Bridging the evidence–practice gap in cardiovascular care using Retrieval-Augmented Generation and Multi-Agent System (MAS).
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally. An estimated 19.8 million people died from CVDs in 2022, representing approximately 32% of all global deaths. WHO

Over the past decades, major professional bodies—such as the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA), the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), and the World Health Organization (WHO)—have published comprehensive guidelines that define optimal diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive strategies of cardiovascular diseases.
However, real-world clinical practice frequently fails to align with these guidelines. This persistent discrepancy, commonly referred to as the evidence–practice gap, results in suboptimal treatment decisions and failure to achieve recommended clinical targets for many patients with CVD. NIH
A study conducted in 5 Europe countries have identified 5 most common barriers cited by physicians in implementation of these guidelines. NIH
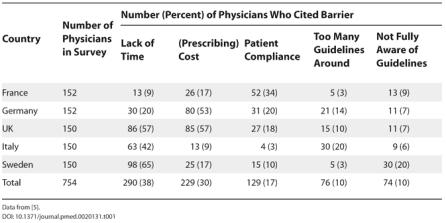
These are not purely medical problems — they are information, cognition, and coordination problems, which makes them ideal targets for AI systems.
This project addresses the evidence–practice gap by building a modular AI system that:
The system is designed as a Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) — it assists clinicians, not replaces them.
This project builds a 3-layered AI ecosystem:
┌─────────────────────────┐
│ Guideline RAG Engine |
│ Evidence Retrieval │
└────────────┬────────────┘
│
┌────────────▼────────────┐
│ Multi-Agent System │
│ Care Planning + Support │
└────────────┬────────────┘
│
┌────────────▼────────────┐
│ Production System │
│ (Deployment, UI, EHR) │
└─────────────────────────┘
Each layer solves a different part of the real-world barrier stack.
In this Phase I want to address the first layer which is Guideline RAG engine (Evidence Retrieval). I named the first solution layer CardioCDSS: RAG-based clinical Decision Support System.
CardioCDSS is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) clinical decision support engine that transforms static cardiovascular disease management guidelines into a structured, queryable medical knowledge system. By combining semantic search, knowledge graph retrieval, and evidence-constrained generation, it delivers patient-specific recommendations grounded strictly in authoritative guidelines.
A Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) based CDSS that transforms static cardiovascular guidelines into a queryable clinical reasoning system.
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Patient Clinical Summary │
│ + |
| Clinician Query │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Query Rewriting Layer │
│ (Medical Variant Generator)│
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
Expanded Medical Queries
│
▼
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Retrieval Funnel │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ │
│ │ Vector Search │ │ Graph Search │ │
│ │ (ChromaDB) │ │ (Neo4j KG) │ │
│ │ "Similar Text" │ │"Related Entities"│ │
│ └─────────┬────────┘ └────────┬─────────┘ │
│ │ │ │
│ └───────────┬────────────┘ │
│ ▼ │
│ Candidate Guideline Chunks │
└─────────────────────────┬────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Context-Aware Reranker │
│ (Patient-Specific Scoring) │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
Top-K Evidence Snippets
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Guardrailed LLM Generator │
│ (Evidence-Constrained CDSS)│
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Guideline-Aligned Output │
│ + Citations + Transparency │
└─────────────────────────────┘
Hybrid Recall Engine: Dual-stream retrieval using ChromaDB (semantic similarity) and Neo4j Knowledge Graph (relational clinical links).
Multi-Query Expansion: Automatically generates medical variants of a query to ensure that different clinical terminologies (e.g., "MI" vs. "Myocardial Infarction") all trigger relevant results.
Context-Aware Reranking: Filters hundreds of potential guideline chunks down to the top 5 most clinically relevant snippets using cross-attention.
Modular Architecture: Strict separation of Query Rewriting, Retrieval, and Generation logic for high maintainability.
Clinical Guardrails: Abstention mechanism to prevent hallucinations when guidelines do not cover a specific patient scenario.
The system follows a 5-layer clinical RAG pipeline:
Ingestion Layer
Standardized guideline PDFs are parsed, cleaned, and split into overlapping chunks to preserve medical context.
Knowledge Structuring Layer
Subject–Predicate–Object triplets are extracted (e.g., Drug → Contraindicated in → Condition) and stored in a Neo4j knowledge graph to model clinical relationships.
Hybrid Retrieval Layer
Context-Aware Reranking Layer
Retrieved candidates are scored against the patient summary (age, BP, LDL-C, comorbidities) using a cross-attention reranker to select the most clinically relevant evidence.
Evidence-Constrained Generation Layer
A guardrailed LLM synthesizes recommendations strictly from retrieved evidence and includes citations. If evidence is insufficient, the system abstains.
| Component | Choice | Reason for Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Vector Store | ChromaDB | Lightweight, persistent, and supports the metadata filtering required for guideline recency (publication year). |
| Graph DB | Neo4j | Industry standard for representing complex relationships (e.g., Drug A → interacts with → Condition B). |
| Reranker | Cohere v3.0 | Specifically trained for "long-context" document relevance, outperforming standard cosine similarity for dense medical text. |
| Extraction Model | sciphi/triplex | Pre-trained specifically for (s, p, o) triplet extraction. Much higher graph accuracy than general models. |
| Hosting Engine | Ollama | Local model hosting reduces data exposure and improves privacy control and No API cost |
| Graph Logic | Graphiti | Automates the complex "Temporal Graph" logic. Handles node deduplication (knowing "HBP" and "Hypertension" are the same). |
| Embedder | nomic-embed-text | 8k context window and high performance on medical benchmarks. |
| Memory | Stateless (None) | Intentionally omitted to prioritize clinical safety and data integrity(see below) |
⚠️ The Decision for Statelessness (No Memory)
While conversational memory (Chat History) is common in RAG systems, CardioCDSS is designed as a Stateless tool to mitigate high-risk medical errors:
- Preventing Context Pollution: Memory poses a risk where data from "Patient A" might persist in the buffer when a clinician begins a query for "Patient B," leading to hallucinated, mixed-patient treatment plans.
- Mitigating Guideline Drift: Long-form conversations often cause LLMs to "drift" from their system instructions. Omitting memory ensures the model strictly adheres to the provided guideline context for every single query without the noise of previous exchanges.
- Clinical Data Integrity: Every recommendation is generated based solely on the current patient summary and retrieved evidence, ensuring a clean audit trail for every clinical decision.
| Standard RAG | CardioCDSS |
|---|---|
| Text similarity only | Vector + Knowledge Graph retrieval |
| Free-form generation | Evidence-constrained output |
| Conversational memory | Stateless for clinical safety |
config/ ├── config.yaml # Global settings (Model names, chunk sizes, DB URIs) ├── prompts.yaml # Centralized YAML for version-controlling LLM instructions data/ ├── guidelines/ # Input directory for authoritative ESC/ACC PDF guidelines ├── patient_cases/ # JSON/CSV repository of structured patient summaries prompts/ ├── recommendation.txt # Prompt for clinical synthesis & strength of recommendation ├── system_cdss.txt # Core system identity and medical safety guardrails src/ ├── ingestion/ │ └── loader.py # PDF processing, chunking, and dual-DB ingestion ├── generation/ │ ├── rewriter.py # Multi-query variant generation (Recall booster) │ ├── generator.py # LCEL chain logic for guideline-based response synthesis │ └── pipeline.py # The Orchestrator (Coordinates the Hybrid RAG flow) ├── graph/ │ ├── manager.py # Local Graphiti client & Ollama (Triplex) configuration ├── retrieval/ │ └── retriever.py # Singleton manager for ChromaDB and BM25 └── utils/ │ ├── logger.py # Centralized logging with trace decorators │ └── config_loader.py # Configuration and prompt management tests/ │ ├── test_generator.py # Unit tests for clinical response faithfulness │ ├── test_loader.py # Validation for PDF chunking and metadata enrichment │ ├── test_rag_pipeline.py # End-to-end integration tests for the Hybrid RAG flow │ └── test_rewriter.py # Evaluation for query expansion and medical terminology ├── vectorstore/ ├── .env.example ├── app.py # Streamlit web interface for clinical consultation ├── main.py # Command-line interface for developer testing ├── README.md ├── requirements.txt
Clone the project repository to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/anaboset/cardio-rag-cdss cd cardio-rag-cdss
Using Conda or venv is recommended to isolate medical libraries.
Windows:
python -m venv venv .\venv\Scripts\activate pip install -r requirements.txt
Linux / Mac:
python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate pip install -r requirements.txt
Create a .env file in the root directory:
GROQ_API_KEY=your_key_here (or your choice of model) COHERE_API_KEY=your_key_here neo4j_uri=bolt://localhost:7687 neo4j_username=neo4j neo4j_password=your_password
You can run and use the app in two ways:
Command line interface
Streamlit UI
Before running either interface, you must have your medical evidence ready:
Action: Download clinical guidelines (PDF format).
Note: Use authoritative documents for the best results (e.g., ESC 2025 Guidelines).
Need Guidelines? You can find authoritative documents here:
American College of Cardiology (ACC)
European Society of Cardiology (ESC)
World Health Organization (WHO)
Best for a visual, button-click experience.
Launch the App: Open your terminal and run:
streamlit run app.py
Upload Documents: Use the Upload button on the sidebar to select your guideline PDFs.
Process Knowledge: Click the "Run Ingestion Pipeline" button. Wait for the success message (this builds your Knowledge Graph and Vector Store).
Consult: Once complete, enter the Patient Summary and your Clinical Question in the chat box to get a recommendation.
Best for fast, text-based interaction.
Place your clinical guidelines in the data/guidelines folder.
Ingest Data: Process your guidelines into the system by running:
python -m src.ingestion.loader
(You will see a progress bar as the AI "reads" your PDFs).
Start the Assistant: Launch the interactive chat:
python main.py
Follow the Prompts: The system will ask you to:
👤 Enter Patient Summary (e.g., "65yo Male, Smoker, BP 155/95")
🔍 Enter your Clinical Question (e.g., "What is the first-line treatment?")
CardioCDSS provides evidence retrieval and synthesis only.
It does not:
CardioCDSS is evaluated as a clinical decision support system, not a chatbot.
Evaluation focuses on evidence alignment, retrieval performance, and safety behavior.
Measures whether the correct guideline evidence is found.
Ensures outputs do not contradict retrieved evidence.
Verifies that cited guideline sources actually contain the referenced recommendations.
Tests system response when guidelines do not contain relevant evidence.
Clinical usability requires near-real-time performance.
To validate the system as a reliable CDSS:
Faithfulness: Does the answer contradict the retrieved guidelines?
Citation Accuracy: Are the sources cited (e.g., "ESC 2024") actually the ones containing the data?
Recall @ K: Does the multi-query retrieval successfully find the correct guideline 95% of the time?
This software is intended for research and decision-support purposes only.
It is not a medical device and not intended for diagnosis, treatment, or
clinical decision-making without qualified human oversight.
All clinical decisions must be made by licensed healthcare professionals.
The authors assume no liability for clinical use of this system.