This project demonstrates the application of parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) to adapt the Qwen3-1.7B-Base large language model for the task of scientific article summarization. Leveraging 4-bit quantization, LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation), and QLoRA techniques, I successfully fine-tune the model on a subset of the PubMed summarization dataset while maintaining feasibility on a single consumer-grade GPU.
The goal is to improve the model’s ability to generate concise, factual summaries of biomedical research articles — a critical capability for accelerating scientific literature review and knowledge extraction.
We use Qwen3-1.7B-Base, the base (non-instruct) variant of the Qwen3 series developed by Alibaba Cloud. Key characteristics:
The base model is instruction-agnostic and requires supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to perform domain-specific tasks like summarization.
I use a curated subset of the PubMed Summarization dataset (originally from ccdv/pubmed-summarization), which contains scientific article–abstract pairs from biomedical literature.
| Split | Size | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Train | 10,000 | ./dataset/train.parquet |
| Validation | 1,000 | ./dataset/valid.parquet |
| Test | 1,000 | ./dataset/test.parquet |
Each sample contains:
article: Full text of a scientific paper sectionabstract: Expert-written summary (target)The dataset was preprocessed and saved in Apache Parquet format for fast, memory-efficient loading.
Before fine-tuning, I evaluated the zero-shot performance of the quantized Qwen3-1.7B-Base model on the test set using greedy decoding (max_new_tokens=1024, do_sample=False).
ROUGE scores (F1, %) were computed against ground-truth abstracts:
| Metric | Baseline |
|---|---|
| ROUGE-1 | 38.03 |
| ROUGE-2 | 12.26 |
| ROUGE-L | 21.35 |
| ROUGE-Lsum | 31.45 |
The model produced generic or incomplete summaries (e.g., “The article discusses…”), confirming the need for domain adaptation.
To assess whether fine-tuning on summarization degrades the model’s general commonsense reasoning capabilities, I evaluated it on the HellaSwag benchmark — a multiple-choice dataset testing physical and social reasoning via sentence completion.
Using a fully offline, custom implementation compatible with quantized models, I computed zero-shot accuracy by ranking candidate endings via log-probability:
| Setting | HellaSwag Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Before QLoRA | 47.04% |
| After QLoRA | 46.36% |
| Δ | –0.68 pp |
🟡 Key insight: Fine-tuning on PubMed led to a minor degradation in commonsense reasoning (–0.68 pp), which is negligible and within typical run-to-run variance. This suggests the model retained strong general language understanding despite domain specialization.
💡 Crucially, the drop is small (<1 pp), indicating no catastrophic forgetting — the model remains broadly competent while gaining domain-specific summarization skills.
We employed a full QLoRA pipeline to maximize efficiency and stability:
bitsandbytesbfloat16 compute dtype for numerical stabilityr=8, α=16) applied to q_proj and v_proj layers onlyYou are a helpful assistant who writes concise, factual summaries…
Article:
{full_text}
Summary:
{abstract}
add_special_tokens=True for the prompt, False for the summary-100 for prompt tokens (loss computed only on summary)| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 1 (early stopping enabled) |
| Batch size | 1 (gradient accumulation not used) |
| Optimizer | paged_adamw_8bit |
| Learning rate | 2e-4 (cosine schedule) |
| Warmup | 250 steps |
| Mixed precision | bf16 |
| Gradient checkpointing | Enabled |
| Eval frequency | Every 200 steps |
| Early stopping | Patience = 10, Δ = 1e-4 |
A custom collator ensured correct padding and label masking. ROUGE metrics were computed post-hoc to avoid OOM during training.
After fine-tuning, the model shows consistent improvement across all ROUGE metrics:
| Metric | Baseline | After QLoRA | Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROUGE-1 | 38.03 | 39.75 | +1.72 |
| ROUGE-2 | 12.26 | 15.37 | +3.11 |
| ROUGE-L | 21.35 | 22.21 | +0.86 |
| ROUGE-Lsum | 31.45 | 36.53 | +5.08 |
💡 ROUGE-Lsum improved by +5.1 points — indicating significantly better sentence-level summary coverage.
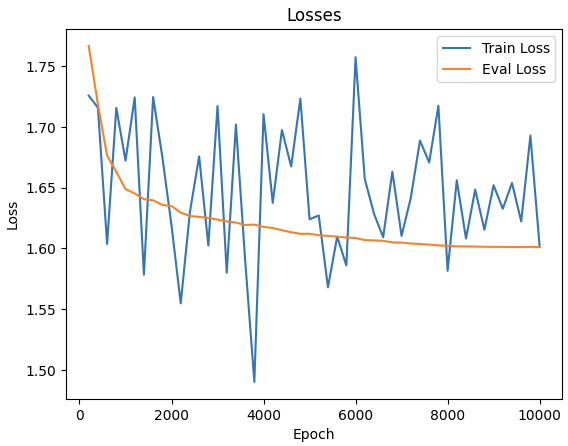
Qualitatively, generated summaries became:
We successfully demonstrated that QLoRA enables effective domain adaptation of Qwen3-1.7B on consumer hardware, yielding measurable gains in scientific summarization quality with minimal computational cost.
This project serves as a reproducible blueprint for efficient LLM adaptation in low-resource research settings — particularly valuable for biomedical NLP where domain expertise and compute often compete.