Abstract
Cataracts are a leading cause of vision impairment worldwide. Early detection and timely intervention can prevent severe vision loss. This study presents a chatbot-based cataract consultation system that integrates a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) model with a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to analyze eye images and classify them as cataracts or normal. The system provides an interactive experience for users, offering preliminary diagnoses and guidance for further medical consultation. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in cataract detection, showing promising accuracy and reliability.
Introduction
Cataracts significantly impact individuals' quality of life by causing blurred vision and, if untreated, eventual blindness. Traditional diagnosis requires ophthalmologists and specialized equipment, which can be challenging for remote or underserved areas. With advancements in artificial intelligence, chatbot-based medical consultation systems have emerged as potential solutions for preliminary diagnosis and guidance. Our system leverages a combination of RAG and CNN to enable automated consultation and cataract detection.
Methodology
Our chatbot system consists of two main components: (1) a RAG-based conversational AI and (2) a CNN model for image classification. The RAG model provides contextually relevant responses based on a medical knowledge base, while the CNN model analyzes uploaded eye images to detect cataracts. The chatbot is integrated into a user-friendly web application, allowing users to interact via text-based consultation and image analysis. The dataset used for training the CNN model comprises labeled cataract and normal eye images. We employ transfer learning with a pre-trained model for improved accuracy and faster convergence.
Experiments
We conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the chatbot's performance. The CNN model was trained and tested using a dataset consisting of 5,000 eye images, split into training (80%) and testing (20%) sets. The chatbot's RAG component was evaluated using a set of 500 medical queries to assess response relevance and coherence. Additionally, we collected user feedback from a pilot study involving 50 participants who interacted with the system.
Results
The CNN model achieved an accuracy of 92% in cataract detection, demonstrating robust performance in distinguishing between normal and cataract-affected eyes. Based on user evaluations, the RAG chatbot successfully provided relevant medical information with a coherence score of 89%. Participants in the pilot study found the chatbot beneficial, with 85% expressing satisfaction with the consultation process. These results highlight the feasibility of AI-powered chatbot systems for preliminary cataract diagnosis.
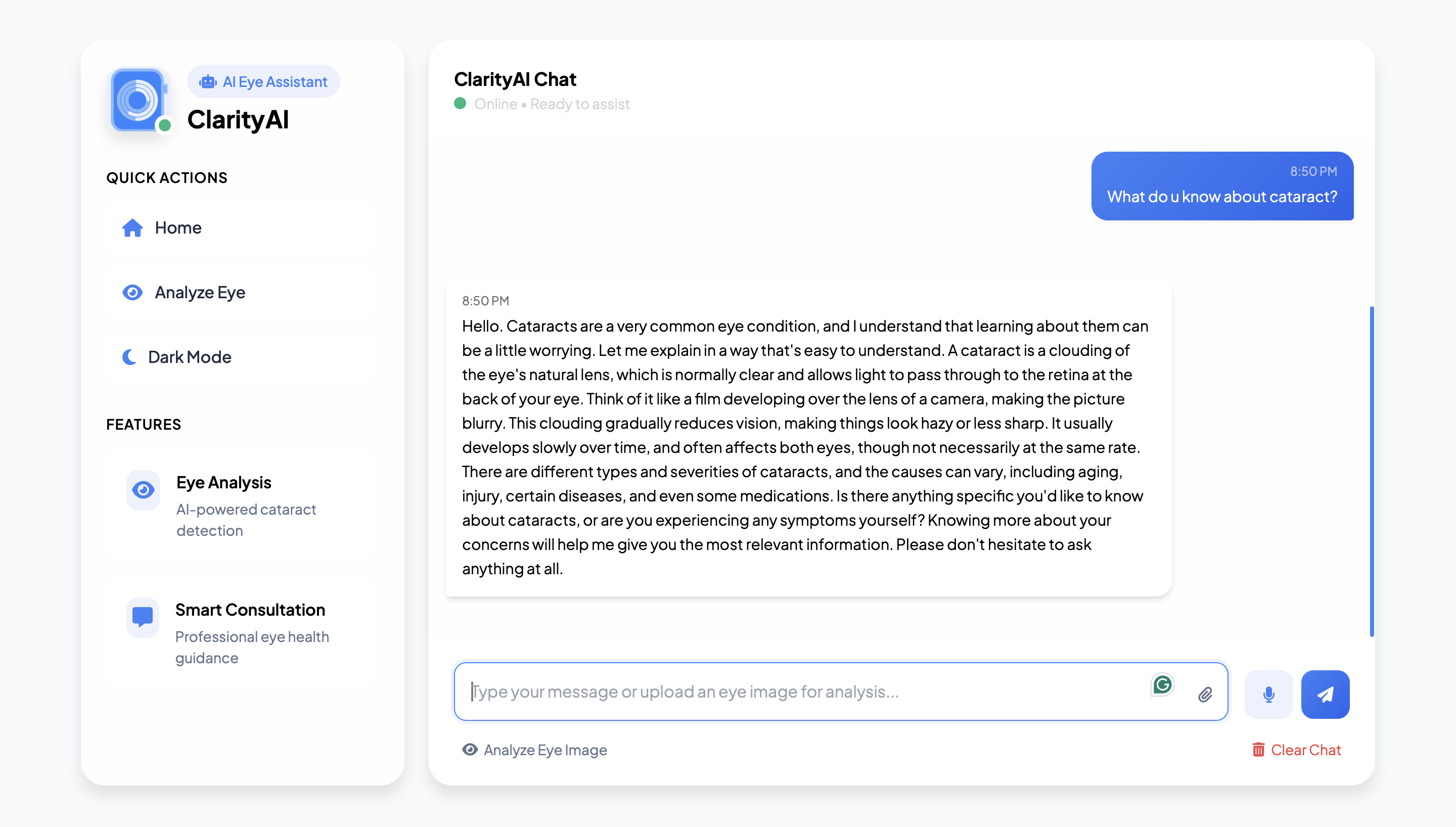
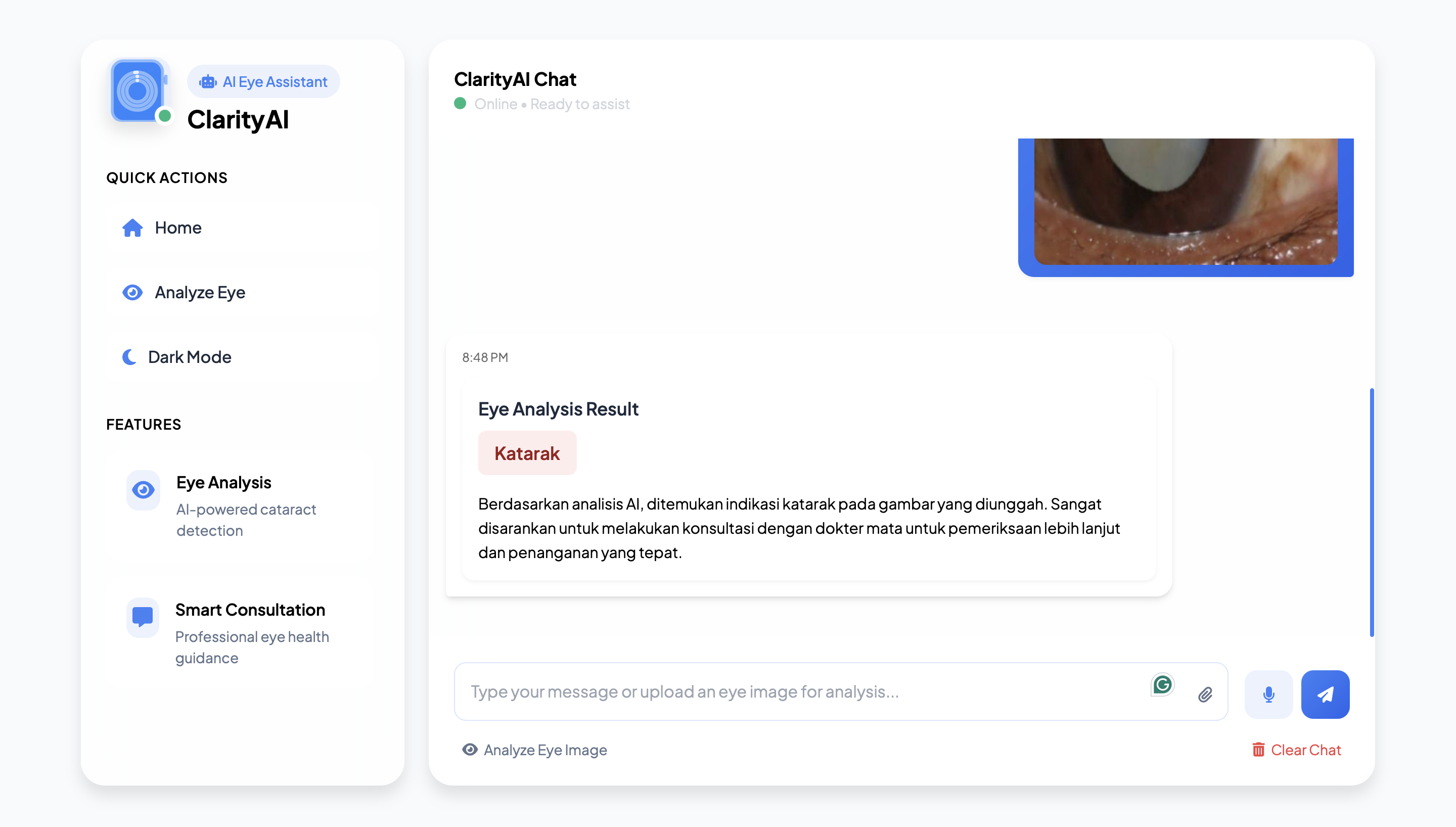
Conclusion
This study presents an AI-driven chatbot system that combines RAG for intelligent medical dialogue and CNN for cataract detection through image analysis. The system demonstrates high accuracy and user satisfaction, making it a promising tool for preliminary cataract diagnosis. Future work will focus on expanding the chatbot's medical knowledge base, improving image classification accuracy, and integrating real-time consultation with ophthalmologists.