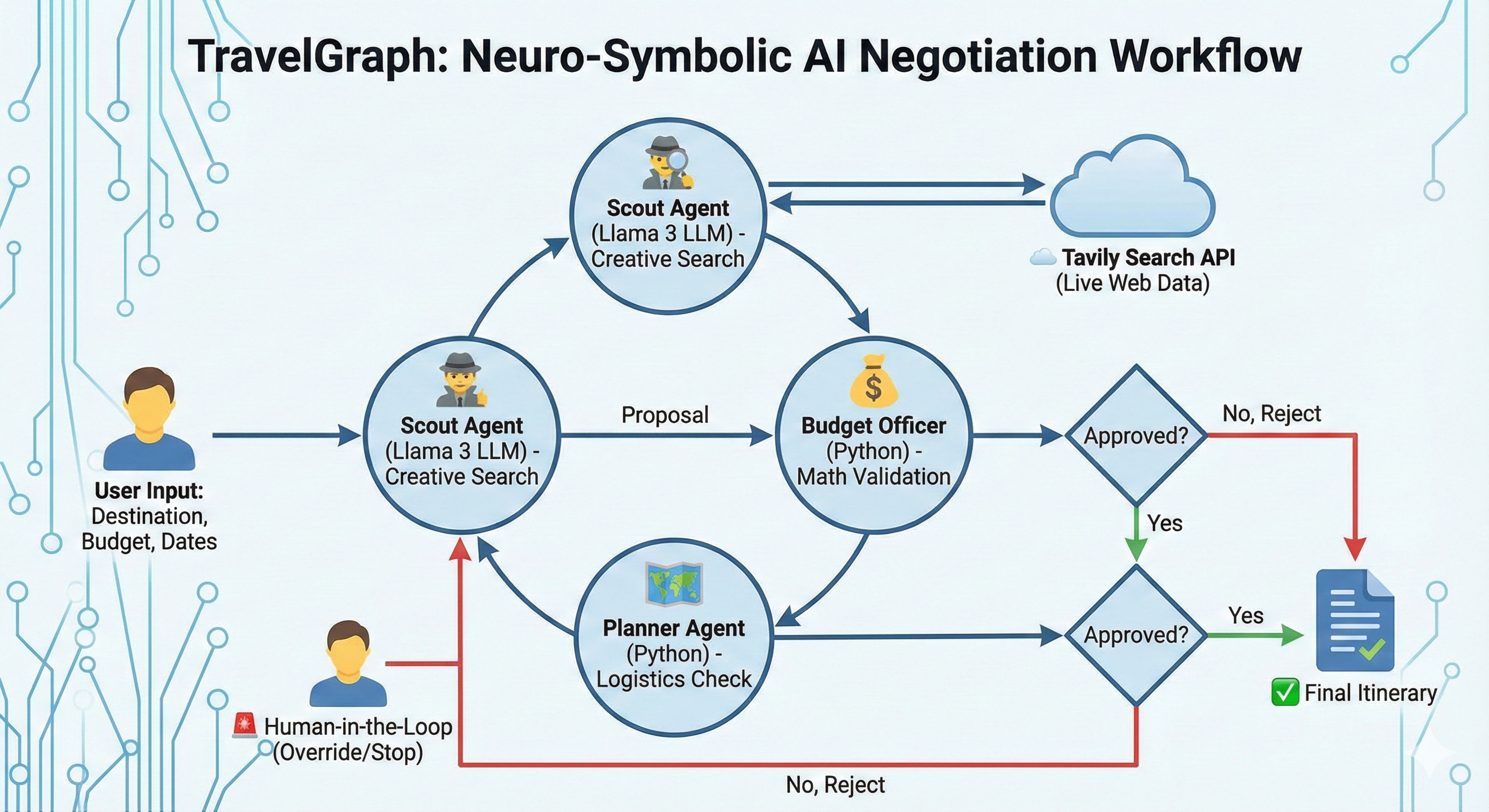
In the current era of Generative AI, large language models (LLMs) are celebrated for their creativity and reasoning capabilities. However, when tasked with strict constraints—such as planning a trip within a specific budget—they often fail. Users frequently encounter "hallucinations" in which the AI suggests nonexistent hotels, miscalculates total costs, or ignores distance constraints entirely. This limitation inspired the creation of TravelGraph, a neuro-symbolic multi-agent system powered by LangGraph and Groq.
The primary purpose of this work is to demonstrate how to build reliable autonomous agents by combining the reasoning power of LLMs with the deterministic precision of code. Unlike standard chatbots that try to do everything via text generation, TravelGraph orchestrates a team of specialised agents: a "Scout" for creative search, and strict "Budget" and "Planner" officers powered by pure Python logic. This hybrid approach ensures that, while the search process remains flexible and creative, cost and logistics validation remain mathematically accurate.
Through this project, readers will gain a practical understanding of "Neuro-Symbolic" architecture, cyclic state graphs, and Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) patterns. The work demonstrates how to transform fragile AI demos into robust engineering systems that can negotiate, self-correct, and handle real-world data without hallucinating.
Planning a travel itinerary involves a complex interplay of conflicting constraints: location, quality, and cost. Relying solely on pure LLMs (such as ChatGPT) to handle this poses several engineering challenges. First, LLMs are probabilistic, meaning they cannot guarantee mathematical accuracy; they often state that "
This project introduces TravelGraph, a system that treats travel planning as a negotiation rather than a generation task. The process begins with the Scout Agent (powered by Llama 3 on Groq), which interprets the user's destination and uses the Tavily API to fetch real-time hotel data. Crucially, the Scout uses a robust Regex-based extraction method to parse messy web text into clean JSON.
Once a proposal is made, it is passed to the Budget Officer and Planner Agent. Unlike the Scout, these agents do not use LLMs. Instead, they utilise deterministic Python functions to calculate total trip costs (including food and taxes) and verify geolocation constraints. If a proposal violates a rule (e.g., "Too expensive"), the system does not crash; it loops back to the Scout with specific feedback. The Scout then uses this feedback to pivot its strategy—for example, switching from searching "Luxury" hotels to "Budget" options—mimicking human problem-solving.
A common approach to building agents is to let a single powerful LLM (like GPT-4) handle all reasoning, math, and tool calling. However, in this project, a "Pure LLM" approach exhibited significant latency and reliability issues. LLMs are comparatively slow and costly when performing simple arithmetic, and they are prone to subtle calculation errors. To overcome these limitations, a Neuro-Symbolic architecture was adopted. This method assigns "Neuro" tasks (unstructured search, strategy) to the LLM and "Symbolic" tasks (math, distance checks) to Python code. This switch drastically reduced latency (as code executes in microseconds) and guaranteed 0% hallucination rates on budget calculations. It provides a stable foundation where the AI can be creative, while code ensures it remains correct.
The system is architected as a decoupled microservice, with the core intelligence hosted on a FastAPI backend. The reasoning engine is designed around a State Graph using the LangGraph framework, where a shared state object (AgentState) circulates among independent nodes.
APPROVED. If failed, the state is marked REJECTED with a specific reason appended to the shared history.retry_count.N=3), the backend pauses execution and returns a WAITING_FOR_HUMAN status code (422 or 200 with specific flags).To evaluate the efficiency and reliability of the TravelGraph system, several stress tests were conducted to focus on error handling and negotiation logic.
Here is the updated "Getting Started" section. It replaces the old single-command instruction with the required Client-Server workflow (Two Terminals).
Follow these steps to deploy the Microservices architecture locally.
1. Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/your-username/travel-negotiator.git cd travel-negotiator
2. Install Dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
3. Set Environment Variables
Create a .env file in the project root and add your API keys:
GROQ_API_KEY=gsk_... TAVILY_API_KEY=tvly-...
4. Run the Application
Because the system uses a decoupled architecture, you must run the Backend (Brain) and Frontend (UI) in separate terminal windows.
Terminal 1: Start the Backend API
This launches the FastAPI server that hosts the AI agents.
uvicorn src.api:app --reload # Wait for the message: "Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000"
Terminal 2: Start the Frontend UI
Open a new terminal window and launch the Streamlit client.
streamlit run frontend_client.py
5. Start a Negotiation
Open your browser to the URL shown in Terminal 2 (usually http://localhost:8501). Enter your destination and budget to trigger the multi-agent debate:
(Price * Days) and strictly enforces the budget cap..png?Expires=1770171774&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=yv~pl-hVz7eXHp9V2ioRK6MeY15TUo9B7Gh-vTUnalW80-JqRAGW7QKYPz0jnVDqbh7M6~IArMaroqffvC4v8PB1XipnYkfX9nlKjW3KgTtFtjfpG1skqManfKdFwxFX8LBDEVwf3QB1M4BXDrAZPd9ixAh94GtLVclSd6WZq6keSava9GJGtPJEcb3vcl57OmAdq~M4c~rebjedjODVdR9cbf8zMWwYRP4s25NYSX1PDJoX5utpU4xct5OcbIMSxmDN63AVEmY36adJmYQVfDRB1IpgYq2E9d1O2IoIqG4w1TENH9ZaxAq1NZG4q7BDwQvsxbh~55VrwrNdwCzjWA__)
The web interface of this project can be viewed using this link: https://travelnegotiator-xskhdqyqyoucroffxxggg4.streamlit.app/
To evolve the system from a functional prototype to a production-grade microservices architecture, significant engineering effort was directed toward reliability, observability, and automated validation. The following enhancements ensure the system operates deterministically under real-world conditions.
A tiered automated testing strategy was implemented using pytest and FastAPI TestClient to ensure regression-free development:
total_cost <= budget) are strictly enforced with 100% accuracy, independent of the AI's probabilistic nature.unittest.mock to simulate agent interactions within the LangGraph state machine. This validates complex routing logic—specifically Deadlock Detection and Human-Handoff—without incurring API latency or costs.@pytest.mark.live) is employed for production health checks. These tests interact with live Groq and Tavily endpoints to continuously benchmark the effectiveness of prompts and the fidelity of data parsing against real-time web data.To mitigate the inherent unpredictability of Large Language Models, the system incorporates multiple layers of defensive programming:
r"\{.*?\}"). This decouples the structured JSON payload from conversational "fluff," ensuring downstream agents receive only valid, parseable data.retry_count variable. Upon exceeding a configurable threshold (N=3), the system suspends autonomous execution and raises a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) interrupt. This mechanism prevents resource exhaustion from infinite negotiation loops.Proxy-Aware Networking:
The networking layer includes custom middleware to handle localhost proxy bypassing. This ensures the frontend-backend handshake remains stable even in restricted network environments (e.g., corporate/university firewalls).
Operational Observability:
logging module to generate timestamped, severity-graded telemetry (INFO, WARNING, ERROR), facilitating rapid root-cause analysis in production.The system architecture prioritises resilience and observability to ensure consistent performance during complex multi-agent negotiations.
A. Failure Handling & Graceful Degradation
The system treats failures not as terminal errors, but as control flow events:
retry_count. Upon reaching the retry limit, control is gracefully transferred to the user via the Human-in-the-Loop interface.try-except blocks. In the event of malformed web data or parsing errors, the system triggers a fallback mechanism, logging the error while maintaining the application state to prevent a crash.Budget Officer are captured as structured error messages and fed back into the Scout agent’s context window, allowing the LLM to "learn" from the failure and adjust its subsequent search parameters dynamically.To maintain operational visibility, the system moves beyond simple console outputs:
logging library is configured to emit timestamped, severity-graded logs. This provides a clear audit trail of the negotiation lifecycle, identifying exactly which agent (Scout, Planner, or Budget) triggered a state change or rejection.The technology stack was selected to optimise for scalability, maintainability, and distinct separation of concerns:
Microservices Architecture (FastAPI + Streamlit):
The system adopts a decoupled Client-Server model. The FastAPI Backend acts as the dedicated "Brain," hosting the LangGraph agents and managing state. The Streamlit Frontend serves as a lightweight presentation layer that consumes the API via REST endpoints. This separation allows for independent scaling of the reasoning engine and the user interface.
Inference Engine (Groq):
The system leverages Groq for Llama 3 inference. This choice was critical for the multi-agent architecture; the ultra-low latency of Groq’s LPU (Language Processing Unit) allows for multiple agent "turns" to occur in seconds, ensuring the "propose-critique-revise" loop feels instantaneous.
Orchestration (LangGraph):
LangGraph was chosen over linear chains due to its support for cyclic graphs and persistent state. This capability is essential for implementing the iterative negotiation workflow where agents must remember previous rejections to improve future proposals.
The main advantage of this project is the reliability gained by decoupling reasoning from calculation. By using a neuro-symbolic approach, TravelGraph ensures that financial and logistical constraints are enforced by rigid code, eliminating the risk of costly hallucinations. The integration of Tavily ensures that all data is real-time, preventing LLMs from recommending closed businesses or outdated prices. Furthermore, the Human-in-the-Loop architecture provides a safety net, ensuring the system never gets stuck in an infinite loop without user oversight. The Streamlit UI wraps this complexity in a user-friendly, universal-theme interface that makes the internal negotiation transparent and engaging.
While the current implementation provides a robust framework for travel negotiation, several avenues for improvement remain. Integrating the Google Maps API would provide precise travel time calculations rather than the current proxy logic. Expanding the toolset to include flight search APIs (like Amadeus or Skyscanner) would turn this into a full-stack travel booking agent. Additionally, deploying the application to Streamlit Cloud with a persistent database would allow users to save and share their negotiated itineraries. Finally, fine-tuning a smaller Llama 3 model specifically for JSON extraction could further reduce latency and API costs.
This project showcases the potential of LangGraph and Neuro-Symbolic AI to transform how we build autonomous agents. By acknowledging LLMs' limitations and supporting them with deterministic code and human oversight, TravelGraph delivers a planning experience that is both creative and trustworthy. The adoption of a cyclic graph architecture enabled sophisticated self-correction behaviours that linear chains cannot match. Ultimately, this work provides a practical blueprint for engineers looking to build agents that must operate within the strict constraints of the real world.