ChatSphere - Advanced College Chatbot Framework
Introduction
ChatSphere is an advanced chatbot framework developed from scratch using Python with enhanced NLP capabilities, specifically designed for college environments. It features a custom-built institutional dataset and robust deployment pipeline.
Key capabilities:
- Intent classification (Multinomial Naive Bayes, Decision Tree, Random Forest)
- Advanced text preprocessing with MWE recognition and contraction handling
- TF-IDF feature extraction with mathematical rigor
- Containerized deployment on Google Cloud with Vercel frontend
- Contextual dialogue management
System Architecture
Core Components
Text Preprocessing Pipeline
Multi-Word Expression (MWE) Recognition using WordNet
Comprehensive contraction handling
Advanced hyphen/punctuation management
Case normalization and token splitting
Feature Extraction
- Custom TF-IDF Vectorizer with smoothing:
TF-IDF(t,d) = (Count(t,d)/∑Count(t',d)) × [log((N+1)/(DF(t)+1)) + 1] - Vocabulary construction from tokenized corpus
class PreProcessing: class Tokenizer: def __init__(self): try: self.wordnet = wn self.MWEs = self.list_MWEs() # converts new york to -> New_york - as its one entity except: print("WordNet initialization failed. Using basic tokenization.") self.MWEs = [] #Replacing or extracting parts of strings. #Cleaning and preprocessing text. self.compile_regex_patterns() def list_MWEs(self): MWEs = [] try: # Get multi-word nouns nouns = self.wordnet.synsets(pos="n") MWEs.extend([syn.lemmas()[0] for syn in nouns if " " in syn.lemmas()[0]]) # Get multi-word verbs verbs = self.wordnet.synsets(pos="v") MWEs.extend([syn.lemmas()[0] for syn in verbs if " " in syn.lemmas()[0]]) except: print("Error extracting MWEs. Using empty list.") return MWEs def compile_regex_patterns(self): if self.MWEs: mwe_patterns = [rf"\b{re.escape(mwe)}\b" for mwe in self.MWEs] self.regex_pattern = re.compile("|".join(mwe_patterns)) else: self.regex_pattern = re.compile(r"") self.hyphen_pattern = re.compile(r"\b(\w+)-(\w+)\b") self.number_unit_pattern = re.compile(r"(\d+)([a-zA-Z]+)") self.punctuation_pattern = re.compile(r"[^\w\s\-_]") self.contraction_pattern = re.compile(r"\b(" + "|".join(map(re.escape, contractions_dict.keys())) + r")\b", re.IGNORECASE) def tokenize(self, text): """Tokenize the input text with preprocessing steps.""" text = text.lower() if self.MWEs: text = self.regex_pattern.sub(lambda match: match.group(0).replace(" ", "_"), text) text = self.contraction_pattern.sub(lambda match: contractions_dict.get(match.group(0).lower(), match.group(0)), text) text = self.hyphen_pattern.sub(r"\1 \2", text) text = self.number_unit_pattern.sub(r"\1_\2", text) text = self.punctuation_pattern.sub("", text) tokens = text.split() return tokens class tf_idf_Vectorizer: def __init__(self, max_features=None): self.vocabulary = {} self.idf = {} self.max_features = max_features self.fitted = False def fit(self, corpus): if isinstance(corpus[0], str): tokenizer = PreProcessing.Tokenizer() corpus = [tokenizer.tokenize(doc) for doc in corpus] elif not isinstance(corpus[0], list): raise ValueError("Corpus must be a list of strings or tokenized documents (list of lists).") df = Counter() for doc in corpus: unique_words = set(doc) df.update(unique_words) sorted_words = [word for word, _ in df.most_common(self.max_features)] if self.max_features else list(df.keys()) self.vocabulary = {word: idx for idx, word in enumerate(sorted_words)} N = len(corpus) self.idf = {word: np.log((N + 1) / (df[word] + 1)) + 1 for word in self.vocabulary} self.fitted = True return self def transform(self, documents): if not self.fitted: raise ValueError("Vectorizer needs to be fitted before transform") if isinstance(documents[0], str): tokenizer = PreProcessing.Tokenizer() documents = [tokenizer.tokenize(doc) for doc in documents] elif not isinstance(documents[0], list): raise ValueError("Input documents must be strings or tokenized documents (list of lists).") tfidf_matrix = np.zeros((len(documents), len(self.vocabulary))) for i, doc in enumerate(documents): tf = Counter(doc) total_words = len(doc) for word, count in tf.items(): if word in self.vocabulary: word_idx = self.vocabulary[word] tfidf_matrix[i][word_idx] = (count / total_words) * self.idf.get(word, 0) return tfidf_matrix def fit_transform(self, documents): self.fit(documents) return self.transform(documents)
Intent Classifiers
- Multinomial Naive Bayes (90.48% accuracy)
- Laplace smoothing implementation
P(t|c) = (Count(t,c)+1)/(∑Count(t',c)+|V|) - Decision Tree (89.08% accuracy)
- Gini Index and Entropy based splitting
- Random Forest (91.11% accuracy - best performing)
- Ensemble of decision trees with mode aggregation
class MultinomialNBFromScratch(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin): def __init__(self, alpha=1.0): self.alpha = alpha # Smoothing parameter def fit(self, X, y): X, y = check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse=True) self.classes_ = unique_labels(y) n_classes = len(self.classes_) n_features = X.shape[1] # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X # Ensure all values are non-negative for Multinomial NB if np.any(X_array < 0): raise ValueError("Input X must be non-negative for MultinomialNB") # Initialize parameters self.class_count_ = np.zeros(n_classes, dtype=np.float64) self.feature_count_ = np.zeros((n_classes, n_features), dtype=np.float64) # Count samples in each class for i, c in enumerate(self.classes_): X_c = X_array[y == c] self.class_count_[i] = X_c.shape[0] self.feature_count_[i] = np.sum(X_c, axis=0) # Calculate log probabilities with smoothing smoothed_fc = self.feature_count_ + self.alpha smoothed_cc = np.sum(smoothed_fc, axis=1) self.feature_log_prob_ = np.log(smoothed_fc) - np.log(smoothed_cc.reshape(-1, 1)) self.class_log_prior_ = np.log(self.class_count_) - np.log(np.sum(self.class_count_)) return self def predict_log_proba(self, X): check_is_fitted(self, ['feature_log_prob_', 'class_log_prior_']) X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True) # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X # Calculate log probabilities for each class joint_log_likelihood = np.zeros((X_array.shape[0], len(self.classes_))) for i, c in enumerate(self.classes_): joint_log_likelihood[:, i] = self.class_log_prior_[i] joint_log_likelihood[:, i] += np.dot(X_array, self.feature_log_prob_[i]) # Normalize to get probabilities (using logsumexp trick for numerical stability) log_prob_x = np.max(joint_log_likelihood, axis=1) log_prob_x_adjusted = log_prob_x + np.log(np.sum( np.exp(joint_log_likelihood - log_prob_x.reshape(-1, 1)), axis=1 )) log_probas = joint_log_likelihood - log_prob_x_adjusted.reshape(-1, 1) return log_probas def predict_proba(self, X): return np.exp(self.predict_log_proba(X)) def predict(self, X): log_probas = self.predict_log_proba(X) return self.classes_[np.argmax(log_probas, axis=1)] class DecisionTreeClassifierFromScratch(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin): def __init__(self, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, criterion='gini', max_features=None, random_state=None): self.max_depth = max_depth self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf self.criterion = criterion self.max_features = max_features self.random_state = random_state self.tree_ = None self.feature_importances_ = None class Node: def __init__(self, feature=None, threshold=None, left=None, right=None, value=None): self.feature = feature # Which feature to split on self.threshold = threshold # Threshold value for the split self.left = left # Left child self.right = right # Right child self.value = value # Class distribution or prediction def _gini(self, y): """Calculate Gini impurity""" m = len(y) if m == 0: return 0 # Use bincount with proper handling of class indices counts = np.bincount(y, minlength=len(self.classes_)) probas = counts / m return 1 - np.sum(probas**2) def _entropy(self, y): """Calculate entropy""" m = len(y) if m == 0: return 0 # Use bincount with proper handling of class indices counts = np.bincount(y, minlength=len(self.classes_)) probas = counts / m # Avoid log(0) by filtering zero probabilities nonzero_probas = probas[probas > 0] return -np.sum(nonzero_probas * np.log2(nonzero_probas)) def _calculate_impurity(self, y): """Calculate impurity based on the criterion""" if self.criterion == 'gini': return self._gini(y) elif self.criterion == 'entropy': return self._entropy(y) else: raise ValueError(f"Unknown criterion: {self.criterion}") def _best_split(self, X, y, features_to_consider): """Find the best split for the data""" m, n = X.shape if m <= 1: return None, None # Get current impurity current_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y) best_gain = 0.0 best_feature, best_threshold = None, None # Only consider the randomly selected features for feature in features_to_consider: # Get unique values for the feature feature_values = X[:, feature] # Check if all values are identical if np.all(feature_values == feature_values[0]): continue # Use a more efficient approach for finding potential thresholds # Instead of using every unique value, sample a reasonable number of thresholds # For small datasets, still use all unique values unique_values = np.unique(feature_values) if len(unique_values) > 10: # For large number of unique values, use percentiles instead percentiles = np.linspace(5, 95, 10) thresholds = np.percentile(feature_values, percentiles) else: thresholds = unique_values # Try each threshold for threshold in thresholds: # Split the data left_indices = X[:, feature] <= threshold right_indices = ~left_indices # Skip if either side has fewer than min_samples_leaf if np.sum(left_indices) < self.min_samples_leaf or np.sum(right_indices) < self.min_samples_leaf: continue # Calculate impurity for each side left_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y[left_indices]) right_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y[right_indices]) # Calculate the weighted average impurity n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_indices), np.sum(right_indices) weighted_impurity = (n_left / m) * left_impurity + (n_right / m) * right_impurity # Calculate information gain gain = current_impurity - weighted_impurity # Update best split if this is better if gain > best_gain: best_gain = gain best_feature = feature best_threshold = threshold return best_feature, best_threshold def _select_features(self, n_features, random_state=None): """Select features to consider for splitting""" if self.max_features is None: return np.arange(n_features) rng = np.random.RandomState(random_state) if isinstance(self.max_features, int): n_features_to_consider = min(self.max_features, n_features) elif isinstance(self.max_features, float): n_features_to_consider = max(1, int(self.max_features * n_features)) elif self.max_features == 'sqrt': n_features_to_consider = max(1, int(np.sqrt(n_features))) elif self.max_features == 'log2': n_features_to_consider = max(1, int(np.log2(n_features))) else: n_features_to_consider = n_features return rng.choice(n_features, size=n_features_to_consider, replace=False) def _build_tree(self, X, y, depth=0, node_idx=0, feature_importances=None): """Recursively build the decision tree""" n_samples, n_features = X.shape # Convert class labels to indices for proper bincount y_idx = np.searchsorted(self.classes_, y) # Get the class distribution (use the class indices to ensure proper counts) value = np.bincount(y_idx, minlength=len(self.classes_)) # Create a leaf node if stopping criteria are met if (self.max_depth is not None and depth >= self.max_depth) or \ n_samples < self.min_samples_split or \ n_samples < 2 * self.min_samples_leaf or \ np.unique(y).size == 1: return self.Node(value=value) # Select features to consider (for random forest) features_to_consider = self._select_features( n_features, random_state=self.random_state + node_idx if self.random_state is not None else None ) # Find the best split best_feature, best_threshold = self._best_split(X, y_idx, features_to_consider) # If no good split was found, create a leaf node if best_feature is None: return self.Node(value=value) # Split the data left_indices = X[:, best_feature] <= best_threshold right_indices = ~left_indices # Track feature importance if feature_importances is not None: # Compute node impurity reduction and weight by node size current_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y_idx) left_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y_idx[left_indices]) right_impurity = self._calculate_impurity(y_idx[right_indices]) n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_indices), np.sum(right_indices) weighted_impurity = (n_left / n_samples) * left_impurity + (n_right / n_samples) * right_impurity # Update feature importance impurity_decrease = current_impurity - weighted_impurity feature_importances[best_feature] += impurity_decrease # Build subtrees left_subtree = self._build_tree( X[left_indices], y[left_indices], depth + 1, node_idx * 2 + 1, feature_importances ) right_subtree = self._build_tree( X[right_indices], y[right_indices], depth + 1, node_idx * 2 + 2, feature_importances ) return self.Node( feature=best_feature, threshold=best_threshold, left=left_subtree, right=right_subtree, value=value ) def fit(self, X, y): # Check that X and y have correct shape and convert sparse to dense X, y = check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse=True) # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X self.classes_ = unique_labels(y) # Initialize feature importances array self.feature_importances_ = np.zeros(X_array.shape[1]) # Set random seed if provided if self.random_state is not None: np.random.seed(self.random_state) # Build the tree self.tree_ = self._build_tree(X_array, y, feature_importances=self.feature_importances_) # Normalize feature importances to sum to 1 if np.sum(self.feature_importances_) > 0: self.feature_importances_ /= np.sum(self.feature_importances_) return self def _predict_one(self, x, node): """Predict for a single instance""" if node.feature is None: # Leaf node # Handle division by zero safely if np.sum(node.value) == 0: # Return uniform distribution if value is all zeros return np.ones(len(self.classes_)) / len(self.classes_) return node.value / np.sum(node.value) # Return probability distribution if x[node.feature] <= node.threshold: return self._predict_one(x, node.left) else: return self._predict_one(x, node.right) def predict_proba(self, X): check_is_fitted(self, ['tree_', 'classes_']) X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True) # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X # Make predictions for each instance probas = np.array([self._predict_one(x, self.tree_) for x in X_array]) return probas def predict(self, X): probas = self.predict_proba(X) return self.classes_[np.argmax(probas, axis=1)] class RandomForestClassifierFromScratch(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin): def __init__(self, n_estimators=100, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, criterion='gini', max_features='sqrt', bootstrap=True, random_state=None, n_jobs=-1): self.n_estimators = n_estimators self.max_depth = max_depth self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf self.criterion = criterion self.max_features = max_features self.bootstrap = bootstrap self.random_state = random_state self.n_jobs = n_jobs self.estimators_ = [] self.feature_importances_ = None def _bootstrap_sample(self, X, y, random_state): """Create a bootstrap sample for a single tree""" n_samples = X.shape[0] rng = np.random.RandomState(random_state) if self.bootstrap: indices = rng.choice(range(n_samples), size=n_samples, replace=True) else: indices = np.arange(n_samples) return X[indices], y[indices] def _build_tree(self, X, y, tree_idx): """Build a single decision tree""" # Set random state for both bootstrapping and tree building tree_random_state = None if self.random_state is not None: tree_random_state = self.random_state + tree_idx # Create a decision tree tree = DecisionTreeClassifierFromScratch( max_depth=self.max_depth, min_samples_split=self.min_samples_split, min_samples_leaf=self.min_samples_leaf, criterion=self.criterion, max_features=self.max_features, random_state=tree_random_state ) # Get bootstrap sample X_sample, y_sample = self._bootstrap_sample(X, y, tree_random_state) # Fit the tree on the bootstrap sample tree.fit(X_sample, y_sample) return tree def fit(self, X, y): # Check that X and y have correct shape and convert sparse to dense X, y = check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse=True) # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X self.classes_ = unique_labels(y) self.n_features_in_ = X_array.shape[1] # Set the global random state if provided if self.random_state is not None: np.random.seed(self.random_state) # Get number of jobs n_jobs = self.n_jobs if n_jobs < 0: n_jobs = min(abs(n_jobs), os.cpu_count() or 1) n_jobs = max(1, n_jobs) # Ensure at least 1 job # Build trees in parallel if n_jobs != 1 if n_jobs == 1: self.estimators_ = [self._build_tree(X_array, y, i) for i in range(self.n_estimators)] else: self.estimators_ = Parallel(n_jobs=n_jobs)( delayed(self._build_tree)(X_array, y, i) for i in range(self.n_estimators) ) # Combine feature importances from all trees self.feature_importances_ = np.zeros(self.n_features_in_) for tree in self.estimators_: self.feature_importances_ += tree.feature_importances_ # Normalize feature importances if self.n_estimators > 0: self.feature_importances_ /= self.n_estimators # Further normalize to sum to 1 if np.sum(self.feature_importances_) > 0: self.feature_importances_ /= np.sum(self.feature_importances_) return self def predict_proba(self, X): check_is_fitted(self, ['estimators_', 'classes_']) X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True) # Convert sparse matrix to dense if needed X_array = X.toarray() if issparse(X) else X # Collect predictions from all trees all_probas = np.array([estimator.predict_proba(X_array) for estimator in self.estimators_]) # Average predictions return np.mean(all_probas, axis=0) def predict(self, X): probas = self.predict_proba(X) return self.classes_[np.argmax(probas, axis=1)]
Deployment Architecture
- Containerized using Docker
- Flask backend on Google Cloud
- Express/Node.js frontend on Vercel
- Vertex AI with L4 GPU for training
Data Files
- intents.json - Custom college dataset with tags, patterns and responses

(Sample Dataset)
Random Forest
n_estimators=200,
max_depth=10,
min_samples_split=5
ChatBot
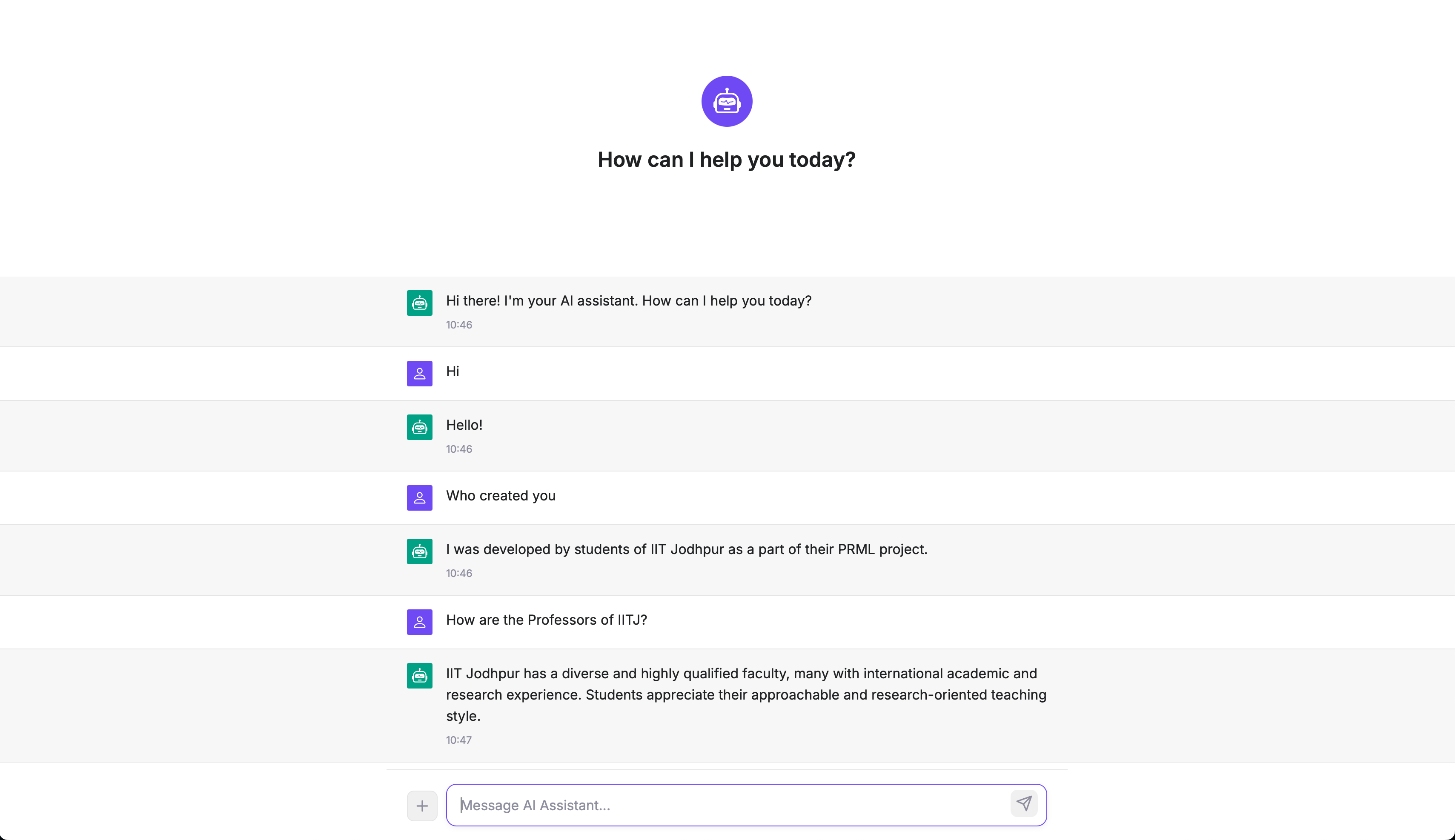
Future Work
Future enhancements will focus on:
-
Advanced NLP Techniques: Incorporate advanced techniques including contextual embeddings,
transformer architectures, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
networks, and hybrid models that combine classical machine learning with neural approaches to boost
classification performance and enable dynamic response generation. -
Data Expansion: Expand the custom-built dataset with continuous feedback to ensure the data remains representative and up-to-date.
-
Continuous Training : Implement continuous training and deployment pipelines that allow the
model to evolve with incoming data and feedback. -
Dynamic Response Generation: Investigate the use of advanced NLP models to facilitate more
dynamic and context-aware responses. -
Chat History Integration: Connect a robust database system (MySQL, MongoDB, etc.) to store
chat histories, enabling detailed analysis and continuous improvement of chatbot responses. -
Platform Integration: Integrate the chatbot with mobile platforms and additional college services
to extend reach and functionality.