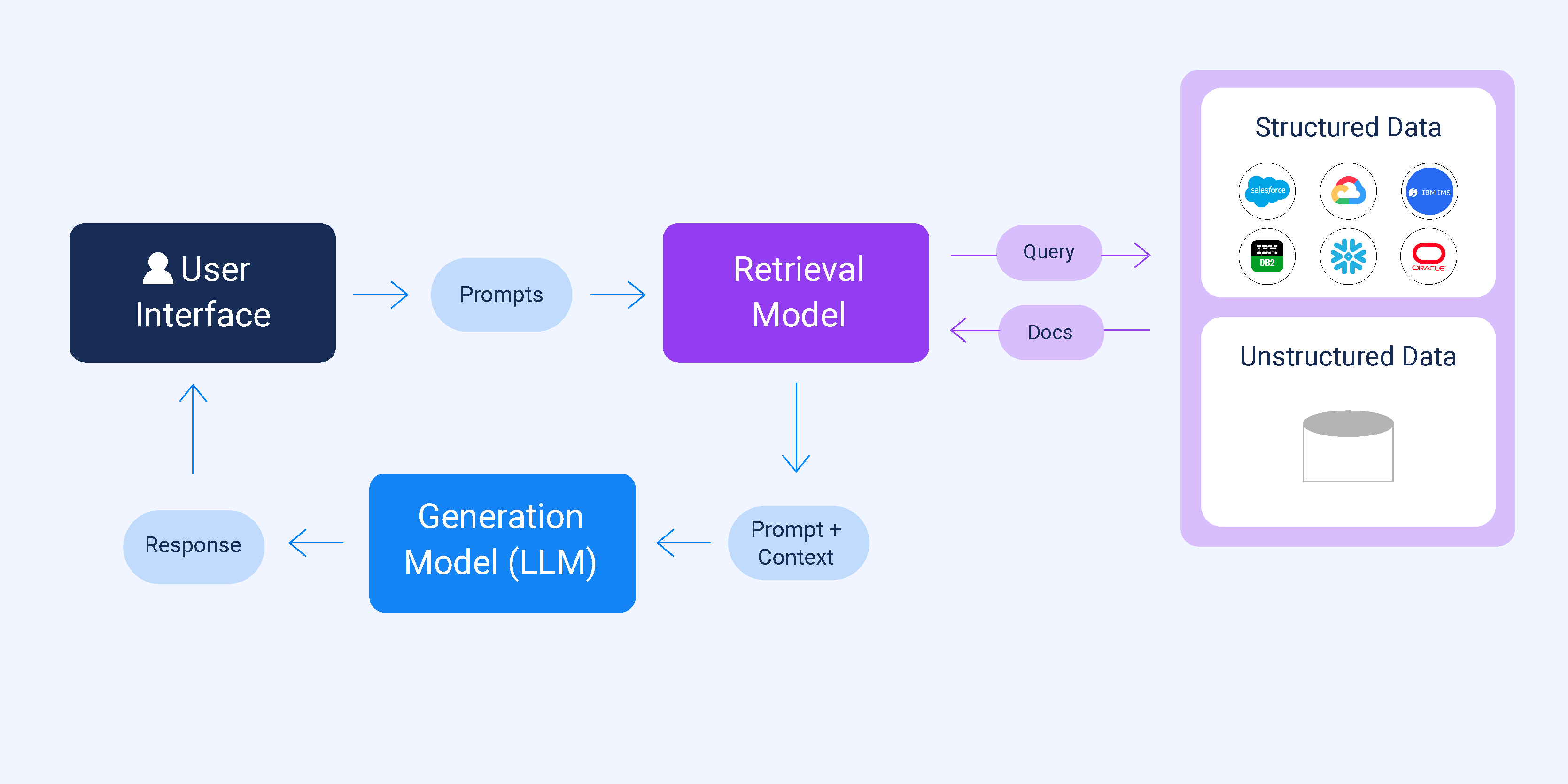
This project presents a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) chatbot that integrates dense vector search with a lightweight language model to provide accurate, context-grounded responses. Unlike conventional chatbots that rely purely on model knowledge, this system retrieves relevant information from structured JSON documents before generating its responses.
The chatbot is designed to be lightweight, easily deployable on local machines, and adaptable for various real-world knowledge bases, research archives, or organizational document retrieval. It supports both OpenVINO for Intel accelerators and PyTorch for CPU or CUDA-enabled GPUs, making it flexible across hardware environments.
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive conversational abilities, yet they can produce incorrect or hallucinated information when external context is lacking. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses this limitation by combining retrieval of relevant document information with model-based generation.
In this project, a RAG chatbot was designed, which is capable of loading structured JSON datasets, splitting documents into semantically coherent chunks, indexing them using FAISS for fast retrieval, and generating accurate answers with a lightweight LLM backend. This approach ensures that all responses are grounded in actual data, fast, and hardware-agnostic.
The methodology was designed to maximize retrieval accuracy and generate context-aware responses.
Input documents are stored in JSON format with title and content fields. Each document is converted into a langchain.Document object. Text is then split into overlapping chunks using RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, which maintains semantic coherence for efficient retrieval.
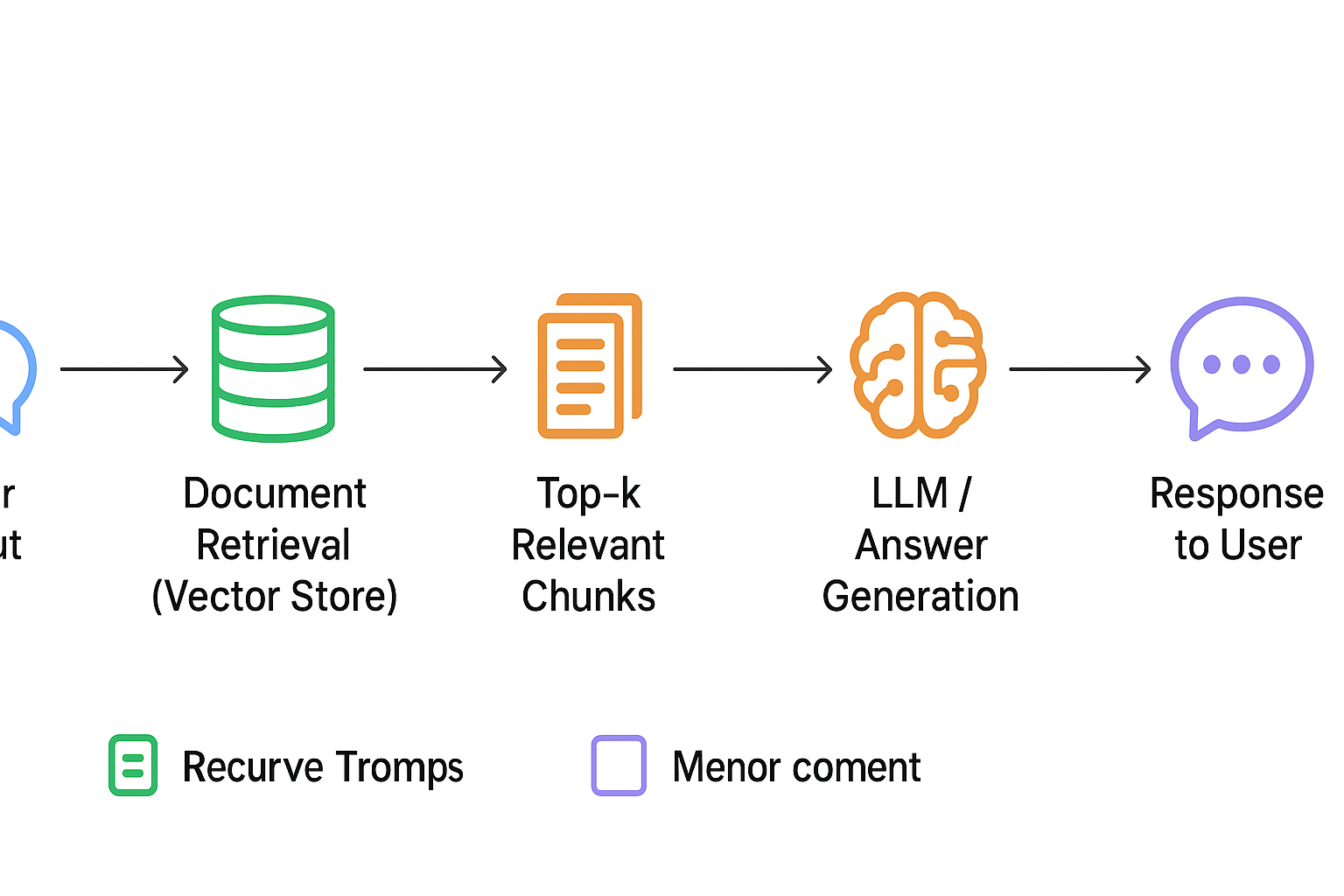
Chunks are converted into dense vector embeddings using Hugging Face Sentence Transformer (all-MiniLM-L6-v2). These vectors are indexed using FAISS, enabling fast and accurate similarity searches for any user query.
The chatbot uses a dual-backend strategy:
The model is wrapped with a Hugging Face pipeline, allowing seamless integration with langchain.
When a user submits a query, the system:
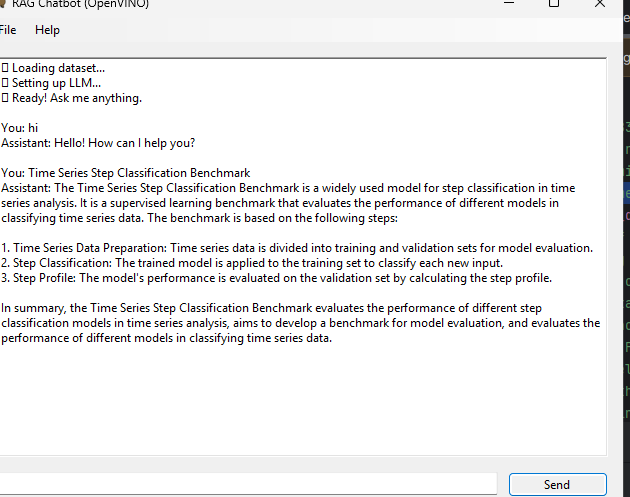
A GUI built with Toga allows users to interact with the chatbot in a clean, intuitive environment. Messages and responses are logged for easy tracking.
The RAG chatbot was tested on multiple hardware configurations to evaluate retrieval accuracy, response speed, and overall output quality.
Hardware Tested: Intel UHD GPU, NVIDIA GPU, CPU fallback supported
Dataset: Sample JSON file with multiple publication entries
Embedding Model: sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
Generation Model: HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-360M-Instruct
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Chunk Size | 1000 characters |
| Overlap | 200 characters |
| Top-k Retrieved Chunks | 10 |
| Similarity Threshold | 0..1 |
This project shows how Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can make chatbots more reliable by grounding responses on real data instead of relying only on a language model.
By combining a retriever, a vector database, and a generation model, the chatbot provides accurate and context-aware answers to document-based queries.
Although the system performs well, there’s still room for improvement in speed, memory handling, and scalability for larger datasets.
Overall, this work is a practical example of how RAG can turn traditional chatbots into smarter, knowledge-driven assistants.