Solving Retirement Complexity with a RAG Assistant: Clear, Document-Backed Answers for Advisors and Investors
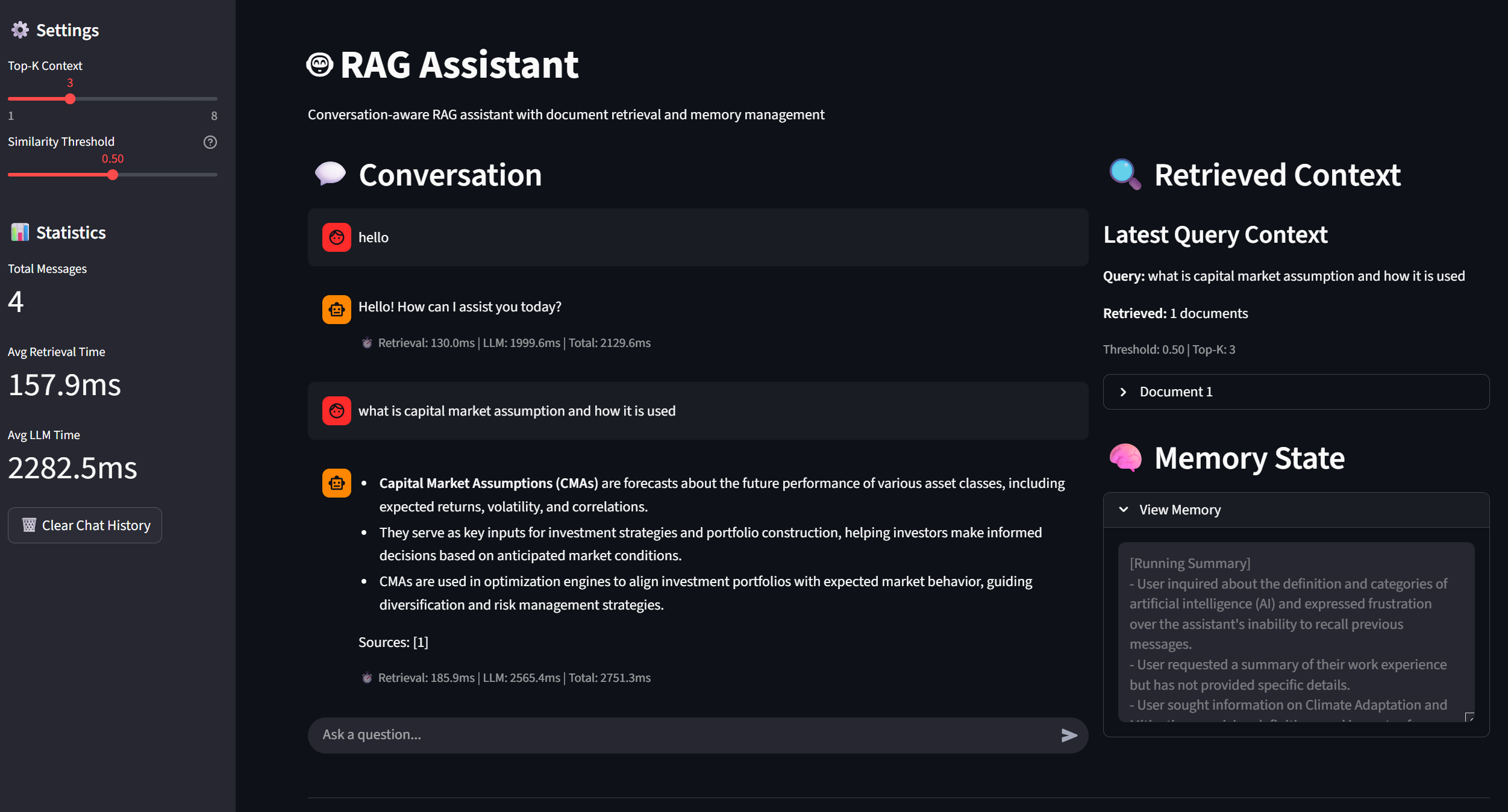
A Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant designed to help financial advisors and investors make evidence-backed retirement and investment decisions. The system retrieves information from a curated set of documents covering capital market assumptions, portfolio optimization, yield-curve modeling, and retirement income strategies.
The assistant answers domain-specific questions such as "How do Nelson–Siegel factors influence bond ladder construction?" or "Compare Roth vs Traditional IRA drawdown rules for a client retiring at 62." Responses are grounded in source documents to maintain traceability.
Figure 1: RAG System Architecture
High-level architecture showing the flow from query to response.
graph LR A[Query] --> B[Vector<br/>Search] B --> C[Retrieve<br/>Chunks] C --> D[Build<br/>Prompt] E[Memory] --> D D --> F[LLM] F --> G[Response] G --> E H[Documents] --> I[Embeddings] I --> B style A fill:#e1f5ff style G fill:#d4edda style F fill:#fff3cd style B fill:#f8d7da style E fill:#d1ecf1
Research Purpose & Significance
This project explores challenges in applying RAG systems to domain-specific financial advisory applications. Generic RAG frameworks work well for general knowledge but face difficulties with specialized domains requiring precision and context preservation.
Context preservation across long documents: Financial planning documents contain interconnected concepts spanning multiple sections. For example, capital market assumptions inform portfolio optimization, which drives retirement income projections. These relationships require chunking strategies that maintain semantic coherence when concepts are split across boundaries.
Conversational continuity: Financial advisors engage in extended conversations where later questions depend on earlier context. The system needs to remember prior discussion (e.g., a client's risk profile) while maintaining grounding in source documents.
Retrieval quality evaluation: Many RAG systems lack transparent metrics for assessing retrieval accuracy, making it difficult to tune similarity thresholds and chunking parameters for specific use cases.
This implementation demonstrates a configurable chunk overlap strategy, structured evaluation metrics in logging, and memory-efficient conversation management. The system serves as a reference for domain-specific RAG applications where accuracy and traceability are important.
Document Chunking & Context Preservation
Figure 2: Chunking Strategy Visualization
Illustration of the recursive character text splitter with 25% overlap, showing how context is preserved across chunk boundaries.
graph LR A[Document Text] --> B[Chunk 1<br/>400 chars] B --> C[Overlap<br/>100 chars] C --> D[Chunk 2<br/>400 chars] D --> E[Overlap<br/>100 chars] E --> F[Chunk 3<br/>400 chars] B -.->|25% Overlap| C C -.->|Shared Context| D D -.->|25% Overlap| E E -.->|Shared Context| F style C fill:#fff3cd style E fill:#fff3cd style B fill:#d4edda style D fill:#d4edda style F fill:#d4edda
Example: A query about "Nelson-Siegel factors" may match:
- Chunk 1 ending: "The Nelson-Siegel model uses three factors:"
- Chunk 2 beginning: "level, slope, and curvature. These factors..."
- Both chunks are retrieved due to overlap, providing complete context.
The system uses a recursive character text splitter with configurable overlap to preserve context across chunk boundaries. Default parameters are 400 characters per chunk (approximately 80-100 tokens) with 100-character overlap (25% ratio), configurable in utils/vectordb.py.
The 400-character size balances context richness and embedding quality. Smaller chunks (200-300 chars) risk losing context, while larger chunks (800+ chars) may dilute semantic focus. The 25% overlap preserves information spanning chunk boundaries, which is important for financial documents where concepts often include examples or caveats.
The implementation uses LangChain's RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, which splits on paragraph boundaries first, then sentence boundaries, and finally character boundaries if needed. Overlap is applied at each level to maintain continuity.
Retrieval Performance Evaluation
Figure 3: Evaluation Framework
Evaluation framework showing retrieval metrics, automated evaluation pipeline, and performance assessment.
graph LR A[Query] --> B[Retrieval<br/>Metrics] B --> C[Similarity<br/>Distance] B --> D[Latency] B --> E[Traceability] F[Ground Truth<br/>Q&A] --> G{Test Cases<br/>Cached?} G -->|Yes| H[Load Cache] G -->|No| I[Generate] I --> J[RAG Processing] J --> K[DeepEval] H --> K C --> K K --> L[Answer<br/>Relevancy] K --> M[Contextual<br/>Relevancy] K --> N[Faithfulness] L --> O[Performance<br/>Assessment] M --> O N --> O D --> O E --> O style A fill:#e1f5ff style O fill:#d4edda style K fill:#fff3cd style B fill:#f8d7da
The system tracks retrieval metrics including similarity distance (cosine distance, default threshold 0.5), retrieval latency, and document traceability. Evaluation uses DeepEval with three metrics: Answer Relevancy, Contextual Relevancy, and Faithfulness (all threshold 0.7).
Evaluation is run via python evaluation/evaluate_rag.py with options for --max-cases and --force-regenerate. Results from 40 test cases show 100% pass rates across all metrics. The evaluation dataset is stored in evaluation/rag_evaluation_cases.json, with cached test cases saved to outputs/evaluation_results/.
System Architecture
Figure 4: System Component Diagram
Component diagram showing interaction between system modules.
graph TB subgraph "User Interfaces" UI1[CLI<br/>app.py] UI2[Streamlit UI<br/>app_streamlit.py] end subgraph "Core RAG Pipeline" RAG[RAGAssistant] VDB[VectorDB<br/>vectordb.py] MEM[MemoryManager<br/>memory_utils.py] PROMPT[PromptBuilder<br/>prompt_builder.py] end subgraph "LLM Integration" LLM1[OpenAI] LLM2[Groq] LLM3[Google Gemini] end subgraph "Supporting Modules" FILE[File Utils<br/>file_utils.py] LOG[Log Utils<br/>log_utils.py] PATH[Paths<br/>paths.py] end subgraph "Evaluation" EVAL[RAGEvaluator<br/>evaluate_rag.py] CASES[Test Cases<br/>rag_evaluation_cases.json] end UI1 --> RAG UI2 --> RAG RAG --> VDB RAG --> MEM RAG --> PROMPT PROMPT --> LLM1 PROMPT --> LLM2 PROMPT --> LLM3 RAG --> LOG VDB --> FILE MEM --> FILE FILE --> PATH LOG --> PATH EVAL --> RAG EVAL --> CASES EVAL --> LOG style RAG fill:#fff3cd style VDB fill:#d4edda style MEM fill:#d1ecf1 style EVAL fill:#f8d7da
The system supports CLI and Streamlit interfaces, both accessing the same RAG pipeline. Core components include app.py and app_streamlit.py for interfaces, utils/vectordb.py for vector database operations, utils/memory_utils.py for memory management, utils/log_utils.py for logging, and utils/prompt_builder.py for prompt construction.
The system supports multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Groq, Google Gemini), automatically selecting based on available API keys. The RAG pipeline uses MiniLM embeddings for vector search, with configurable retrieval parameters.
Memory Management Strategy
Figure 5: Memory Management Flow
Rolling summary memory strategy.
graph LR A[New User Turn] --> B[Recent Window<br/>Last 12 turns] B --> C{Window Size<br/>Check} C -->|>12 turns| D[Remove<br/>Oldest Turn] C -->|≤12 turns| E[Keep All] D --> E E --> F{Summarize<br/>Every N?} F -->|Yes| G[Update Running<br/>Summary] F -->|No| H[Skip Summary] G --> I[Persist to Disk] H --> J[Build Prompt<br/>Context] I --> J E --> J J --> K[LLM Prompt<br/>with Memory] style A fill:#e1f5ff style G fill:#fff3cd style I fill:#d4edda style K fill:#d1ecf1
The system uses a dual-layer memory approach: a recent window maintains the last 12 turns verbatim, while a running summary provides a compact bullet-style brief updated every N turns. Memory is persisted to outputs/memory/memory_summary.json for session continuity. The combined memory stays within LLM context limits.
Logging and Observability
Text logs are stored in outputs/rag_assistant.log with rotating file handlers. JSONL traces in outputs/rag_assistant_traces.jsonl (CLI) and outputs/rag_assistant_ui_traces.jsonl (UI) provide structured data including timestamps, document counts, memory excerpts, and answer snippets for analysis.
Prompt Design
The prompt distinguishes between memory (for conversational continuity) and context (for factual answers). When context is insufficient, the system responds with "I don't know" rather than hallucinating. Safety rules prohibit revealing secrets, jailbreaks, or speculating about personal data. Configuration is stored in config/prompt_config.yaml.
System Flow
When a user asks a question, the system retrieves top-K chunks from the vector database based on similarity, filters by threshold, and builds a prompt combining retrieved context, memory, and the question. The LLM generates a response, memory is updated, and the UI displays the answer with context and memory state.
Requirements and Quick Start
Requires Python 3.10+ (3.11 recommended) and dependencies including langchain-core, sentence-transformers, chromadb, streamlit, and deepeval. Install via pip install -r requirements.txt and configure .env with API keys for LLM providers.
Run CLI mode: python app.py
Run Streamlit UI: streamlit run app_streamlit.py
Run evaluation: python evaluation/evaluate_rag.py
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Contribution & Compliance
Contributing
Contributions are welcome. Follow existing code style, include logging and error handling, update documentation, and test with both CLI and Streamlit interfaces.
Security & Privacy
API keys must never be committed to version control. Store keys in .env (gitignored). Logs may contain query text and document excerpts—review config/app_config.yaml for privacy-sensitive deployments. Report security issues responsibly through private channels.
Compliance Notes
This software is provided "as is" without warranty. Users are responsible for compliance with LLM provider terms of service, data privacy regulations, and organizational policies. Project maintainers are not responsible for misuse.