
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transcended its role as a mere technological advancement to become a pivotal force reshaping global security dynamics. From autonomous weaponry and surveillance systems to cyber warfare and information manipulation, AI's integration into national defense strategies has outpaced the development of corresponding ethical and regulatory frameworks.
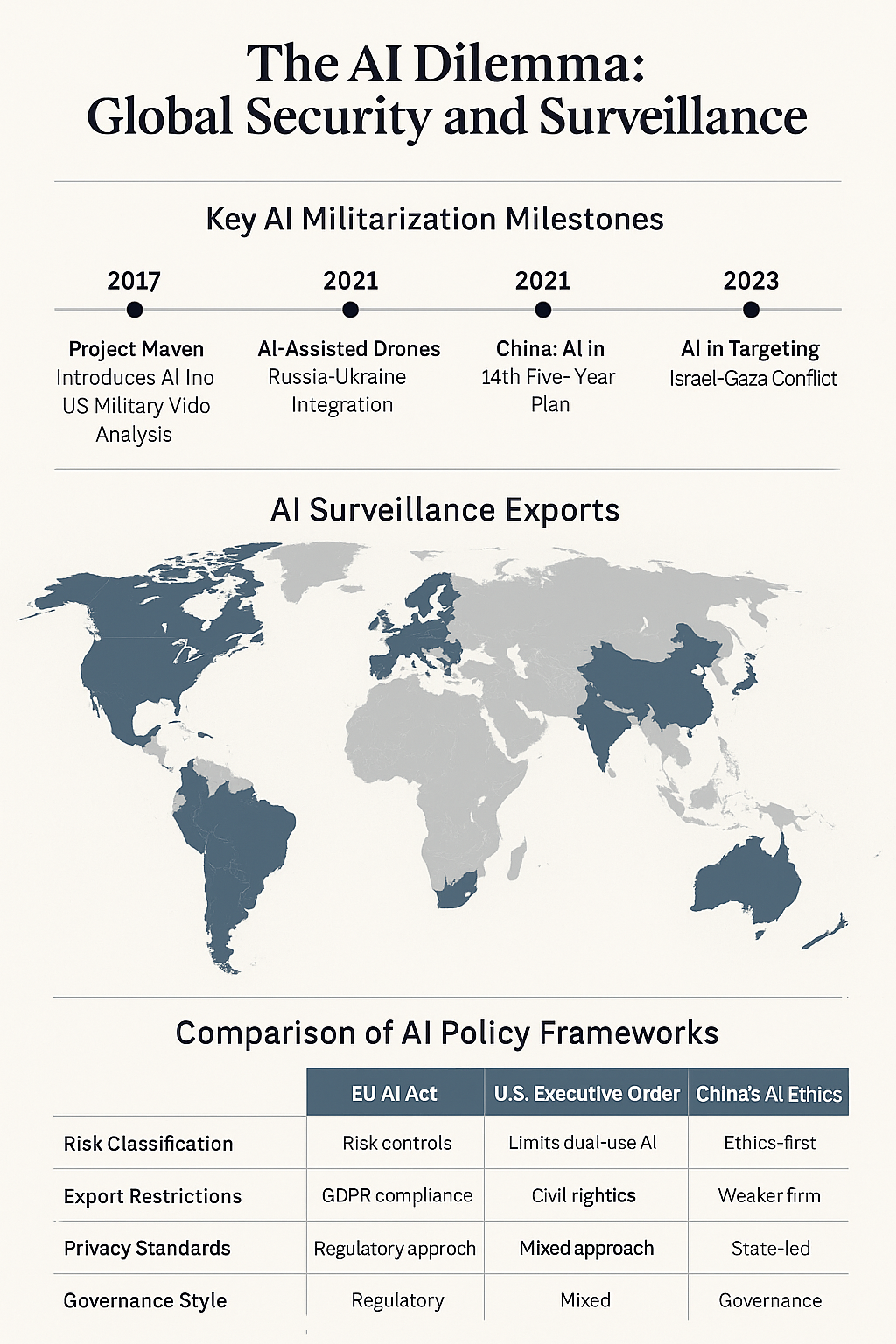
Modern militaries are increasingly deploying AI to enhance Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, automate decision-making processes, and improve operational efficiency. For instance, the U.S. Department of Defense's Project Maven utilizes machine learning to analyze vast amounts of video data, aiding in target identification. Similarly, Israel's Defense Forces have implemented AI systems like "Lavender" and "Gospel" for target selection during conflicts .
Militaryembedde CyberDefensereView
The potential for AI systems to make life-and-death decisions without human intervention challenges existing ethical norms and international humanitarian laws.
AI-driven systems may misinterpret signals or actions, leading to unintended escalations without human oversight.
Determining responsibility for AI-induced actions remains a complex legal and moral issue.
The international community exhibits varied approaches to AI governance, reflecting differing priorities and values.
The U.S. emphasizes innovation, with federal agencies issuing guidelines and executive orders to steer AI development. However, the absence of binding regulations has led to concerns about inconsistent oversight and ethical considerations .
knowledge.dlapiper.com
The EU's Artificial Intelligence Act represents a comprehensive attempt to regulate AI, focusing on risk assessment and transparency. While aiming to set global standards, critics argue that stringent regulations may hinder innovation .
Pernot-Leplay
China's approach integrates AI development into national strategies, emphasizing state control and surveillance capabilities. The export of Chinese AI surveillance technologies to various countries has raised concerns about the proliferation of authoritarian practices .
eh4s.eu
To enhance understanding, the following visual aids are recommended:
Global distribution of AI surveillance exports, highlighting China's leading role.
Key milestones in AI militarization from 2015 to 2025, illustrating the rapid integration of AI into defense strategies.
Side-by-side analysis of AI policy frameworks in the U.S., EU, and China, showcasing differences in regulatory approaches.
The fragmented nature of AI governance necessitates the establishment of cohesive international frameworks:
Develop binding agreements to regulate the development and deployment of AI in military contexts.
Implement universal ethical guidelines to govern AI applications, ensuring respect for human rights and international laws.
Establish global bodies to monitor AI developments, facilitate information sharing, and enforce compliance.
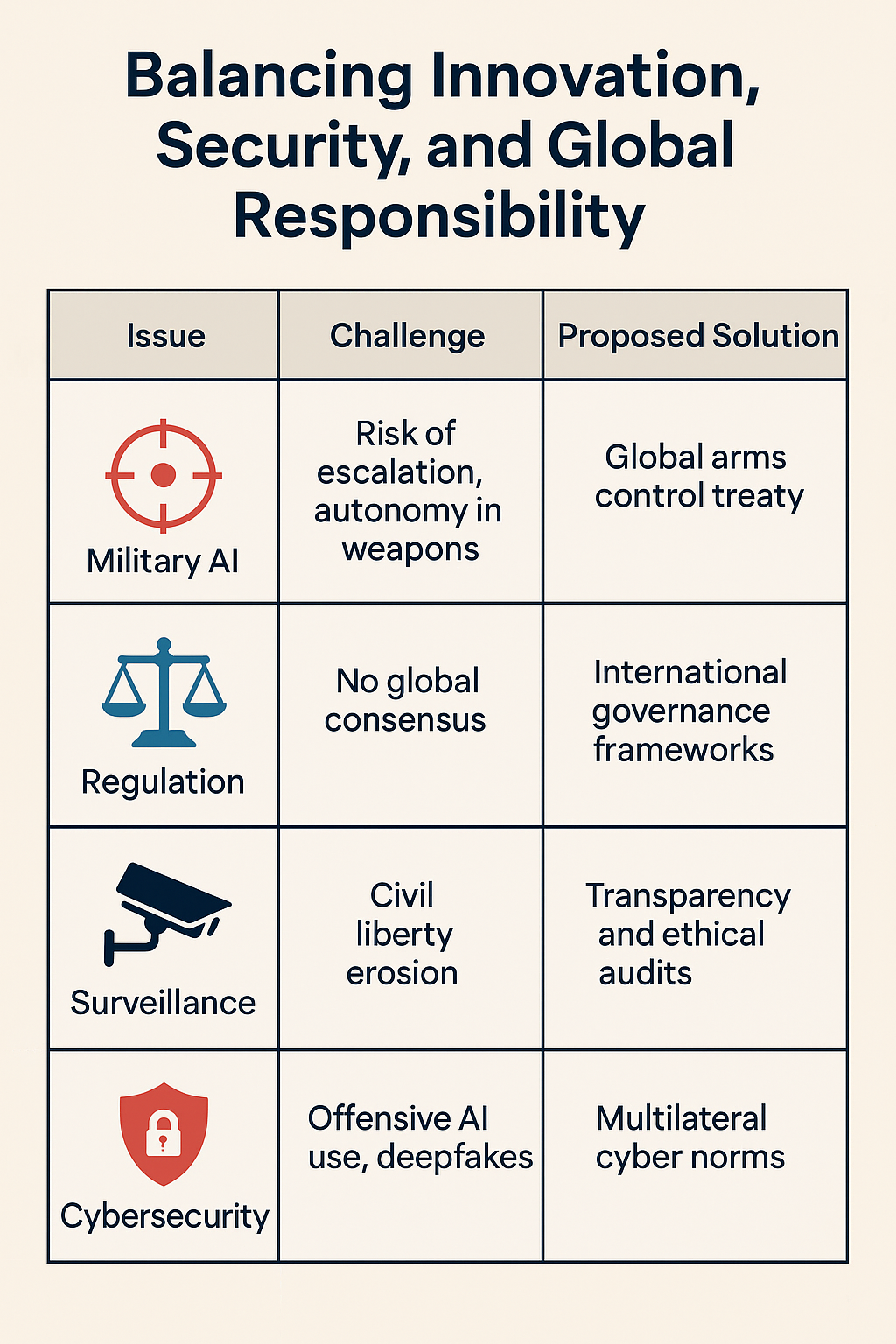
As AI continues to redefine global security paradigms, it is imperative to balance technological advancement with ethical responsibility. Collaborative efforts among nations, guided by shared values and mutual interests, are essential to harness AI's potential while mitigating its risks.