This project implements a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Assistant that combines a vector database (ChromaDB) with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs), supports OpenAI GPT, Groq LLaMA, and Google Gemini. The system enables users to ask questions over their own local text documents and receive accurate, context-aware responses.
User documents are converted into embeddings using HuggingFace models and stored in a vector database for semantic search. Relevant content is retrieved at query time and passed to the selected LLM to generate grounded and meaningful answers.
The project demonstrates an end-to-end, lightweight AI-powered knowledge retrieval system designed for research, educational, and practical use cases, with a focus on simplicity, flexibility, and extensibility.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a practical approach used in modern AI systems to produce accurate and reliable answers by grounding responses in real documents. Unlike traditional language models that may generate unsupported or incorrect information, RAG retrieves relevant content first and then generates answers strictly based on that context.
This project implements a lightweight RAG pipeline using embeddings, LLM, and ChromaDB for vector storage. Text documents are processed, embedded, and stored for semantic search, allowing the system to retrieve relevant information and answer user queries with factual support.
The project demonstrates how a simple and well-structured RAG system can provide context-aware answers for use cases such as documentation assistants, knowledge search, and AI-powered project tools.
.txt files from data directoryRecursiveCharacterTextSplitter (500 characters, 10% overlap)all-MiniLM-L6-v2)| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Python 3.9+ | Core language |
| LangChain | RAG orchestration |
| ChromaDB | Vector store |
| SentenceTransformers (all-MiniLM-L6-v2) | Embedding & Generation |
| LangChain RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter | Chunking documents |
| OpenAI GPT, Groq Llama, Google Gemini | Multi-model support |
| Text files | Document source |
This project uses the content from .txt file in the data\ folder. All files are committed into the repository.
For this project, I am using the same txt files provided in the project template by ReadyTensor.
Each file size is around 2-3K.
These documents are splitted into chunks which is converted into embeddings using HuggingFace models and stored in a vector database for semantic search.
Before starting, make sure you have:
Important: This project uses specific packages:
Clone and install dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/techbrij/rag-aaidc-project1 cd rag-aaidc-project1
python3 -m venv venv
Activate the virtual environment:
On Windows:
venv\Scripts\activate
On macOS/Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Configure your API key:
# Create environment file (choose the method that works on your system) cp .env.example .env # Linux/Mac copy .env.example .env # Windows
Edit .env and add your API key:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_key_here # OR GROQ_API_KEY=your_key_here # OR GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_key_here
Add any API key and comment the other API key parameters to avoid the conflicts. At a time, only one key should be active.
Run the application:
python src/app.py
The system automatically processes documents in the data/ directory and provides an interactive interface for asking questions. You can enter your question and it will answer from the documents.
First step is to prepare all the documents and put them in data/ folder. The directory contains sample files on various topics. Each file contains text content you want your RAG system to search through.
For simplicity, I am using the same files provided in the template.
Location: src/app.py
Function load_documents
data/ directoryLocation: src/vectordb.py
Function chunk_text
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter)Location: src/vectordb.py
Function add_documents
chunk_text() method to split documentsself.embedding_model.encode()self.collection.add()Location: src/vectordb.py
Function search
self.embedding_model.encode()self.collection.query()documents, metadatas, distances, idsLocation: src/app.py
ChatPromptTemplate.from_template() to create the template{context} (retrieved documents) and {question} (user query)Location: src/app.py
Function query
self.vector_db.search() to find relevant contextself.chain.invoke() to generate a responserag-aaidc-project1/ ├── src/ │ ├── app.py # Main RAG application (implement Steps 2, 6-7) │ └── vectordb.py # Vector database wrapper (implement Steps 3-5) ├── data/ # Replace with your documents (Step 1) │ ├── *.txt # Your text files here ├── tests/ │ ├── test_performance.py # Performance test ├── requirements.txt # All dependencies included ├── .env # Environment template └── README.md # The project guide
To assess the performance of our Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant, we developed a dedicated test class using the pytest framework. The evaluation focused on three core components:
For each component, we executed the relevant function multiple times and recorded the elapsed time using Python’s time module. For the assistant’s response, we used a set of diverse questions and averaged the response times over several runs to ensure reliability and account for variability due to external API calls.
The test module is in tests folder. First you need to install pytest:
pip install pytest
run following command to run the test
pytest tests/test_performance.py -s
Note: tune the configuration based on your requirement. I used 5 iterations with gemini-2.5-flash LLM.
Infrastructure: Windows 11, 32 GB RAM, 2TB SSD, i7-13650HX
Environment: Python 3.13.7, gemini-2.5-flash, LangChain 0.3.27
Total Documents: 7
Total Chunks: 35
Used different types of questions for different test cases:
Q1: What is artificial intelligence? (Simple)
Q2: What are Machine Learning and MLOps? (Multi-documents question)
Q3: Who is home minister of India? (Out of context)
The following metrics were obtained from our evaluation (example values, replace with your actual results):
| Metric | Value (seconds) |
|---|---|
| Document Load Time | <0.001 |
| Document Ingestion | 0.41 |
| Avg. Response Time Q1 | 2.94 |
| Avg. Response Time Q2 | 4.33 |
| Avg. Response Time Q3 | 2.07 |
All responses were successfully generated and validated for non-emptiness. The assistant demonstrated consistent performance across different queries, with response times suitable for interactive use.
Avg time for assistant.invoke('What is artificial intelligenc...') over 5 runs: 2.9413 seconds Avg time for assistant.invoke('What are Machine Learning and ...') over 5 runs: 4.3323 seconds Avg time for assistant.invoke('Who is home minister of India?...') over 5 runs: 2.0753 seconds
Last question was out of context and it generated the following expected response in each iteration:
The question is not answerable from the provided documents.
.txt files. Other formats (pdf, html...etc.) are not supported.RAG enhances large language models by providing them with relevant context from external documents. Instead of relying solely on pre-trained knowledge.
Traditional LLMs have limitations:
RAG solves these problems by grounding responses in actual documents
This work demonstrates the practical significance of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) as an effective approach to overcome key limitations of large language models, particularly hallucination, lack of transparency, and dependency on static parametric knowledge. By combining semantic retrieval over a curated knowledge base with controlled text generation, the proposed RAG-based assistant delivers context-grounded, verifiable, and domain-specific responses.
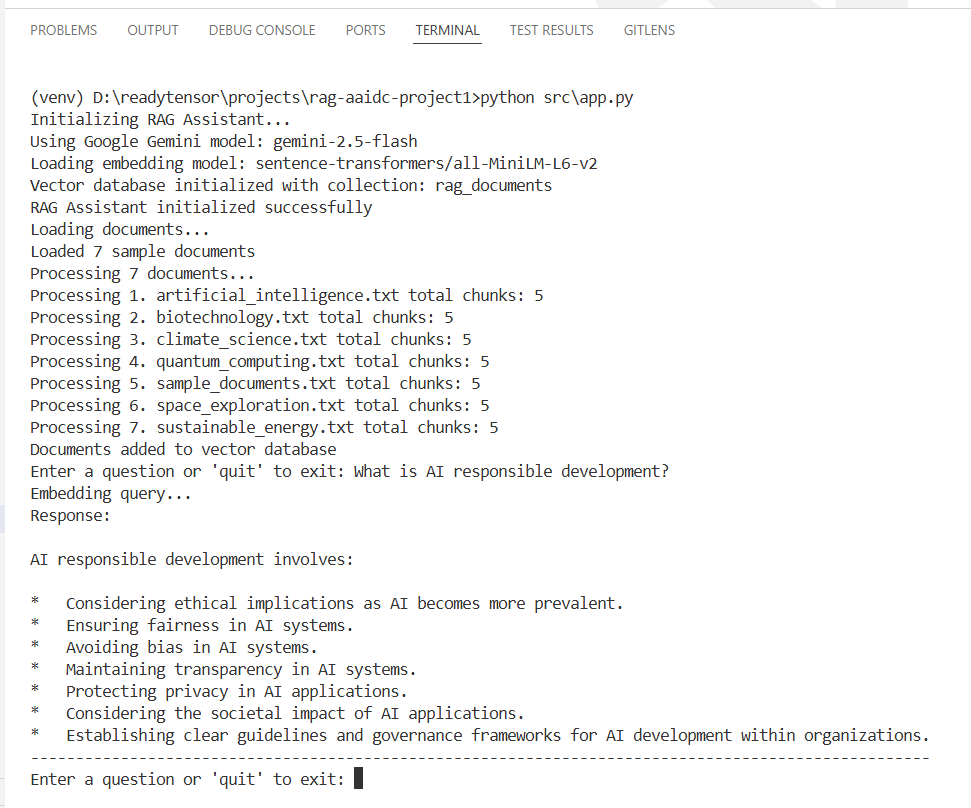
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed RAG-based Assistant, we conducted a comparative examination against traditional large language models (LLMs) and with RAG configurations. We tested with around 10 questions and checked answer relevancy and context accuracy manually. For example, I asked the same question (as shown in output screenshot) to Gemini directly, I got the general and long response while our system generates accurate result based on the provided data.
This project is maintained as part of the ReadyTensor Agentic AI Essentials Certification Program and is intended as an educational and reference implementation of a multi-agent system.
Maintenance Status: Actively maintained for learning, experimentation, and certification purposes.
Support: Community-driven. Issues and pull requests are welcome through the GitHub repository.
While using this project, it is recommended to monitor API usage and error rates. For any dependencies, LLM or API changes, it should be updated accordingly.
This project is licensed under the MIT License, allowing free use, modification, and distribution with proper attribution.
This project implements a complete RAG pipeline using embeddings, LLM, and ChromaDB for vector storage. Text documents are processed, embedded, and stored for semantic search, allowing the system to retrieve relevant information and answer user queries.
https://github.com/techbrij/rag-aaidc-project1
Brij Mohan