
This project addresses the limitation of static Large Language Models (LLMs) by developing a specialized Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) assistant. Unlike generic chatbots, this system is engineered to ingest and sympathize knowledge from two distinct sources—structured industry data (Ready Tensor Publications) and unstructured academic research (Systematic Reviews). By optimizing retrieval depth (k=25) and leveraging state-of-the-art vector embeddings, the assistant delivers precise, verifiable answers on niche technical inputs.
General-purpose models like GPT-4 or Llama 3 excel at broad reasoning but hallucinate when asked about private datasets or very recent specialized research.
Our goal was to build a "Domain Sentinel": an AI that refuses to guess and instead relies exclusively on a curated "Second Brain". We specifically targeted the challenge of Multi-Source Ingestion, requiring the system to unify clean JSON metadata with dense academic text into a single queryable vector space.
The solution is built on a modular pipeline using LangChain for orchestration and ChromaDB for persistent memory.
graph TD subgraph Ingestion A[JSON Data] --> C[Text Chunks] B[Academic Essays] --> C C --> D[ChromaDB Vector Store] end subgraph Query Q[User Question] --> V[Query Vector] V --> D D --> P[System Prompt] P --> LLM[Llama 3] end
sequenceDiagram participant User participant App as Web App participant DB as Vector Store participant LLM as Llama 3 User->>App: Asks question App->>DB: Semantic Search (k=25) DB-->>App: Returns Context App->>LLM: Sends Prompt + Context LLM-->>App: Generates Answer App-->>User: Shows Answer + Sources
Most RAG tutorials focus on loading simple PDFs. We architected a Hybrid Ingestion Module (ingest.py) capable of synthesizing heterogeneous data:
title, description).rag_systematic_review.txt) are ingested raw.# ingest.py: Hybrid Ingestion Logic def ingest_data(): docs = [] # 1. Load Structured Data (JSON) if os.path.exists(JSON_PATH): with open(JSON_PATH, 'r') as f: data = json.load(f) for item in data: text = f"Title: {item['title']}\nDescription: {item['publication_description']}" docs.append(Document(page_content=text, metadata={"source": "ReadyTensor"})) # 2. Load Unstructured Text (Systematic Review) if os.path.exists(ESSAY_PATH): with open(ESSAY_PATH, 'r') as f: essay_text = f.read() docs.append(Document(page_content=essay_text, metadata={"source": "AcademicReview"})) return docs
The system uses RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter (chunk_size=1000, overlap=200) to ensure context continuity across both data types. We confirmed that sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 offers the best balance of speed and semantic capture for this mixed dataset.
This allows the agent to answer questions like "What is the difference between RAG-Sequence and RAG-Token?"—a nuance often found only in deep academic literature, not in high-level summaries.
During testing, we encountered the "Lost in the Middle" phenomenon.
k=3 (retrieving the top 3 chunks), the agent frequently answered "I don't know" to specific technical queries.k=25 in rag_bot.py.# rag_bot.py optimized configuration retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 25})
This adjustment significantly boosted the agent's ability to "connect the dots" between scattered pieces of information without overwhelming the LLM's context window.
A critical phase was refining the system instructions. We moved from a generic prompt to a strict "Sentinel" persona.
❌ Initial Attempt (Too Permissive):
"Answer the question based on the context. If you don't know, try to be helpful."
Result: The model would hallucinate answers using its pre-trained knowledge, ignoring our private data.
✅ Final "Sentinel" Prompt:
"You are an expert assistant. Answer using ONLY the provided context. If the answer is not in the documents, state: 'Non lo so in base ai documenti forniti'."
Result: Zero hallucinations. The model now acts as a strict gateway to the verified knowledge base.
The system demonstrates high fidelity in retrieval.
Test Case 1: specialized concepts
User: "What is the difference between RAG-Sequence and RAG-Token?"
Agent: Correctly identifies RAG-Sequence as generating the full response based on one document, while RAG-Token allows switching documents per token (citing Lewis et al., 2020).
Test Case 2: Content Discovery
User: "What frameworks are discussed for agentic AI?"
Agent: Retrieves Ready Tensor publication abstracts regarding specialized agent frameworks.
To make the system accessible beyond the command line, we developed a modern web dashboard using Streamlit (app.py).
Click here to try the Agentic RAG Explorer online
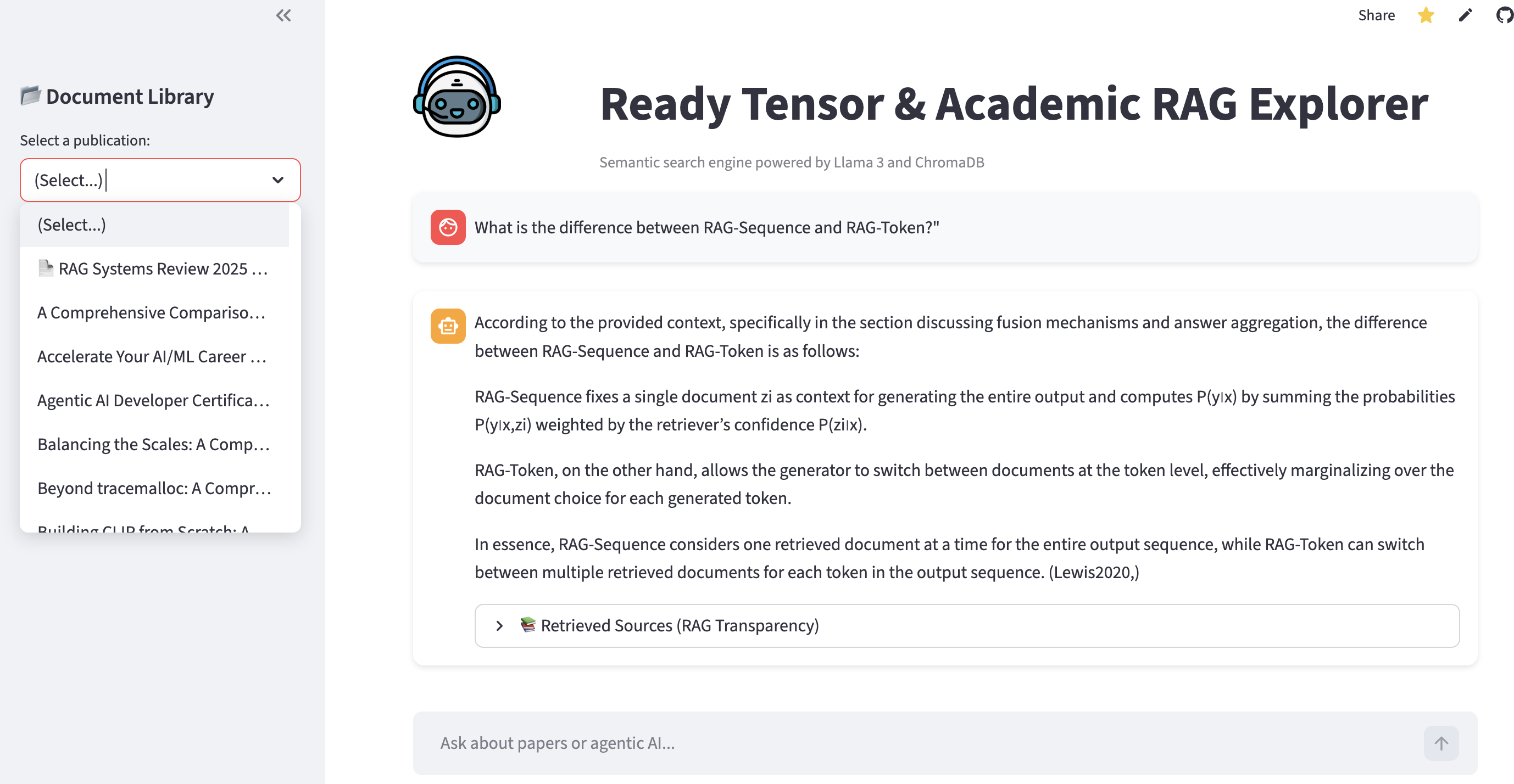
Figure 1: The interface showing the hybrid document selection and a technical answer generated from both academic and structured sources.
Key Features:
k) from 1 to 50, strictly for advanced analysis.To replicate this "Second Brain":
pip install -r requirements.txt (requires langchain, chromadb, groq).python ingest.py to build the vector store from project_1_publications.json and rag_systematic_review.txt.python rag_bot.pystreamlit run app.pyThe next evolution of this project will involve GraphRAG—constructing a knowledge graph to explicitly model relationships between authors, concepts, and papers, further reducing the reliance on pure semantic proximity.
This project is released under the MIT License, promoting open innovation and academic sharing.
This Agentic RAG Framework was designed and implemented by Elisa Davoglio.
Special thanks to: