AUTOSAR standards form the backbone of modern automotive software development, but their extensive and highly structured documentation makes efficient knowledge retrieval challenging for engineers. Traditional keyword-based search and manual navigation often fail to provide precise, context-aware answers. This publication presents an AUTOSAR-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant that enables accurate, document-grounded question answering over AUTOSAR specification documents. The proposed system ingests AUTOSAR standard PDFs, performs semantic chunking, generates vector embeddings, and retrieves relevant sections using similarity search. A large language model is then constrained through prompt engineering to generate responses strictly based on the retrieved AUTOSAR content, minimizing hallucinations. The solution demonstrates how domain-specific RAG systems can significantly improve productivity, reduce onboarding time, and enhance comprehension of complex automotive standards. This approach is scalable to multiple AUTOSAR modules and adaptable to evolving specifications.
Modern automotive software development relies on standardised specifications, specifically defined by AutoSAR consortium.These standard documents define how an Electronic Control Unit (ECU) should behave and be configured. However, the documents are voluminous and complex, making it difficult for engineers to quickly locate accurate and relevant information.
To address this, we explore how AI driven RAG system can be built specifically for AutoSAR documentation, enabling focused, accurate and grounded answer.
The sample implementation we refer to is the AutoSAR-RAG-Assistant, a Python-based RAG pipeline that processes AutoSAR standards and delivers precise responses to technical queries.
AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) is a global automotive standard for designing automotive software. It enables component-based architectures and modular software development, easing collaboration across suppliers and OEMs.
Key features include:
• Structured XML-based specification (ARXML files)
• Layered architecture separating application from infrastructure
• Reuse of software components across projects
While powerful, these documents are rich and detailed, making traditional search and manual lookup time-consuming.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that augments language models with retrieved context from a large document corpus. Instead of relying on internal model memory alone, RAG makes vector search and semantic retrieval part of the pipeline, resulting in more accurate, context-driven answers.
A typical RAG pipeline includes:
• Document ingestion → convert documents into text chunks
• Embedding & vector indexing → map text into dense vectors for semantic search
• Query embedding & retrieval → find relevant chunks for user queries
• Generation → supply the retrieved context to a large language model to generate a grounded answe
The core idea is: find the right knowledge fragment first, then generate the answer only from that fragment, drastically reducing hallucinations.
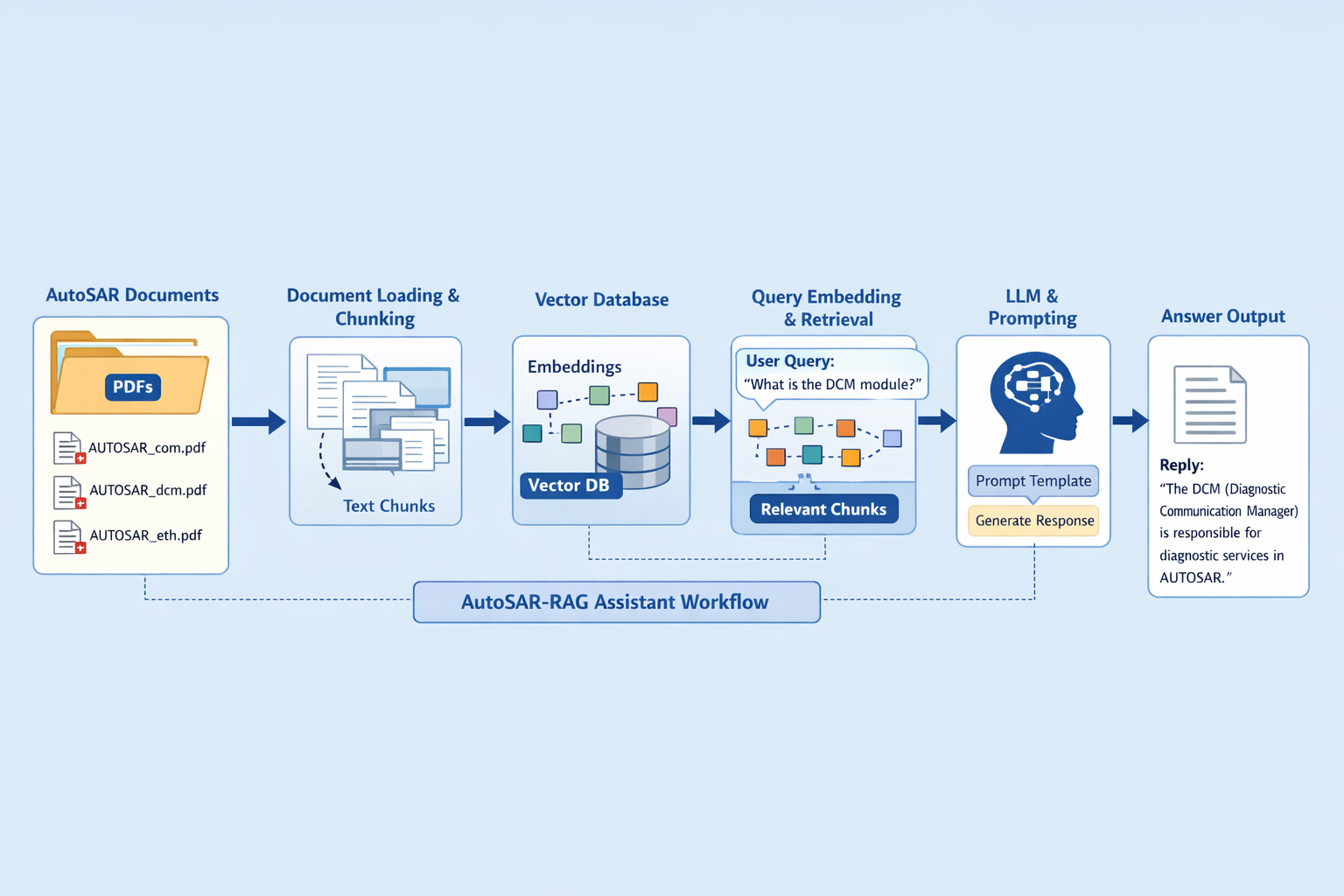
The AutoSAR-RAG-Assistant repository implements a RAG system tailored for AutoSAR standards. Here’s how it works:
The user populates a data directory with AutoSAR standard PDFs — one per topic or module. The assistant loads these for processing.\
data/
├── AUTOSAR_com.pdf
├── AUTOSAR_dcm.pdf
├── ...
Each PDF is read entirely, and text is extracted using a PDF loader (e.g., PyPDFLoader). Each document becomes a long text unit fed to the next stages.
AUTOSAR documents are typically published in PDF format and can be accessed from the official AUTOSAR website at:
https://www.autosar.org/search?tx_solr%5Bfilter%5D%5B4%5D=platform%3ACP&tx_solr%5Bfilter%5D%5B9%5D=category%3AR25-11&tx_solr%5Bq%5D=
Large documents are broken into smaller, semantically meaningful chunks (e.g., around 500 characters). This improves retrieval relevance. Overlapping chunks help preserve context across boundaries.
Using an embedding model and a vector database (e.g., Chroma), the system stores embedding for all chunks. At query time, it efficiently retrieves the top-N chunks most similar to the query
A strict prompt template ensures the language model only uses the retrieved context and rejects out-of-scope questions. Responses must be concise and clearly grounded in document content.

• API Keys: Store in .env, never commit to repository
• Environment Variables: Use python-dotenv for configuration
• Error Handling: Graceful handle for service failures
• The user must provide an API key from a supported LLM provider such as OpenAI, Groq, or Gemini.
• ChromaDB stores embeddings locally; therefore, scaling the system requires integration with an external vector database.
• Quality of source docs : broken PDFs can reduce retrieval accuracy.
• Document updates : AutoSAR standards evolve; maintaining fresh ingestion is key.
The AutoSAR-RAG-Assistant is a compelling example of how RAG systems can be tailored for domain-specific knowledge bases here, the complex and deeply-structured AutoSAR standards. By combining vector search, precise chunking, and constrained generation, it empowers automotive engineers with quick, accurate answers grounded in official documentation.
ChromaDB: https://docs.trychroma.com
HuggingFace SentenceTransformers: https://www.sbert.netGoogle
Gemini API:https://ai.google.dev
LangChain Documentation:https://python.langchain.com