Project: Info_Extraction
Repository: https://github.com/hudasaleh97188/info_Extraction
Author: Huda Saleh
Info_Extraction is a streamlined, intelligent framework designed to transform unstructured document data into clean, structured formats. By leveraging modern Large Language Models (LLMs) and robust parsing techniques, it automates the tedious process of manual data entry. The system ingests various document types (such as PDFs or images), extracts key information fields with high precision, and outputs the data in standardized formats like JSON or CSV, making it immediately ready for downstream analysis or database integration.
In the modern data ecosystem, valuable information is often locked away in unstructured formats. Businesses process thousands of invoices, receipts, contracts, and resumes daily. While databases require structured inputs (rows and columns), the real world operates in PDFs, scanned images, and free-text emails.
Bridging this gap has traditionally required either brittle rule-based systems (Regex) that break with the slightest format change, or expensive human manual entry. Info_Extraction addresses this challenge by providing a flexible, code-centric solution that utilizes the reasoning capabilities of AI to understand and extract data contextually, regardless of the document's layout.
Standard approaches to document processing face significant hurdles:
Info_Extraction is designed to be a generalized, adaptable extraction pipeline. Instead of relying on rigid templates, it treats information extraction as a semantic understanding task.
The workflow consists of the following stages:
YYYY-MM-DD format).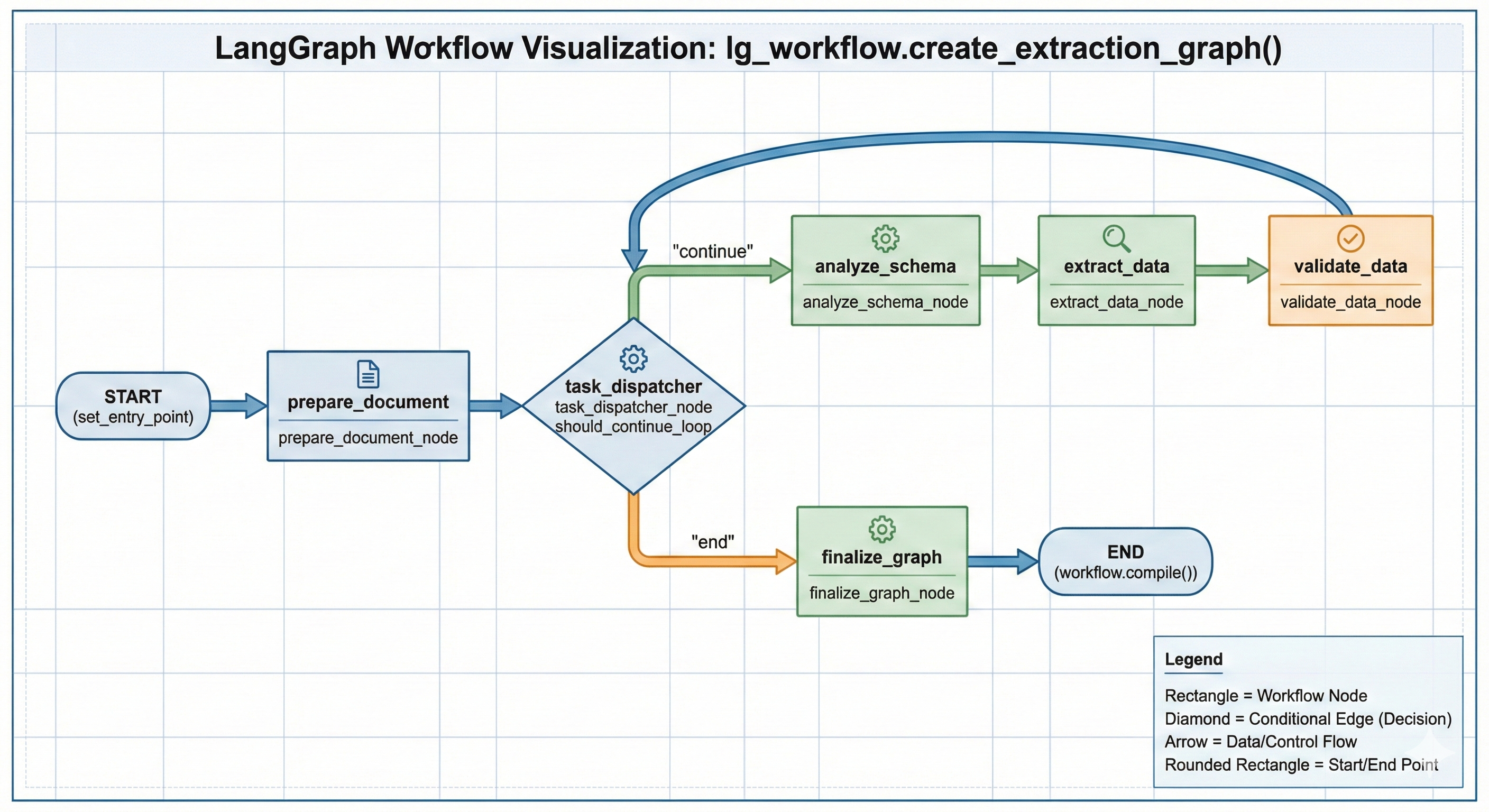
The workflow is orchestrated as a StateGraph with the following lifecycle:
prepare_document_node)ExtractionTask objects.ExtractionGraphState).Node: task_dispatcher_node
Logic: This node acts as a traffic controller. It checks the tasks_to_process queue in the state.
If tasks remain: It pops the next task, loads it into current_task, and routes the flow to the Analysis phase.
If queue is empty: It routes the flow to Finalization.
Benefit: This cyclic design allows you to run 10 different extraction queries on a single document upload without reloading or re-OCR'ing the file.
Once a task is dispatched, it moves through a strict three-step pipeline:
A. Schema Analysis (analyze_schema_node):
Before extracting, the system analyzes the user's requested schema. It breaks down complex requirements (e.g., nested JSON objects or multi-row tables) into a clear "Extraction Aim" that helps the LLM understand intent before it sees the data.
B. Extraction (extract_data_node):
Model: Google Gemini 2.5 Flash.
Process: The system combines the Mistral Markdown (Context) + Analysis Result (Instructions) into a specialized prompt. Gemini generates a raw JSON candidate.
C. Validation & Cleaning (validate_data_node):
Self-Correction: The raw output is not trusted blindly. It is passed back to the LLM with a validation prompt.
Standardization: The model corrects formatting errors (e.g., converting "Five Hundred Dollars" to 500.00 or fixing broken JSON syntax) and casts data to the strict Pydantic types defined in your schema.
Loop Back: Once validated, the result is appended to completed_results, and the graph loops back to the Task Dispatcher for the next task.
finalize_graph_node)FinalExtractionOutput object, returning a clean, unified JSON response containing results for every requested task, execution metadata, and token usage stats.A critical aspect of the info_Extraction repository is its approach to reliability. Testing stochastic systems requires a layered strategy that separates code logic (speed/stability) from model intelligence (quality).
We test the individual deterministic functions to ensure the "plumbing" works before any AI is involved.
pytest tests/unitThese tests validate the LangGraph wiring.
create_extraction_graph workflow.prepare_document task_dispatcher finalize_graph. It ensures the state machine correctly loops through multiple tasks and handles errors gracefully.Added based on your code.
Since LLM APIs are inherently slow, we need to ensure our internal code doesn't add unnecessary delay.
@pytest.mark.performance with Mocking. By replacing the slow Mistral and Gemini API calls with instant fake responses (MagicMock), we measure the execution time of the Graph Logic only.execution_time < MAX_EXECUTION_TIME (e.g., 2.0s).pytest -m performanceThe evaluation process ensures the reliability of the extracted data by leveraging DeepEval, an open-source testing framework designed for Large Language Models. Rather than relying on manual verification, the workflow implements automated unit tests where the extraction engine’s results (the "Actual Output") are rigorously compared against validated ground truths.
This framework quantitatively scores performance using key metrics:
To maintain high standards, the system utilizes a "Golden Dataset"—a collection of documents with known, manually verified values. The testing pipeline operates in three smooth steps:
Example Test Case
- Input:
invoice_101.pdf- Expected Output (Golden):
{"date": "2023-10-25", "total": 500.00}- Actual Output (Model):
{"date": "2023-10-25", "total": 500.00}- Result: ✅ PASS
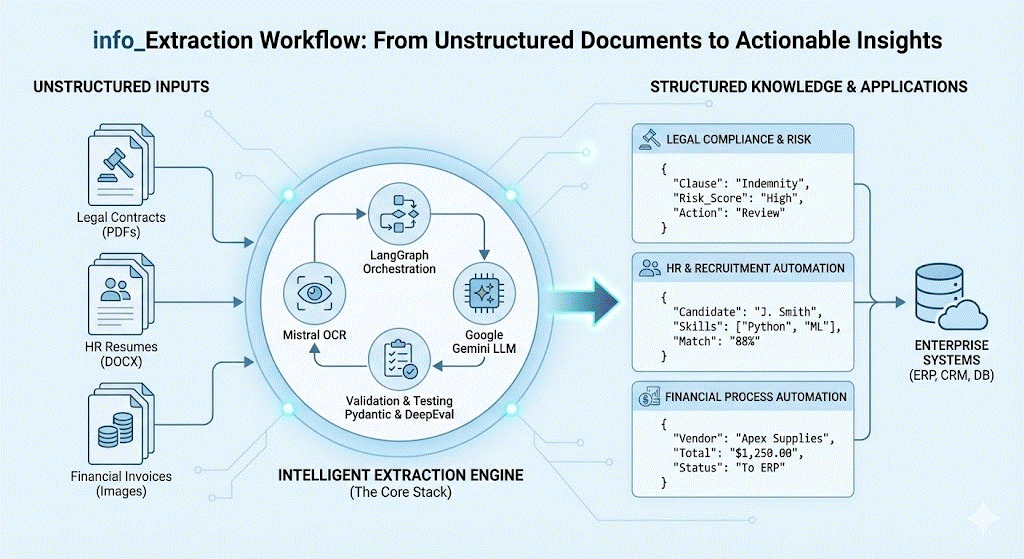
The flexibility of info_Extraction makes it suitable for various domains:
The project is built using a modern Python stack designed for efficiency and readability:
Document Processing (OCR): Mistral OCR
Used to ingest the raw documents (PDFs, images). Mistral's OCR is particularly strong at "reading" complex layouts and converting them into clean text that the LLM can understand.
Orchestration & Flow: LangGraph
Instead of a simple linear chain, LangGraph is used to create a stateful workflow. It manages the steps of the extraction process. This allows the system to loop back and fix errors if the validation fails.
Data Validation: Pydantic
Defines the strict "Schema" (the blueprint) for the data. It forces the output to be structured JSON (ensuring you get a specific date format or integer for amounts) rather than unstructured text.
Intelligence (LLM): Google Gemini
The core reasoning engine. It takes the text from Mistral OCR and the rules from Pydantic to extract the specific information required.
Evaluation & Testing: DeepEval & Pytest
DeepEval serves as the "Judge," scoring the extraction quality (Faithfulness, Recall).
Pytest runs these evaluations automatically to ensure the pipeline is working correctly.
As organizations continue to amass unstructured data, tools like Info_Extraction become essential infrastructure. By combining the power of LLMs with rigorous software engineering practices, this project offers a robust framework for turning documents into data. We invite the community to explore the repository, contribute new parsers, and help standardize the future of information extraction.
*Check out the code and contribute at: https://github.com/hudasaleh97188/info_Extraction*