Mama Amaka is an AI-powered Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant that provides contextual, accurate answers about Nigerian cuisine.
Built with LangChain, ChromaDB, and multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Groq, Google Gemini), the application combines vector-based semantic search with large language models to deliver personalized cooking guidance.
The system indexes traditional Nigerian recipes, chunks them for efficient retrieval, and generates warm, culturally-informed responses through a friendly "Mama Amaka" persona. .png?Expires=1771526296&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=bhQSK3EbCAkcTEEYJ6Iny7mkMWxdTjXCrN634olmhEyygj6L49ImWLbBi1PMNhczVxDgL6t0DHJnoBPQW3-EBInZOcFDocaGVUES0mtxcjshfThrwyGg7STzKG1ak8e0Z3SupCJKUhq5UitGAPwp8dEjJfGCniB1X7lElyNblG0C5-qmcoJji4zqwizrm94eP6UBDrcSczughHpevX5VqBJnzfGgWq9y6m5~aM-pN5ilg68K3NHOKHdJrzRENPWakyAmG2OlPrdGqR1z3JvFHzY~r7TLtWsgVf19Jdjjd-j8ZqKXDcSYSUOtZaA-SUfOL1ZSzxjSsriCO4MCDjoVww__)
This tool addresses the gap in accessible, AI-driven resources for learning traditional Nigerian cooking methods and serves as both a practical culinary assistant and an educational reference for RAG architecture implementation.
Nigerian cuisine represents one of Africa's richest culinary traditions, featuring diverse dishes like Jollof rice, Egusi soup, and Suya that have gained international recognition. However, accessing authentic, detailed information about traditional cooking methods remains challenging for many enthusiasts. Existing recipe resources often lack the conversational, contextual guidance that home cooks need when preparing unfamiliar dishes.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for building knowledge-intensive AI applications. By combining the precision of information retrieval with the generative capabilities of large language models, RAG systems can provide accurate, contextual responses grounded in specific knowledge bases which make them ideal for domain-specific applications like culinary assistance..png?Expires=1771526296&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=rHfJoiHXwXLz-TDwRH5C7MAD9HcNtYAHIL2p1Fqlth1pcBKAj1jpkzBjbTZKg2RMpkHGusC-M08AEM4e3COtXD9CCG2vVfr3d41NrFKxL85aqF0--AnerQMufBp-MwJ8q9IEvGbTfS04sRSa2MkUH1rDbBJ0sqlOv0FRzYX8PtCv7BjhZWgWCYXw8Vt8ItvJq0RlPU8Czt-8A2ujAjEEMR9bMLwRz7P8CYV2cT8FS4EeDLnBHpmk2xkluLeeFZSss9QiMAM7gbxGWWbfhBuS5~9TLLY~GD~jYPPyqs5~gYTDDYqC1oiZSAEZmlhbW~QLxmtWx3zjq2dQFjcBjwTdZg__)
Mama Amaka bridges this gap by creating an intelligent recipe assistant that understands and responds to natural language queries about Nigerian food. Rather than simply returning search results, the system synthesizes information from its recipe knowledge base to provide comprehensive, conversational answers that are complete with a warm, motherly personality that reflects the cultural tradition of learning cooking from family elders.
Mama Amaka implements a standard RAG pipeline that processes user queries through four distinct stages:
↓
↓
↓
The system ingests recipe documents through a multi-step processing pipeline:
Document Loading: Text files containing Nigerian recipes are loaded from the data/ directory. Each recipe includes the dish name, ingredients list, cooking instructions, and optional serving suggestions.
Text Chunking: Documents are split using LangChain's RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter with the following parameters:
.png?Expires=1771526296&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=b2SouhPAB6Zzs5CbRJ4c87futFe4MNRkoc-aKILPaNVlyXnRfOLtpF1nqh~SA7Cwsxu6AQq6eI24zHdQAghv5TnSsD88Mf4VeNXWD44MyekGFiYsGxn0JfMnesUouFawADICL01xMcp-OPwSiHpVVLs3qpW6pq~ZA819BUsLH42YHtH3mF~DRBrysyvMhrU829XAFGuTI4nwnRacrhkatAUyrD45R069d95wjzM7I36fF~XxK70rQ9Eg5AqhCYMOIcW7x0hz0O7VmXdQQ8dEikPEMI7v8E2aU5tGKNoHelyzDcGzDgg2-mYdjRAtt~CIr4xG4N6dpGUxjfBDYwFHtQ__)
This hierarchical approach preserves semantic coherence while creating manageable chunks for embedding and retrieval.
Embedding Generation: Each chunk is converted to a 384-dimensional vector representation using the sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model. This lightweight model provides strong semantic similarity performance while maintaining reasonable computational requirements.
Vector Storage: Embeddings are stored in ChromaDB, an open-source vector database that supports persistent storage and efficient similarity search using cosine distance.
# The VectorDB class handles all vector storage and retrieval operations: from src.vectordb import VectorDB # Initialize vector database vdb = VectorDB(collection_name="mama_amaka_recipes") # Search for relevant recipe content results = vdb.search("jollof rice", n_results=3) print(f"Found {len(results['documents'])} relevant chunks")
When a user submits a query, the system:
Embeds the query using the same sentence transformer model
Performs cosine similarity search against the vector database
Retrieves the top-K most relevant chunks (default K=3)
Formats retrieved chunks with source attribution for context injection
def ask(self, query: str, n_results: int = 3) -> str: """Process user query and generate contextual response.""" # Retrieve relevant context from vector database search_results = self.vector_db.search(query, n_results=n_results) # Combine retrieved chunks into context context = self._format_context(search_results) # Generate response using LLM with retrieved context response = self.chain.invoke({ "context": context, "question": query }) return response
The assembled context is combined with the user query in a structured prompt template that defines the "Mama Amaka" persona which is a warm, knowledgeable Nigerian cooking expert.
Answer based on provided context
Acknowledge when information is not available
Maintain a friendly, encouraging tone
Provide practical cooking guidance
# Chain composition: prompt | llm | parser chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
The system supports multiple LLM providers OpenAI GPT-4o-mini, Groq Llama-3.1, Google Gemini through LangChain's unified interface, allowing users to choose based on performance requirements and cost considerations.
The development and testing environment consisted of:
3.13LangChain, ChromaDB, Sentence-Transformers, python-dotenv# .env configuration file # Choose ONE of the following API keys: # Option 1: OpenAI (Recommended for best quality) OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key_here OPENAI_MODEL=gpt-4o-mini # Option 2: Groq (Fast and free tier available) GROQ_API_KEY=your_groq_api_key_here GROQ_MODEL=llama-3.1-8b-instant # Option 3: Google Gemini GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_google_api_key_here GOOGLE_MODEL=gemini-2.0-flash # Optional: Custom ChromaDB collection name CHROMA_COLLECTION_NAME=mama_amaka_recipes # Optional: Custom embedding model EMBEDDING_MODEL=sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
The initial knowledge base includes 6 traditional Nigerian recipes:
Each recipe document contains comprehensive information including regional variations, ingredient substitutions, and cooking tips.
Jollof rice is a popular party favourite in Nigeria... INGREDIENTS Serves 4 - 500g Long grain rice - 3 cooking spoons Margarine/Vegetable oil - 400g Tomato paste - 2 Onions (chopped) - 3 Scotch bonnet peppers ... METHOD STEP 1 Melt the butter in a large pot... STEP 2 Add the rice and stir to coat... ...
# Document Loading: from src.app import MamaAmakaAgent # Initialize agent and load recipes agent = MamaAmakaAgent() docs = agent.load_recipes() print(f"Loaded {len(docs)} documents") # Output: Loaded 6 documents
# Vector Search: from src.vectordb import VectorDB # Initialize vector database vdb = VectorDB(collection_name="test") # Perform semantic search results = vdb.search("jollof rice", n_results=3) print(f"Found {len(results['documents'])} results") # Output: Found 3 results
# Full RAG Pipeline: i# Initialize and prepare agent agent = MamaAmakaAgent() agent.ingest_data() # Ask a question answer = agent.ask("What is jollof rice?") assert len(answer) > 0 print(answer)
Query Type - Example - Expected Behavior 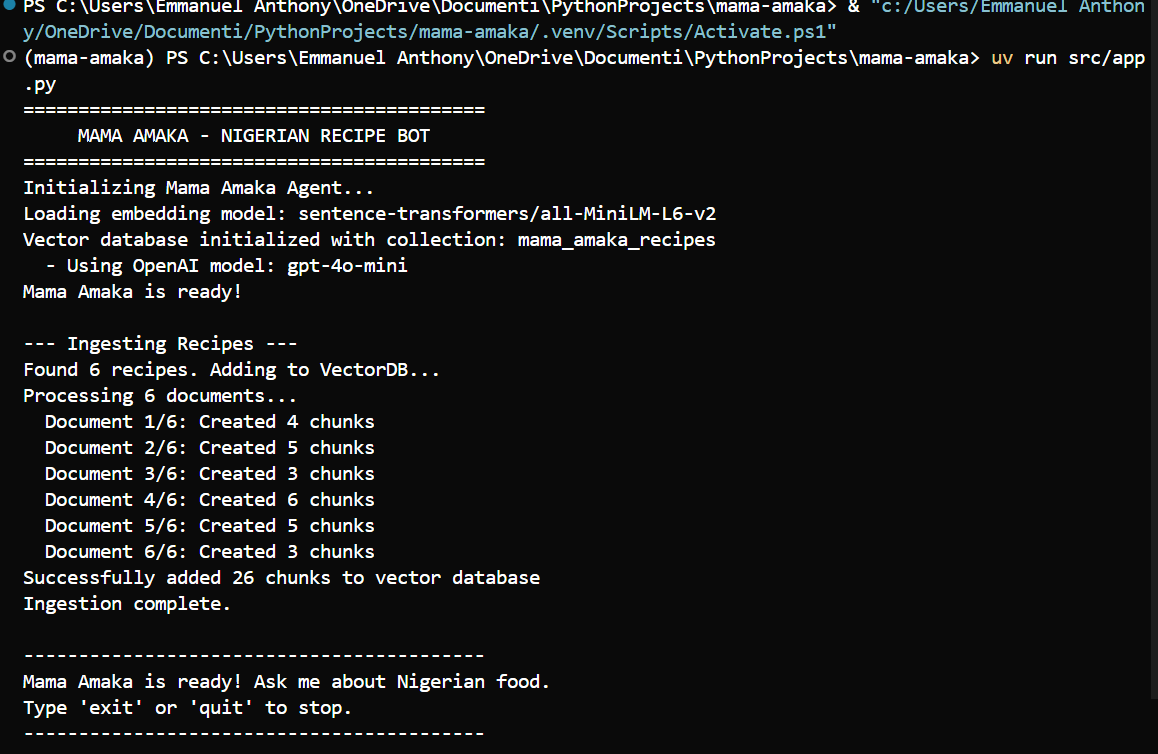
Direct recipe request - "How do I make jollof rice?" - Return complete cooking instructions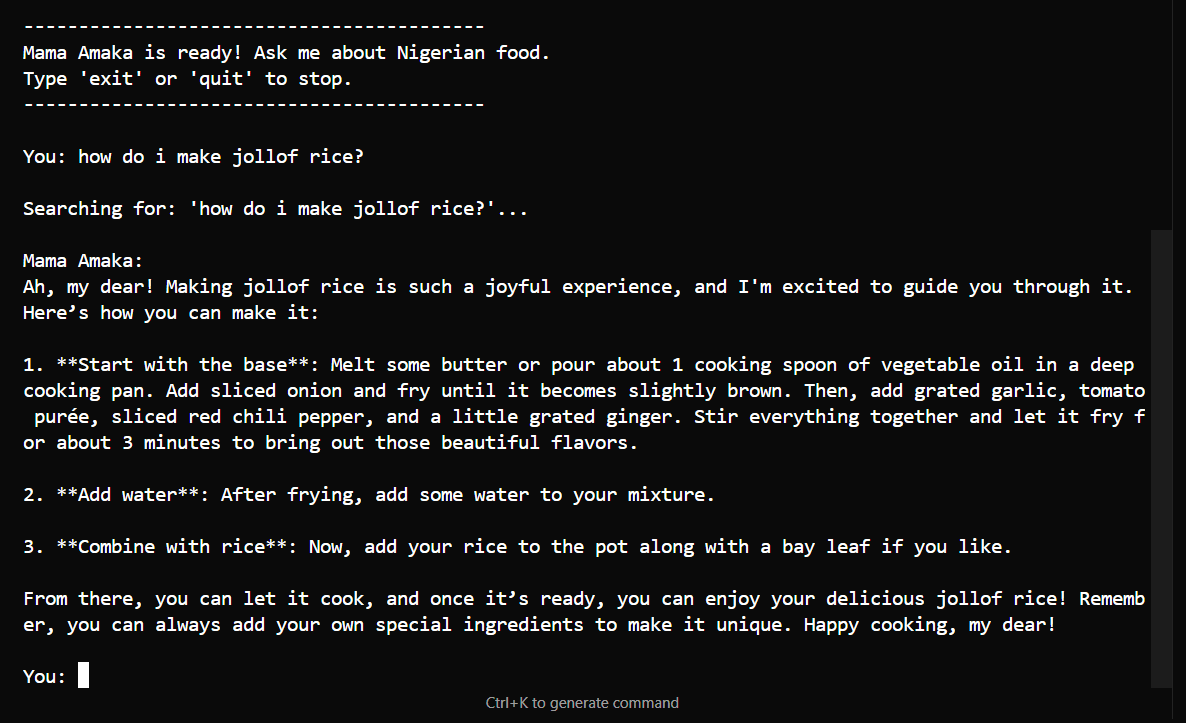
Ingredient inquiry - "What ingredients are in egusi soup?" - List all required ingredients 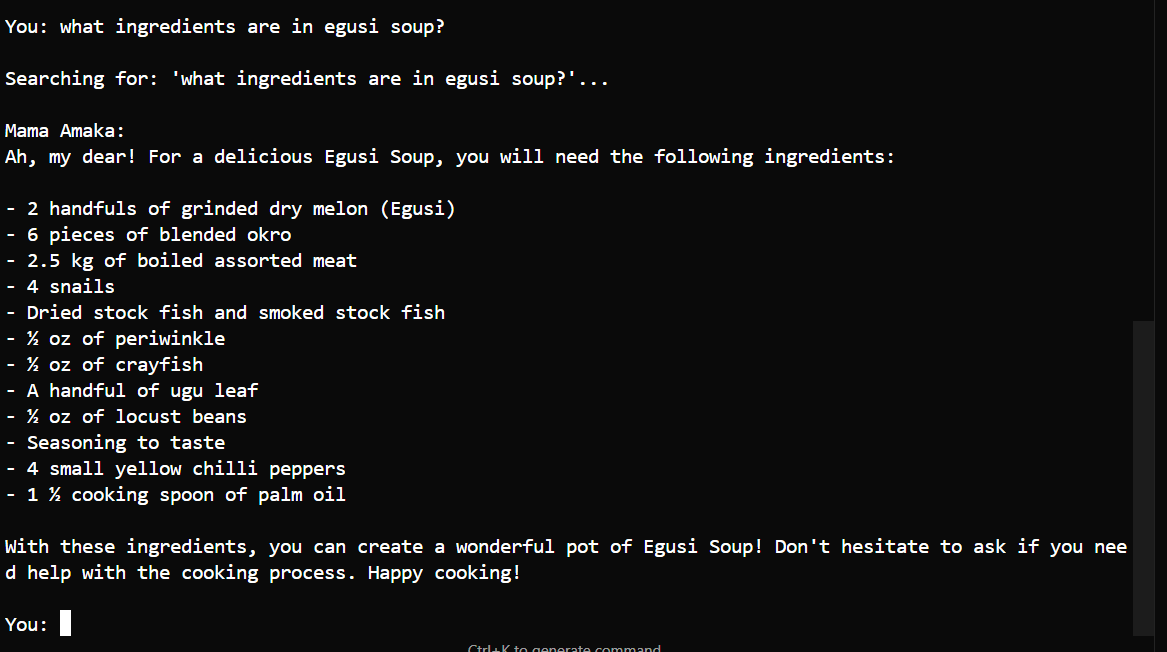
Technique question - "How long does moi-moi take to steam?" - Provide specific timing information 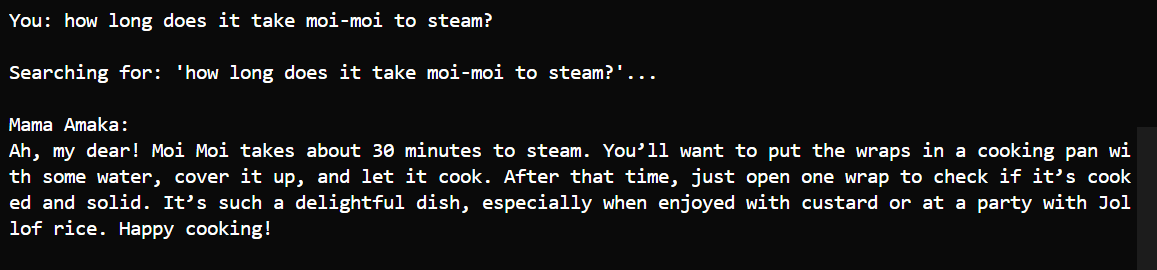
General knowledge - "Tell me about coconut rice" - Offer overview with cultural context 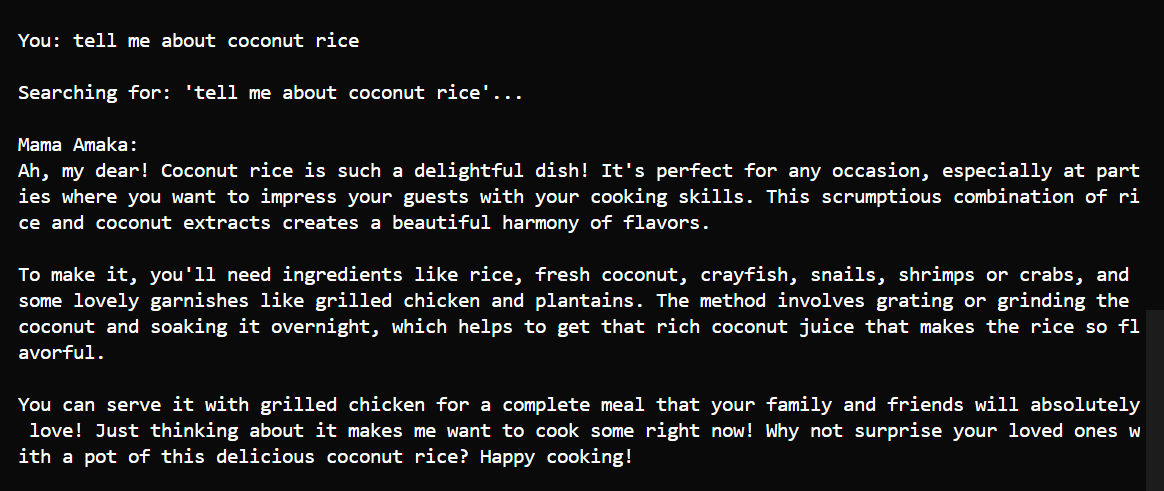
Out-of-scope - "How do I make sushi?" - Acknowledge limitation gracefully 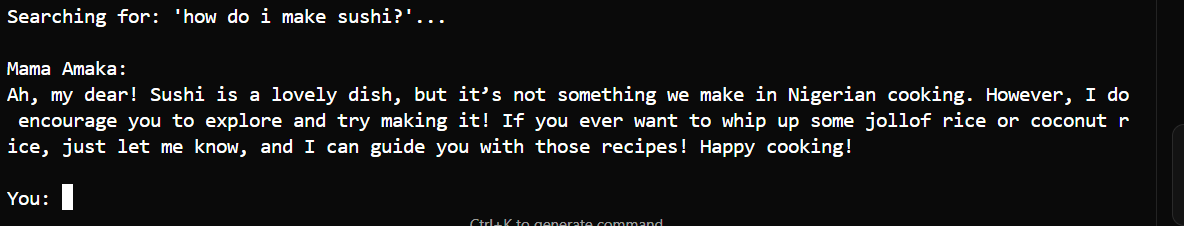
The vector search component demonstrated strong performance characteristics:
.png?Expires=1771526296&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=awDVNQtQ235ocoAyOHIJPoAss~s12E62ruP-Wn4toZ3r-6S-U2SNGRcVXZUQozPn~SqyEQCJYJGej6NfxfFu5DKYzBSZ2l7YTvTrDIwScAjEVwk265RLON8fzeC3Y1VXKI2idy9u-d1fm-GJJMAwqo84dUWVKAqpkeDndr9VjS60ScQTcI2yr7P~yRjHdUpB4BJIrIi5SJ9kyUqrF3PKTuTYNCD17yV9rWiZ2nzK4jsPLoTKbf65mjT~lsAr3BJoWnAj0kmdoSk04Of3J~BIXEjSMXx5WgvjBPckOEecIZrY2kZ28OpDu8Z3XO7siSwiI8-Ve4c4GOH4mZy55YM5OA__)
Qualitative evaluation of system responses revealed:
Mama Amaka demonstrates the practical application of RAG architecture for creating domain-specific AI assistants. By combining semantic search with large language models, the system provides accurate, contextual responses about Nigerian cuisine while maintaining a culturally appropriate conversational style.
.png?Expires=1771526296&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=rAIk0jzb~bTEvDa4UZHjsdgjCVHGTD1thR-Gwv0X67zF~ZxJ0Va0cYK85uX~plmZKiVX--113oBcNL61rxT9VFFg6YOZCC75u5dYeZil8538Qq-y6OyeQdAXfKT4l03NlAAARFxreahVWz9~iZWEFQyR2bjia7-DPUNVGhlUxSpIWHy0H6OSEfshzU0EeSHthUmGRcndtzOcUUhzIxBBiKSEECdnzn~4ppFQVthPfdxekh4yfbNEui~EJu6OFqYRASUnjkTFFY116---lhQCLMfOwR-PuiVwffPDRUjhaWQt13O4dVYIjhc0RoDT0S~1eHj2-PGB4OAmysjme5EqzA__)
Potential enhancements include:
ConversationBufferMemory to persist chat history. This will allow the application to retain context across multiple turns (e.g., remembering you are cooking "Jollof Rice" when you subsequently ask "How much salt do I need?").This ensures that the retrieval mechanism always searches for "Jollof Rice salt quantity" rather than a vague "salt quantity," significantly improving retrieval accuracy for complex, multi-step cooking sessions.
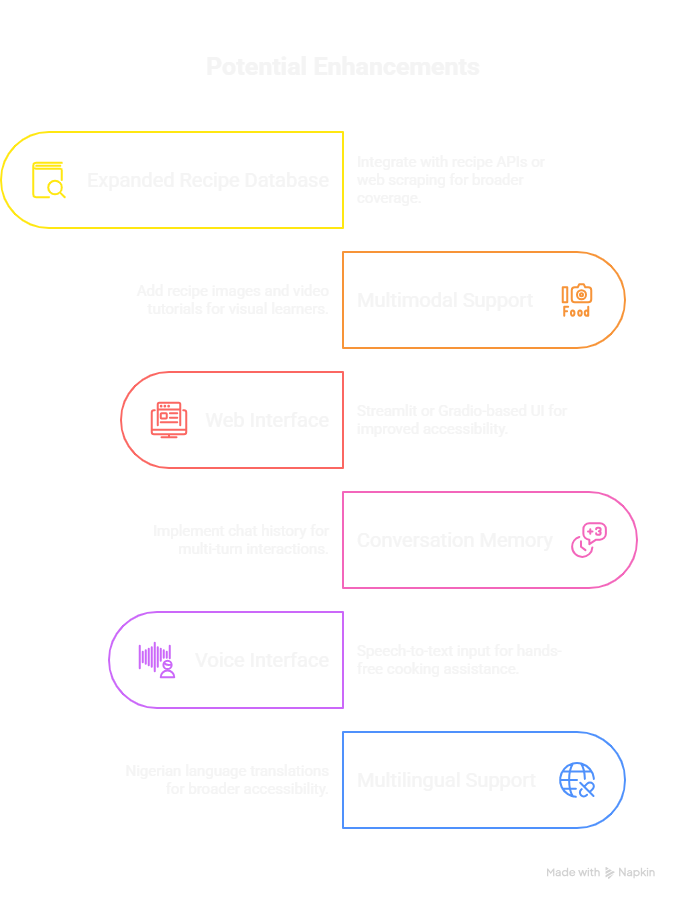
As an open-source initiative, Mama Amaka is actively maintained to ensure reliability and recipe accuracy.
Version Control: The project follows Semantic Versioning practices. Users can track major updates, bug fixes, and new feature releases directly on the GitHub Releases page.
Community Support: We encourage users to report technical issues or suggest new features via the Issues tab on our GitHub repository.
Contribution: Community contributions are welcome! Detailed guidelines for submitting pull requests (for code or new recipes) can be found in the repository's CONTRIBUTING.md file.
git clone https://github.com/Numba1ne/mama-amaka.git
cd mama-amaka
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Linux/macOS
# or: .\venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Configure API key (choose one provider)
echo "OPENAI_API_KEY=your_key_here" > .env
# Run the application
python src/app.py