Abstract
This publication presents a novel multi-agent Large Language Model (LLM) system designed for comprehensive adverse media screening aligned with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) taxonomy. The system employs four specialized agents—entity disambiguation, search quality assessment, classification, and conflict resolution—to automate the identification and categorization of adverse media coverage for entities (individuals and organizations). Our approach addresses critical challenges in financial crime compliance by providing accurate entity involvement detection and precise classification across six FATF-defined adverse media categories.
Introduction
Adverse media screening is a critical component of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance programs. Financial institutions and regulated entities must continuously monitor for negative news coverage that might indicate involvement in financial crimes, corruption, or other serious offenses.
We developed a multi-agent Large Language Model (LLM) system that addresses these challenges through specialized agent coordination. Each agent handles a specific aspect of the adverse media screening pipeline:
- Entity Disambiguation Agent: Ensures accurate entity identification
- Search Quality Agent: Evaluates relevance and credibility of retrieved articles
- Classification Agent: Categorizes articles according to FATF taxonomy
- Conflict Resolution Agent: Reconciles disagreements between agents
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF adverse media taxonomy includes:
- Fraud & Financial Crime: Money laundering, fraud, tax evasion
- Corruption & Bribery: Political corruption, bribery schemes
- Organized Crime: Drug trafficking, arms smuggling
- Terrorism & Extremism: Terrorist financing, extremist activities
- Sanctions Evasion: Violating international sanctions
- Other Serious Crimes: Human trafficking, environmental crimes
Installation and Usage
Quick Setup
The system requires Python 3.8+ and four API keys from external services. After cloning the repository, install dependencies with pip install -r requirements.txt and create a .env file with your API keys for Groq, Brave Search, Tavily, and Together AI.
How to Use
Run adverse media screening through the command line interface. The basic command python main.py "John Smith" screens an entity by name. For entities with common names, add context using python main.py "John Smith" --context "CEO of TechCorp" or specific details like --dob 1985-03-15 --occupation "Software Engineer".
Understanding Results
The system returns four possible outcomes. "CLEAN" means no adverse media was found. "COMPLETED" indicates adverse articles were discovered and classified. "NEEDS_CONTEXT" requests additional information to identify the correct entity among multiple matches. "MANUAL_REVIEW" flags cases requiring human oversight due to conflicting classifications.
Integration Notes
This system is designed to support compliance workflows, not replace human judgment. All results include confidence scores and detailed reasoning to help compliance teams make informed decisions. The system maintains audit trails and provides escalation paths for complex cases that require manual review.
Methodology
Multi-Agent System Architecture
The system employs a modular design with dependency injection and robust error handling. Each agent inherits from BaseDSPyAgent and implements specific functionality via DSPy signatures, enabling specialized task handling within the adverse media screening workflow. This architectural approach ensures fault isolation, where individual agent failures do not compromise the entire screening process, while enabling parallel execution that significantly reduces processing time compared to sequential approaches.
System Orchestration & Communication
Agent Communication Patterns
The multi-agent adverse media screening system employs a sophisticated state-based communication architecture that ensures seamless data flow and coordination between specialized agents. At the core of this communication framework lies the AdverseMediaState object, which serves as a centralized data repository and coordination mechanism throughout the entire screening workflow.
The state object functions as both a data carrier and a workflow coordinator, maintaining comprehensive information about the entity being screened, intermediate processing results, and the status of each agent's execution. This design eliminates the need for direct inter-agent communication, instead allowing agents to communicate asynchronously through shared state updates. Each agent reads the current state, performs its specialized function, and updates the state with its results before passing control to the next stage in the pipeline.
The communication protocol follows a producer-consumer pattern where each agent acts as both a consumer of previous results and a producer of new information. For instance, the Entity Disambiguation Agent consumes the raw entity name and user context, then produces a resolved entity object with confidence scores and candidate alternatives. The Search Strategy Agent subsequently consumes this resolved entity information to construct more targeted search queries, while producing a curated collection of relevant articles for downstream classification.
Dynamic Context Enhancement Pipeline
When additional context is required, the system implements a dynamic input enhancement mechanism that seamlessly integrates new information with original user input. The enhancement process intelligently formats contextual data including dates of birth, occupations, locations, and organizational affiliations into natural language extensions that improve disambiguation accuracy without losing original intent. This context integration creates enriched queries that maintain semantic coherence while providing agents with the additional information needed for confident entity resolution.
State Management & Data Flow
The system implements a robust state management mechanism that tracks both data transformations and processing metadata throughout the screening workflow. The state object maintains multiple data layers including raw input data, intermediate processing results, final outputs, and comprehensive audit trails that capture decision points and confidence levels at each stage.
Data flow management operates through a structured pipeline where each agent enriches the state with additional information while preserving all previous results for traceability and potential rollback scenarios. The Entity Disambiguation Agent populates the state with resolved entity details, candidate alternatives, and disambiguation confidence scores. This enriched state then flows to subsequent agents, with each stage building upon previous results to create increasingly refined and comprehensive adverse media assessments.
The state management system also maintains processing metadata that tracks timing information, confidence evolution, and decision points throughout the workflow. This metadata proves invaluable for performance optimization, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance requirements. The system captures not only what decisions were made but also why they were made and with what level of confidence, creating a complete audit trail for each screening operation.
The system implements sophisticated state serialization that handles complex object hierarchies, automatically converting between dictionary representations for inter-agent communication and rich object models for processing. This includes intelligent reconstruction of EntityCandidate objects, AgentResult tracking, and comprehensive error context preservation across workflow boundaries. This dual-representation approach enables seamless integration with workflow orchestration frameworks while maintaining type safety and rich object behavior during agent processing.
Agent Lifecycle Management
Each agent operates within a well-defined lifecycle framework that ensures proper initialization, execution tracking, and graceful completion or failure handling. The lifecycle begins when an agent calls state.start_agent() with its identifier, which marks the agent as in-progress and initializes timing and status tracking mechanisms. This lifecycle management prevents race conditions and provides clear visibility into which agents are currently processing and which have completed their tasks.
During execution, agents continuously update their status through the _update_agent_status() method, providing real-time visibility into processing progress and any issues that may arise. These status updates serve multiple purposes including progress monitoring for long-running operations, debugging assistance during development, and operational visibility in production environments. The granular status reporting enables operators to understand exactly where processing stands and identify any bottlenecks or failures quickly.
The lifecycle concludes when agents call either state.complete_agent() with successful results or state.fail_agent() when errors occur. Successful completion includes storing output data, final confidence scores, and processing metadata. Failure scenarios trigger comprehensive error logging with sufficient context for diagnosis and potential recovery. This structured approach to lifecycle management ensures that no processing steps are lost or forgotten, and provides clear accountability for each stage of the screening process.
Error Handling & Recovery
The system implements multiple layers of error handling and recovery mechanisms designed to maintain processing continuity even when individual components encounter failures. At the foundational level, circuit breaker patterns protect against cascading failures from external service dependencies such as search APIs, embedding services, and named entity recognition systems. These circuit breakers monitor failure rates and automatically disable failing services temporarily, preventing resource exhaustion and allowing time for recovery.
When external service failures occur, the system employs graceful degradation strategies that maintain core functionality while reducing feature richness. For example, if the embedding service fails during entity disambiguation, the system falls back to simpler text-based matching algorithms. While this may reduce accuracy slightly, it ensures that screening operations can continue rather than failing completely. This approach prioritizes system availability while maintaining acceptable quality levels.
The workflow employs differentiated retry strategies based on failure types, with disambiguation retries handling entity ambiguity, context-enhanced reprocessing for insufficient information scenarios, and adaptive escalation patterns that optimize both accuracy and resource utilization. This intelligent retry orchestration distinguishes between recoverable disambiguation challenges that benefit from additional context and system-level failures that require different intervention strategies.
Error recovery mechanisms include automatic retry logic with exponential backoff for transient failures, alternative processing pathways when primary methods fail, and comprehensive error context preservation for manual intervention when needed. The system distinguishes between recoverable errors that can be handled automatically and critical errors that require human attention. Recoverable errors trigger retry mechanisms and fallback procedures, while critical errors safely halt processing and preserve all state information for manual resolution.
Performance & Resilience Features
The architecture incorporates several performance optimization and resilience features designed to handle production-scale adverse media screening workloads efficiently and reliably. Thread pool management enables parallel execution of independent operations such as multiple search strategies or simultaneous candidate evaluation, significantly reducing overall processing time while maintaining resource control through configurable worker limits.
Caching mechanisms operate at multiple levels throughout the system to minimize redundant external service calls and expensive computations. Search results are cached to avoid repeated queries for the same entities, embedding calculations are cached to prevent recomputation of similarity scores, and intermediate processing results are preserved to enable rapid reprocessing with different parameters. These caching layers dramatically improve response times for repeated queries while reducing external service load and associated costs.
The system implements comprehensive monitoring and metrics collection that tracks processing times, success rates, confidence score distributions, and external service performance. This telemetry data enables proactive identification of performance degradation, capacity planning for scaling decisions, and quality assurance through statistical analysis of processing outcomes. The metrics also provide valuable insights for tuning processing parameters and optimizing the balance between accuracy and performance based on real-world usage patterns.
Entity Disambiguation Agent
The Entity Disambiguation Agent serves as the foundational component, responsible for resolving entity ambiguity through multi-modal analysis that combines search, Named Entity Recognition (NER), and semantic similarity. This comprehensive approach addresses the critical challenge in financial compliance where entity misidentification can lead to false positives or, more critically, missed adverse media coverage.

Multi-Strategy Context Extraction
The agent employs a sophisticated context extraction system that combines DSPy-powered extraction with BERT-based NER fallback mechanisms. This dual approach ensures robustness when primary extraction methods encounter unexpected input formats or fail due to service limitations. The system implements parallel search approaches including exact name matching, context-enhanced searches, and biographical discovery strategies, each optimized for different scenarios commonly arising in KYC processes.
Adaptive Candidate Scoring
Central to the agent's effectiveness is its dynamic weighting system that adjusts scoring based on source credibility rather than applying static weights uniformly. High-trust domains such as LinkedIn and Wikipedia receive 65% weight on search relevance and 35% on context matching, recognizing their reliable entity information. Conversely, unverified sources require stronger context validation, receiving 45% context weight and 55% search weight to compensate for potential inaccuracies.
This dynamic approach delivers measurably superior accuracy compared to static scoring methods because it adapts trust calculations to match the reliability characteristics of each information source.
Entity Consolidation and Quality Control
Entity consolidation operates through embedding similarity analysis, grouping candidates that represent the same entity while boosting confidence scores when multiple credible sources confirm the same individual. This process prevents duplicate processing while leveraging source diversity to increase confidence in entity identification.
The system incorporates resilience features through circuit breakers that gracefully handle failures in search, embedding, and NER services, ensuring continuous operation even when external dependencies experience interruptions. Quality filtering mechanisms assess results against FATF-aligned credible sources, applying domain-specific trust factors that reflect regulatory requirements for adverse media screening.
Decision Logic and Performance
The KYC-standard decision logic provides automated acceptance for high-confidence matches, conflict detection for ambiguous cases, and manual review triggers for edge scenarios requiring human expertise. Performance optimizations include parallel execution across multiple search strategies, intelligent caching to minimize redundant API calls, smart parsing that prioritizes relevant content sections, and real-time monitoring that tracks system health and performance metrics.
Search Strategy Agent
The Search Strategy Agent implements adaptive multi-strategy searches designed to discover adverse media while maintaining high precision through quality assessment and clean entity detection. This agent addresses the fundamental challenge of casting a sufficiently wide net to capture relevant negative coverage while filtering out irrelevant noise that could overwhelm compliance teams with false positives.
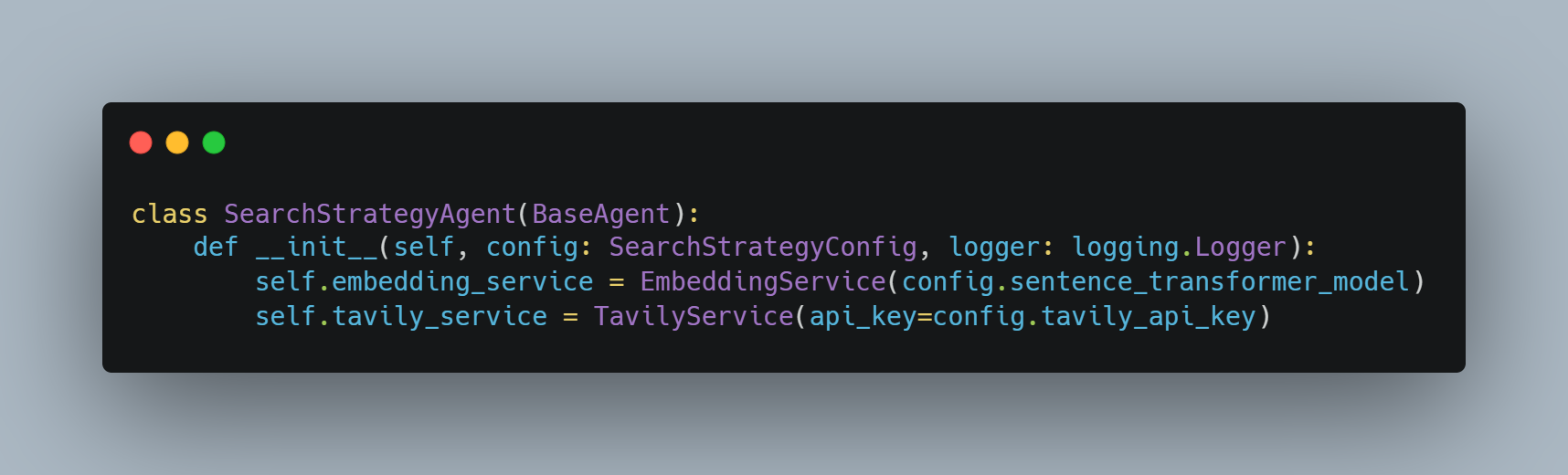
Progressive Search Framework
The search framework employs a four-strategy approach that escalates search complexity based on initial results. The Broad strategy utilizes general FATF keywords to establish baseline coverage, followed by Targeted searches incorporating specific financial crime terminology. When initial strategies yield insufficient results, the Deep Dive approach leverages regulatory enforcement keywords drawn from actual compliance cases, while the Alternative strategy focuses on legal action terms that often accompany adverse media coverage.
This progressive escalation ensures comprehensive coverage while optimizing resource utilization by avoiding unnecessary complex searches when simpler approaches suffice.
Context-Aware Query Construction
Adaptive query construction represents a significant advancement over static search approaches, building context-aware queries that combine entity names with FATF keywords and contextual data including professional roles, industry associations, and geographic locations. This contextual enhancement dramatically improves search precision by incorporating the specific circumstances under which adverse media is most likely to appear.
For instance, queries for financial services executives emphasize regulatory enforcement terms, while searches for political figures prioritize corruption and bribery indicators.
Content Processing and Filtering
Content extraction operates through a sophisticated two-phase process where initial metadata summaries guide decisions about full content extraction via the Tavily API. This approach optimizes both performance and cost by avoiding unnecessary full-content retrieval for clearly irrelevant results.
Multi-dimensional relevance filtering evaluates entity prominence within articles, applies semantic deduplication using embedding similarity to eliminate redundant coverage, analyzes adverse keyword proximity to determine relevance strength, and assesses source credibility against FATF-aligned standards that reflect regulatory expectations for evidence quality.
Optimization Features
Clean entity detection provides crucial efficiency gains through early termination logic that identifies entities with insufficient adverse signals, allowing the system to skip unnecessary downstream processing. Quality assessment mechanisms evaluate search results using comprehensive metrics including article count, relevance scores, source credibility ratings, and composite quality scores.
Workflow optimization features include intelligent early stopping for clean entities, configurable quality thresholds that adapt to different risk tolerance levels, and sophisticated flagging systems that guide downstream processing decisions. Performance enhancements encompass robust retry mechanisms with exponential backoff, parallel execution of search strategies, intelligent caching systems, and configurable resource limits that prevent runaway processing costs.
Classification Agent
The Classification Agent performs FATF taxonomy classification using a dual-LLM approach specifically designed to improve accuracy and detect potential classification conflicts before they impact compliance decisions. This design addresses the inherent variability in large language model outputs, where identical inputs can occasionally produce different results due to the stochastic nature of these systems.
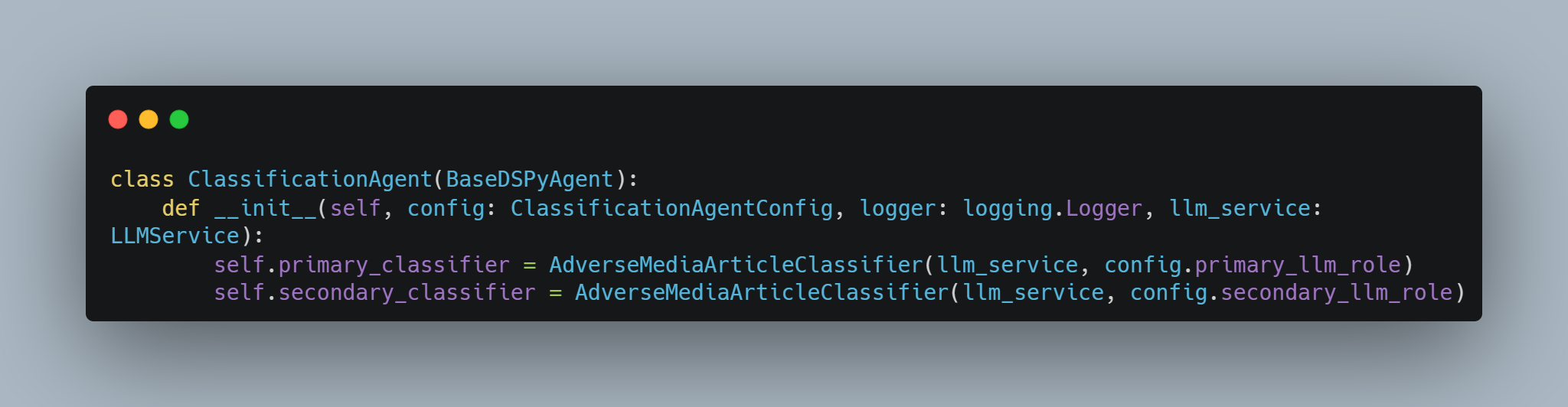
Dual-LLM Framework
The framework utilizes independent primary and secondary LLM classifiers that process identical content separately, enabling cross-validation of classification decisions. This approach significantly improves reliability compared to single-LLM systems because it captures classification uncertainty and flags cases where automated decisions may be questionable.
The system includes graceful fallback capabilities to single-LLM mode when secondary classifiers become unavailable, ensuring operational continuity during service disruptions. The framework supports any LLM accessible through the LLMService interface, providing flexibility to adapt to evolving AI capabilities and cost optimization requirements.
FATF Taxonomy and Processing
Classification operates across the comprehensive FATF taxonomy encompassing Fraud & Financial Crime, Corruption & Bribery, Organized Crime, Terrorism & Extremism, Sanctions Evasion, and Other Serious Crimes. This standardized approach ensures consistency with international regulatory frameworks while enabling automated categorization that supports compliance reporting requirements.
Content preprocessing employs intelligent extraction techniques that identify and prioritize entity-relevant sections within articles while implementing smart truncation strategies to comply with LLM token limits. This preprocessing significantly improves classification accuracy by focusing analytical attention on the most relevant content sections rather than processing entire articles uniformly.
Output and Conflict Detection
The system generates multi-dimensional output including entity involvement classification distinguishing between perpetrator, victim, and neutral roles, precise FATF category assignments, confidence scores that enable risk-based processing decisions, detailed reasoning that supports audit requirements, and comprehensive source metadata that facilitates verification and appeals processes.
Conflict detection mechanisms automatically flag disagreements between the dual classifiers and identify low-confidence cases that require manual review. This proactive approach prevents questionable automated decisions from proceeding without human oversight, thereby reducing compliance risk while maintaining processing efficiency.
Robustness and Performance
Error handling features support high-volume batch processing with continued operation despite individual article failures, configurable error tolerance that balances thoroughness with operational requirements, and intelligent graceful degradation to single-LLM processing when dual-LLM operation becomes unavailable.
Performance optimizations include parallel classification processing that maximizes throughput, sophisticated token budgeting that optimizes API costs while maintaining quality, and efficient state management that supports large-scale operations. Classification metrics provide comprehensive tracking of processed articles, conflict detection rates, error frequencies, and performance benchmarks that facilitate system monitoring and continuous improvement.
Conflict Resolution Agent
The Conflict Resolution Agent addresses classification disagreements between LLM classifiers through a sophisticated multi-layer framework that combines rule-based logic, external validation, and LLM arbitration. This comprehensive approach was specifically designed for financial compliance contexts where classification errors can have significant regulatory and reputational consequences, necessitating multiple validation layers before finalizing adverse media determinations.
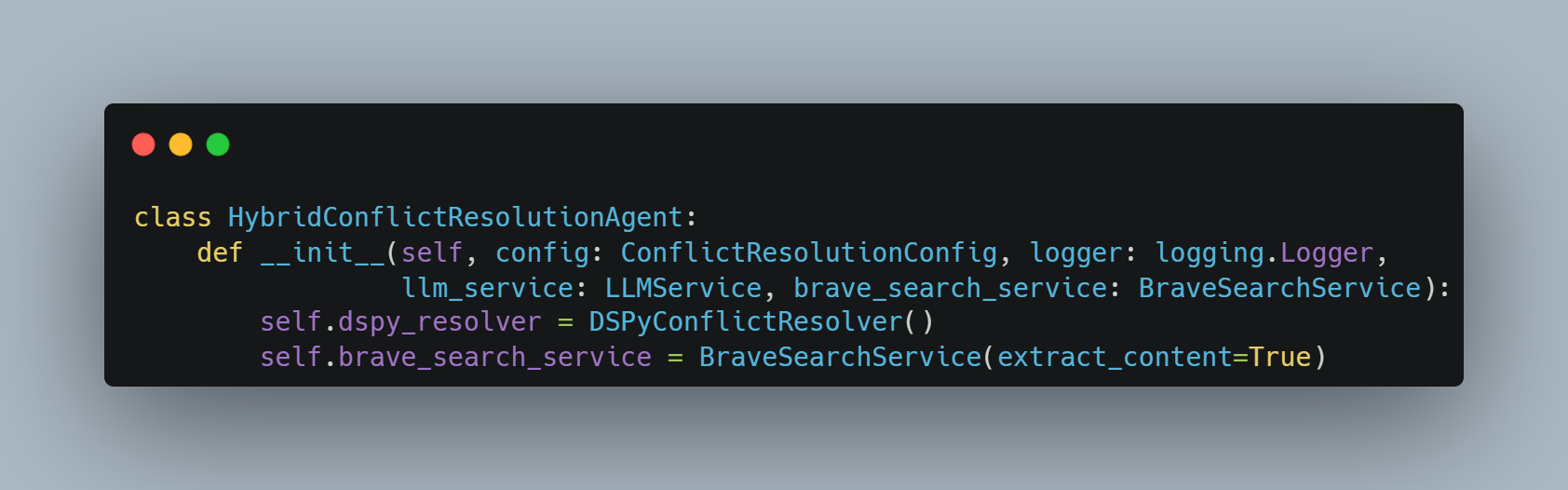
Five-Layer Resolution Framework
The resolution framework represents a carefully orchestrated escalation process that balances automation efficiency with decision accuracy. The process begins with No-Conflict Validation that verifies low-confidence agreements through external search validation, recognizing that unanimous but uncertain classifications may still require additional verification.
Critical Conflict Escalation immediately prioritizes severe conflicts such as Perpetrator versus Victim disagreements, which represent the most serious classification discrepancies that could significantly impact compliance decisions. These conflicts bypass automated resolution and proceed directly to human review, ensuring that potentially high-impact decisions receive appropriate expert attention.
Rule-Based Resolution leverages confidence gap analysis and conservative decision principles to resolve straightforward conflicts automatically. The system applies conservative logic that prioritizes perpetrator classifications and adverse determinations when confidence levels support such decisions, reflecting the regulatory preference for cautious adverse media screening that errs on the side of flagging potential issues rather than missing them.
External Validation and Context Analysis
External Context Analysis represents a significant innovation in adverse media screening, utilizing multi-source content validation and entity mention verification through the BraveSearch API. This layer performs independent research to gather additional context about entities and incidents, providing objective external validation that can resolve conflicts through factual verification.
The system analyzes sentiment indicators, involvement patterns, and consistency across multiple sources to build confidence in classification decisions through external corroboration. This external validation capability significantly enhances classification confidence by providing independent verification of classification decisions through objective external evidence.
LLM Arbitration and Escalation
LLM Arbitration with Context applies advanced DSPy techniques to integrate primary classifications with external context for final conflict resolution. This sophisticated approach leverages the reasoning capabilities of large language models while providing them with comprehensive context that includes both original article content and externally gathered information.
The final layer escalates unresolved conflicts to Human Review with comprehensive context packages that include all automated analysis results, external research findings, confidence assessments, and specific conflict characteristics. This escalation ensures that human reviewers receive complete information to make informed decisions while minimizing the volume of cases requiring manual attention through effective automated preprocessing.
Production Features and Quality Assurance
Advanced conflict analysis measures both involvement and category confidence gaps while applying conservative logic that prioritizes perpetrator and adverse classifications when evidence supports such determinations. The system favors high-confidence results while recognizing that in compliance contexts, false negatives typically carry greater risk than false positives.
Production features include robust batch processing capabilities that maintain high throughput while preserving decision quality, sophisticated circuit breakers that ensure resilient operation despite external API failures, comprehensive metrics tracking that monitors resolution method effectiveness and error patterns, and graceful error recovery mechanisms that prevent individual failures from disrupting large-scale processing operations. These features enable the system to operate reliably in demanding production environments while maintaining the decision quality required for regulatory compliance.
Tools and Technologies
This multi-agent adverse media screening system leverages the following key tools and services:
-
Large Language Model (LLM) Services: Core language models accessed via a flexible
LLMServiceinterface, enabling dual-LLM classification and arbitration. -
DSPy Framework: Base agent classes (
BaseDSPyAgent), DSPy signatures, and DSPy-based conflict resolution capabilities provide modular design and logic implementations. -
Named Entity Recognition (NER): BERT-based NER fallback models for robust entity extraction when primary methods fall short.
-
Embedding Services: Sentence transformer models for semantic similarity and embedding-based entity consolidation and semantic deduplication.
-
Tavily Service: Advanced content extraction API used for two-phase document retrieval—metadata summary and full article content in markdown format.
-
BraveSearch Service: External multi-source search and content extraction used to validate and enrich classification conflict resolution.
Limitations and Future Work
-
Current Evaluation Status:
The system has not yet undergone a comprehensive formal evaluation using diverse benchmark queries or quantitative performance metrics. As such, traditional accuracy and robustness assessments remain pending. -
Human-in-the-Loop Integration:
To maintain quality and compliance, the system incorporates human oversight mechanisms including manual review flags, conflict escalation paths, and professional judgment triggers within the automated workflows. These processes help ensure reliability during ongoing use.
Conclusion
This multi-agent system provides a strong and flexible way to find and handle adverse media information. It uses smart language models, searches, and checks to make sure results are accurate and useful.
The system combines automation with human checks to keep things reliable and trustworthy. While full testing is planned for the future, the current setup is ready to support real-world compliance work.
In short, this design can grow and improve over time, helping teams tackle complex financial crime screening needs effectively.