The Tiger That Writes READMEs A clever tiger, swift and bright, Turns code to words with all her might. She scans your GitHub with careful eye, And crafts a guide that helps you try. With memory sharp, she learns your name, And plays a friendly documentation game. From messy folders, neat she'll weave, So everyone can soon believe. This tigress writes with gentle grace, To put a smile on every face. She makes your project clear and grand, With helpful words and guiding hand.
In the modern software development ecosystem, README files serve as the critical first impression and primary documentation for any project. However, creating comprehensive, professional READMEs remains a significant challenge for developers. The current landscape presents three core issues:
Documentation Debt: Developers often prioritize code over documentation, leading to incomplete or outdated READMEs that fail to communicate project value effectively.
Inconsistency Across Projects: Different projects within the same organization or by the same developer often have wildly varying documentation standards, making it difficult for users to understand and adopt new tools.
Time-Consuming Process: Crafting a thorough README requires analyzing repository structure, understanding dependencies, documenting architecture, and creating installation instructions—a process that can take hours for complex projects.
This problem is particularly significant because in open-source ecosystems, high-quality documentation directly correlates with project adoption, contributor engagement, and overall success. A poor README can doom an otherwise excellent project to obscurity.
Traditional approaches to documentation generation have relied on templates, simple parsers, or manual processes—all of which have significant limitations. Agents represent the ideal solution for several reasons:
Multi-Specialization: Different aspects of README creation require different expertise. Our system employs specialized agents: one for repository analysis, another for initial drafting, a critic for quality assessment, and a refiner for iterative improvement. This mimics how human teams approach documentation but with AI efficiency.
Contextual Understanding: Unlike template-based solutions, agents can understand repository context, recognize project patterns, and generate documentation that's actually relevant to the specific codebase. They can identify whether a project is a web framework vs. a CLI tool and document accordingly.
Iterative Refinement: The critic-refiner loop allows for continuous improvement, mirroring human editing processes. This ensures the final output meets professional standards rather than just being "good enough."
Memory and State Management: By incorporating session state tools, the system maintains context across interactions, enabling features like chatbot assistance that remembers user preferences and project details.
Adaptability: Agents can leverage external tools (like MCP for GitHub integration) and adapt to different project types, technologies, and documentation standards without requiring manual reconfiguration.
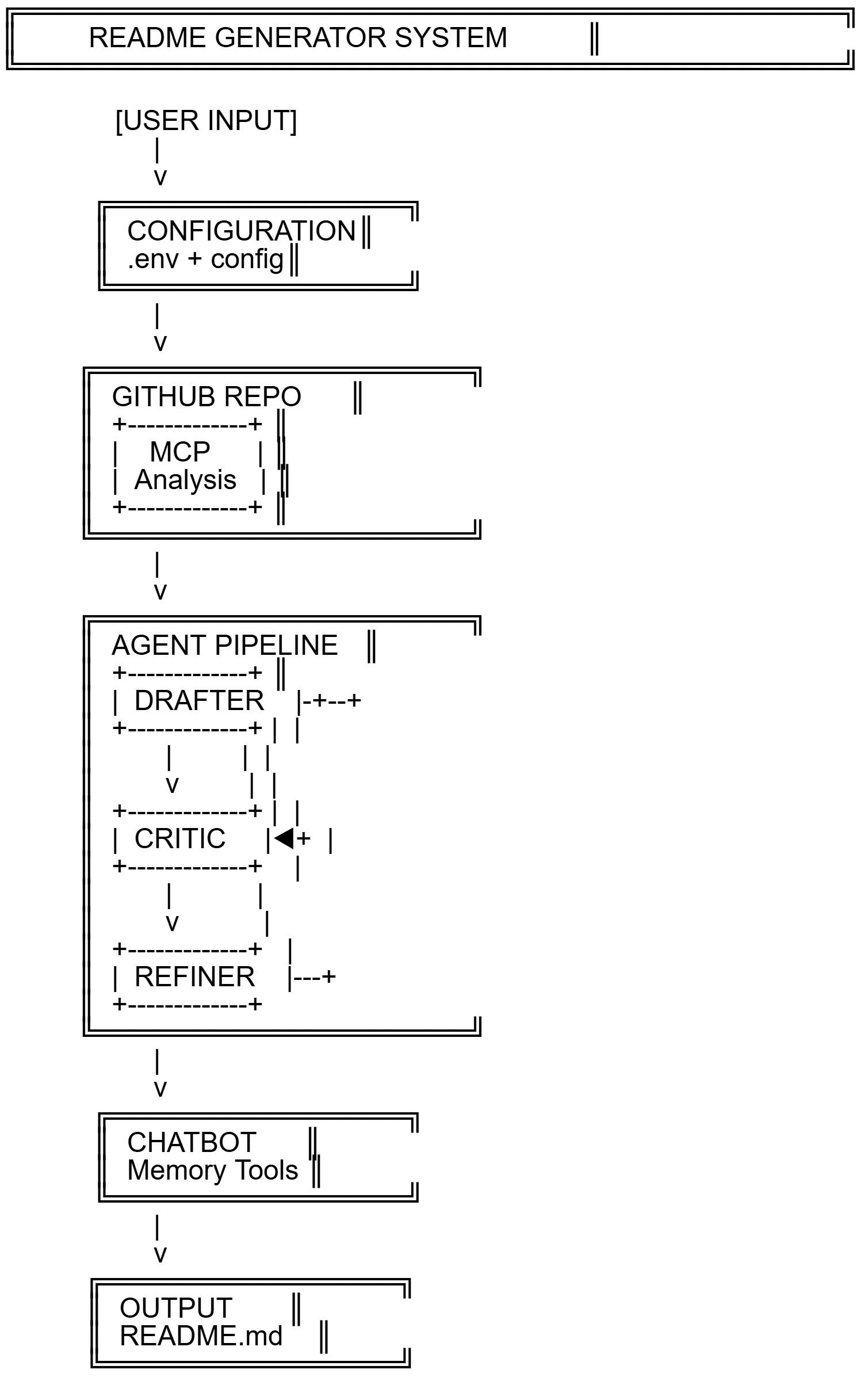
The ADK-README system is a sophisticated multi-agent orchestration platform that transforms repository analysis into professional documentation through a carefully designed pipeline:
System Architecture:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ FOUR-STAGE AGENT ORCHESTRATION │ ├─────────────────────────────────────────────┤ │ │ │ STAGE 1: Repository Analysis │ │ • GitHub MCP integration for live access │ │ • Automated structure and dependency scan │ │ • Metadata extraction (language, license) │ │ │ │ STAGE 2: Draft Generation │ │ • Initial README creation with proper │ │ sections and formatting │ │ • Context-aware content generation │ │ │ │ STAGE 3: Quality Refinement Loop │ │ • Critic agent evaluates completeness │ │ • Refiner agent incorporates feedback │ │ • Loop continues until "APPROVED" status │ │ │ │ STAGE 4: Interactive Chatbot │ │ • Persistent memory for user context │ │ • Tool-based session state management │ │ • Follow-up documentation assistance │ │ │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Google ADK Framework: Provides the foundation for agent creation, tool integration, and orchestration
Multi-Agent Pipeline: SequentialAgent coordinates Draft → Loop (Critic+Refiner) → Chatbot workflow
Session State Management: Custom tools (save_userinfo, retrieve_userinfo) enable persistent memory
MCP Integration: Direct GitHub repository access without local cloning
Events Compaction: Intelligent context management to optimize token usage
Git Agent: Repository analysis using MCP tools
Draft Agent: Initial README creation from repository data
Critic Agent: Quality assessment with approval mechanism
Refiner Agent: Iterative improvement based on feedback
Chatbot Agent: Interactive assistance with memory
👤 User: Hi there, how are you doing today? What is my name? 🤖 Bot: Username not found 👤 User: My name is Sam. I'm from Poland. 🤖 Bot: Nice to meet you, Sam! I've saved your information. 👤 User: What is my name? Which country am I from? 🤖 Bot: Your name is Sam and you're from Poland.
This project represents a comprehensive implementation of modern agent-based systems using Google's cutting-edge tools:
Core Technologies:
Google ADK (0.10.2): Primary framework for agent development and orchestration
Gemini AI Models: Multiple model types (2.0 Flash for drafting, 1.5 Pro for critique) optimized for different tasks
MCP Protocol: GitHub Copilot's Model Context Protocol for repository access
SQLite Database: Persistent session storage for state management
Configuration First: Created a robust Config class with environment validation and model selection
Tool Development: Built custom tools for session state management using ADK's ToolContext
Agent Specialization: Designed each agent with specific instructions and output keys
Pipeline Orchestration: Used SequentialAgent and LoopAgent for workflow coordination
Enhanced Features:
Technical Improvements:
Production Readiness:
Monitoring & Logging: Comprehensive observability with metrics on generation time, quality scores, and error rates
Rate Limiting: Smart rate limiting for API calls to external services
Cost Optimization: Dynamic model selection based on project complexity and budget constraints
Team Collaboration: Features for team review and approval workflows before README publication
Version Control: Track changes to generated READMEs with diff views and rollback capabilities
https://github.com/AhmadTigress/Google_Events
This project is licensed under the MIT License