
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a practical approach for grounding large language models (LLMs) in external knowledge sources. This project presents a simple yet complete RAG-based question answering assistant built using LangChain and ChromaDB. The assistant ingests a custom collection of text documents, converts them into vector embeddings, stores them in a persistent vector database, and retrieves relevant document chunks at query time to generate context-aware answers using a large language model.
The system is designed to be lightweight, modular, and easy to extend. It supports multiple LLM providers and demonstrates the full RAG pipeline end-to-end, including document ingestion, chunking, embedding, retrieval, and response generation through a command-line interface.
Large language models are powerful but inherently limited by their training data and lack awareness of private or domain-specific knowledge. This makes them unsuitable for answering questions about custom documents unless those documents are explicitly provided at inference time.
The goal of this project is to address this limitation by building a Retrieval-Augmented Question Answering assistant that can:
Answer questions based only on a custom document set
Avoid hallucinations when information is not present
Be easily adapted to different domains by swapping document sources
The system follows a standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation architecture:
Document ingestion from local text files
Text chunking to create semantically meaningful segments
Embedding generation using a sentence-transformer model
Vector storage using ChromaDB
Similarity-based retrieval at query time
LLM-based answer generation using retrieved context
The assistant is exposed through a simple command-line interface that allows users to ask natural language questions and receive grounded responses.
Document Ingestion and Chunking
Text documents are loaded from a local documents/ directory. Each document is split into overlapping chunks using a recursive text splitter to preserve semantic continuity across chunks. Chunking ensures better retrieval performance and prevents context overflow when passing data to the LLM.
Embedding Generation
Each text chunk is converted into a dense vector embedding using the sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model. This model was chosen for its balance between performance and efficiency.
Vector Storage with ChromaDB
All embeddings are stored in a persistent ChromaDB collection. Metadata such as document ID and chunk index are stored alongside each embedding to support traceability and future extensions.
Retrieval
At query time, the user’s question is embedded using the same embedding model. A similarity search is performed against the vector database to retrieve the most relevant document chunks.
Prompt Construction and Generation
The retrieved chunks are combined into a context block and injected into a prompt template. The prompt instructs the LLM to answer the question strictly based on the provided context. If relevant information is not found, the system responds accordingly.
The LLM layer supports multiple providers, including OpenAI, Groq, and Google Gemini, selected automatically based on available API keys.
Framework: LangChain
Vector Store: ChromaDB (persistent)
Embedding Model: Sentence Transformers (MiniLM)
LLMs Supported:
OpenAI
Groq
Google Gemini
Interface: Command Line Interface (CLI)
Configuration: Environment variables via .env
The codebase is modular, separating concerns between the RAG pipeline (app.py) and vector database logic (vectordb.py).
Figure 1: Application startup and document ingestion pipeline
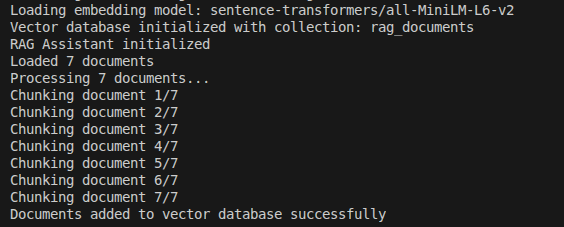
The terminal output demonstrates successful initialization of the RAG system:
sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 embedding modelrag_documentsThis confirms the full ingestion pipeline runs without errors and prepares the knowledge base for retrieval.
After starting the application, users can ask questions such as:
“What is artificial intelligence?”
“What are the ethical considerations of AI?”
“What is quantum computing?”
If a question is unrelated to the provided documents, the assistant explicitly states that the information is not available in its knowledge base.
Figure 2: Successful retrieval and grounded response for a relevant query
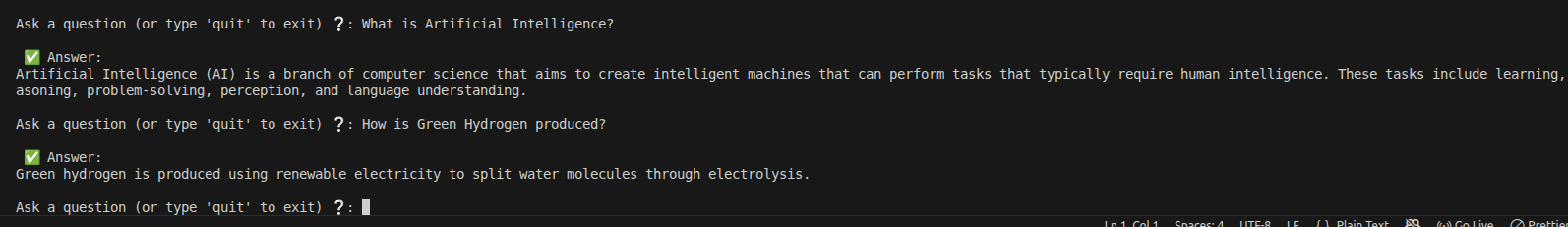
The assistant is asked: "What is artificial intelligence?"
The system retrieves relevant chunks from the custom document set and generates an accurate, context-aware response based solely on the provided knowledge base.
This demonstrates effective similarity search, proper context injection into the prompt, and faithful answer generation by the LLM.
The assistant successfully retrieves relevant document chunks and generates accurate, context-grounded answers. Queries aligned with the document content produce concise and correct responses, while unrelated queries are safely handled without hallucination.
This confirms that the RAG pipeline is functioning as intended and that retrieval quality directly influences answer quality.
To address the absence of memory in the initial implementation, the RAG assistant was extended with a lightweight conversational memory mechanism. The system maintains a rolling window of recent user–assistant interactions, which are injected directly into the prompt during response generation. This enables the assistant to retain short-term conversational context, support follow-up questions, and maintain coherence across multi-turn interactions.
The memory window is intentionally bounded to the most recent exchanges to balance contextual awareness with token efficiency. This prompt-based conversational memory strategy represents a practical and widely adopted baseline for RAG systems, enhancing usability without introducing unnecessary architectural complexity.
Figure 3: Safe handling of unrelated query – prevention of hallucination
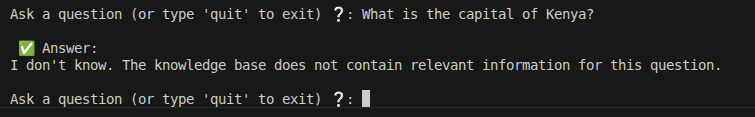
The assistant is asked a question ("What is Agentic AI?") not covered in the custom document collection.
The system correctly identifies the lack of relevant retrieved context and responds:
"I don't know. The knowledge base does not contain relevant information for this question."
This behavior is enforced by the prompt template and shows the RAG system's ability to avoid hallucinations when no supporting evidence is found.
The system currently supports text-based documents only
No reranking or advanced retrieval strategies are applied
There is no conversational memory across queries
Evaluation is qualitative rather than metric-based
These limitations were accepted intentionally to keep the project focused on core RAG concepts.
Potential enhancements include:
Adding conversational memory for multi-turn interactions
Introducing advanced retrieval techniques (reranking, hybrid search)
Supporting additional document formats such as PDF or HTML
Adding a web-based user interface
Incorporating evaluation metrics for retrieval and generation quality
This project demonstrates a complete and practical implementation of a Retrieval-Augmented Question Answering assistant using LangChain and ChromaDB. It highlights how LLMs can be grounded in custom knowledge bases to produce reliable and context-aware responses. The system serves as a strong foundation for more advanced agentic or multi-tool extensions in future work.