extracts plain text.
- Chunking: Splits text into overlapping semantic chunks to preserve coherence.
- Embeddings: Converts each chunk into a dense vector with a Sentence Transformers model.
- Vector Store (ChromaDB): Persists vectors; supports similarity search (approximate nearest neighbors).
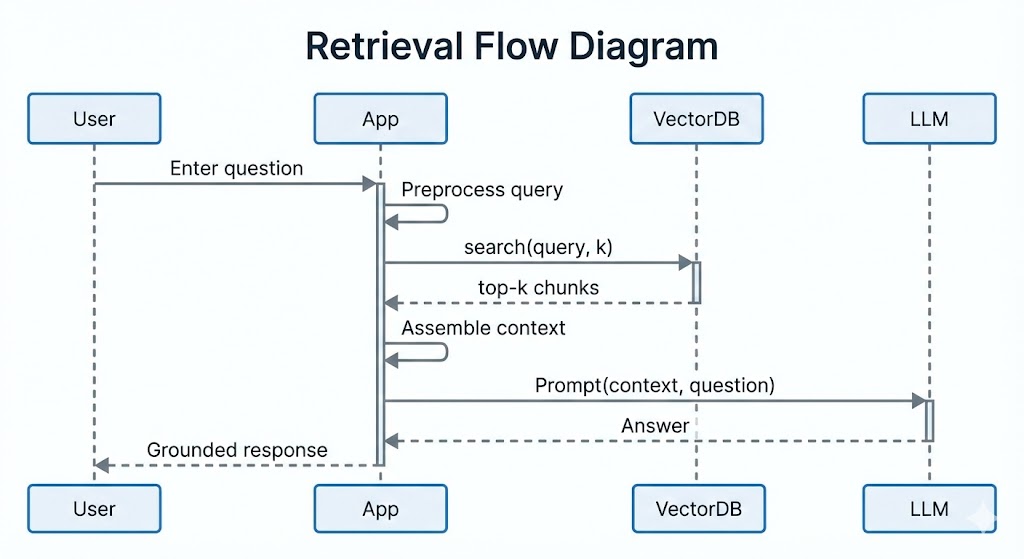
- Query Preprocessing: Normalizes and optionally expands user queries to improve recall.
- Retrieval: Finds top-k relevant chunks.
- Prompt Template: Injects retrieved context + user question with strict instructions against hallucination.
- Generation: LLM produces an answer constrained to provided context.
Real-World Applications
- Developer support (answering questions about APIs and internal services)
- Onboarding assistants (summarize architecture decisions)
- Knowledge base Q&A for internal tools or processes
- Change impact analysis (query past design notes)
- Lightweight documentation search instead of full-text keyword search
Competitive Differentiation
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|
| Vanilla LLM (no retrieval) | Fast, simple | Hallucinations, outdated knowledge |
| Keyword Search + Manual Reading | Precise matching | Time-consuming, lacks synthesis |
| This RAG Assistant | Grounded answers, multi-provider LLM support, extensible preprocessing | Requires embedding/index build |
Retrieval Evaluation & Metrics
Evaluating retrieval ensures the right context reaches the LLM.
- Recall@K: Fraction of relevant chunks found within top K.
- Precision@K: Fraction of retrieved chunks in top K that are actually relevant.
- MRR (Mean Reciprocal Rank): Rewards putting the first relevant chunk early.
- nDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain) (optional): Considers graded relevance & position.
Metric Intuition
High Recall means fewer missed answers; high Precision means less noise; MRR emphasizes ranking quality.
Evaluation Workflow
- Prepare
data/eval/queries.json with objects: { "query": "...", "relevant_ids": ["doc_0_chunk_2", ...] }.
- Run
python src/evaluation.py --queries data/eval/queries.json.
- Review metric summary and per-query diagnostics.
Query Processing Techniques
Implemented (or stubbed) in src/preprocess.py:
- Lowercasing & whitespace normalization
- Punctuation stripping
- Stopword removal (simple list)
- Synonym expansion (configurable map)
- Optional spelling correction (placeholder)
Benefits: Improved matching (recall) and cleaner embeddings.
Safety & Prompt Injection Mitigation
Prompt injection attempts to hijack instructions via malicious context. Countermeasures:
- Instruction boundary: Template explicitly forbids using anything outside provided context.
- Refusal pattern: Respond "I don't have enough information" if answer absent.
- No tool execution or external calls based solely on retrieved text.
- Sanitization: Strip suspicious control phrases (placeholder for future enhancements).
Future improvements: Content filtering (PII masking), rate limiting, audit logging of queries.
Implementation Notes
- Each chunk stored with an ID pattern:
doc_<docIndex>_chunk_<chunkIndex> for labeling.
- Overlap (50 chars) reduces boundary information loss.
- Deterministic embedding model choice via environment variable
EMBEDDING_MODEL.
Using the System
- Place
.docx documentation in data/.
- Run
python src/app.py (after setting an API key).
- Ask a question. System retrieves top chunks and generates grounded answer.
Extensibility
- Swap embedding model (larger transformer) for accuracy vs speed.
- Add re-ranking stage (e.g., cross-encoder) to refine top-K ordering.
- Introduce response citation: append chunk IDs.
- Add web/GUI front-end.
Future Work
- Dataset expansion & relevance labeling automation
- Integration of nDCG & re-ranking
- More robust security (prompt injection pattern detection)
- Multi-lingual document support
References
- LangChain Documentation
- ChromaDB
- Sentence Transformers
- OpenAI / Groq / Google Gemini APIs


