This publication introduces a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) based AI assistant designed to ingest PDF documents from company websites, such as annual 10-K filings submitted to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and provide answers to user queries. By leveraging vector databases, embedding models, and large language models (LLMs), the assistant enables efficient analysis of financial and operational data embedded in these reports.
Corporate annual reports, particularly Form 10-K filings, are comprehensive documents that provide detailed insights into a company's financial health, operations, risks, and future outlook. These filings, mandated by the SEC for publicly traded companies, often span hundreds of pages and include complex tables, narratives, and legal disclosures. Traditional manual analysis is time-consuming and prone to oversight, especially for non-experts.
To address this, we developed a RAG-based AI assistant that automates the ingestion and querying of 10-K PDFs from company investor relations websites, such as Alphabet's (Google's) abc.xyz portal. The assistant extracts text from PDFs, chunks it for efficient retrieval, embeds the chunks using models like Sentence Transformers, stores them in a vector database (ChromaDB), and generates responses using LLMs from providers like OpenAI or Groq.
This system enhances decision-making for investors by answering questions like revenue growth trends or risk factor changes across years. For instance, analyzing Alphabet's 2023, 2024, and 2025 filings (covering fiscal years up to 2024) reveals key metrics such as total revenue increases from
The assistant's pipeline consists of document loading, processing, vector storage, and query handling, implemented in Python with libraries like PyMuPDF for PDF extraction, Sentence Transformers for embeddings, ChromaDB for vector storage, and LangChain for chaining prompts with LLMs.
PDFs are loaded from a data/ directory. Text is extracted using PyMuPDF, which handles layout preservation better than alternatives like PyPDF.
This code extracts text and tags metadata like year for multi-document comparisons.
# Your Python code here. For example: import fitz # PyMuPDF import os from typing import List, Dict, Any import re def load_documents() -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: results = [] data_dir = "data" # ... fallback logic ... for filename in os.listdir(data_dir): file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, filename) ext = os.path.splitext(filename)[1].lower() if ext == ".pdf": with fitz.open(file_path) as doc: page_count = len(doc) text_pages = [page.get_text("text") for page in doc] full_text = "\n\n".join(text_pages) year_match = re.search(r'(202[0-9])', filename) year = int(year_match.group(1)) if year_match else "Unknown" if full_text.strip(): results.append({ "content": full_text, "metadata": { "source": filename, "title": os.path.splitext(filename)[0], "filetype": "pdf", "page_count": page_count, "year": year } }) return results
Chunks are created (e.g., 500 characters with overlap) and embedded using all-MiniLM-L6-v2. Stored in ChromaDB for semantic search.
Queries trigger similarity search, context assembly (with year prefixes), and LLM invocation via LangChain. Sources are appended for transparency.
For example, analyzing revenue changes uses chunks from multiple years
We evaluated the assistant on three Alphabet 10-K PDFs:
Fiscal 2022 (filed 2023)
Fiscal 2023 (filed 2024)
Fiscal 2024 (filed 2025)
Total chunks: ~1,200 across all documents.
Here is an example of an experiment.
Enter a question or 'quit' to exit: What are the main risk factors for Google?
Searching for relevant context for: 'What are the main risk factors for Google?'
Assistant: Based on the provided context, the main risk factors for Google include:
These risk factors could potentially harm Google's business, reputation, financial condition, and operating results.
Sources:
Key observations:
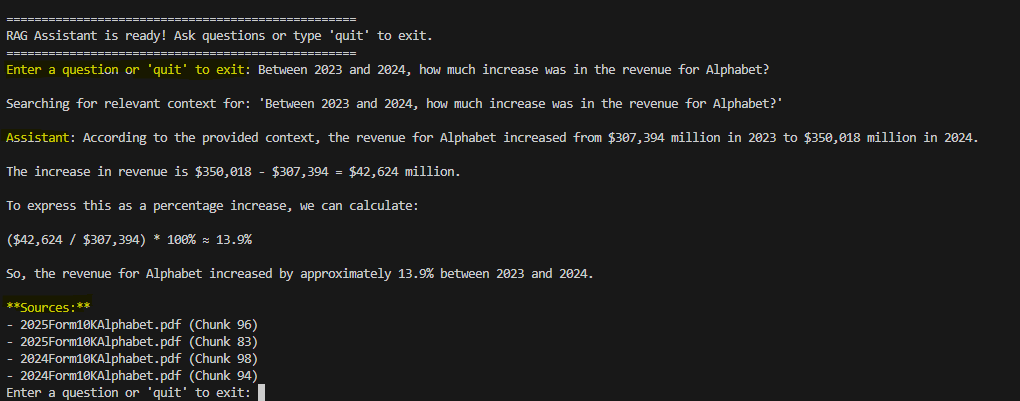
This RAG assistant streamlines the analysis of corporate 10-K filings, transforming dense PDFs into queryable knowledge bases. By automating extraction, embedding, and generation, it empowers users to uncover insights like revenue trends or risk evolutions across years. While effective for Alphabet's filings, future work could incorporate OCR for scanned documents or table parsing for financial metrics. The system demonstrates AI's potential in financial analysis, reducing manual effort and enhancing accuracy.