An automated system is needed to detect anomalies from live camera feed, alert the police and generate a report. This would improve surveillance and law enforcement efficiency and effectiveness. Most crimes occur at night where its very easy for humans to miss clues and hints about the occurrence. Automating it would enable faster response and potentially saving lives.
In this paper, we propose a novel automated surveillance framework utilizing Magnitude-Contrastive Glance-and-Focus Network (MGFN) for real-time video anomaly detection. Our system integrates state-of-the-art weakly-supervised video anomaly detection techniques to identify potential crimes from surveillance feeds with unprecedented speed and accuracy. The proposed method detects anomalies in just 0.2 seconds and generates detailed reports within 3 seconds, enabling immediate response by law enforcement. The Glance Module captures long-term context, while the Focus Module refines local features to enhance detection of anomalous regions.
Magnitude-Contrastive Loss ensures robust differentiation between normal and anomalous activities, further optimized by top-k feature extraction. Additionally, a classification module identifies crime types, instruments, and severity, generating comprehensive reports for police use. Experiments on UCF-Crime and XD-Violence benchmarks demonstrate the efficacy of our system.
Our solution represents a transformative step toward proactive crime prevention and efficient surveillance systems.
Police generate and store a large volume of data relating to crime and criminals. However, the challenge does not end in storing and processing the data but in predicting crime hotspots, forecasting crime trends, and predicting offender characteristics. The problem includes identifying areas of specific crimes like murder, property offenses, and other bodily offenses and predicting future hotspots, using the data to predict when and where these crimes occur and also to link the pattern of crime with that of the offenders and predict the likelihood of future crimes based on demographic information and criminal history. This would improve surveillance and law enforcement efficiency and effectiveness.
The rise in urbanization and technological advancement has led to an exponential increase in the deployment of surveillance systems worldwide. However, traditional surveillance systems face limitations in real-time anomaly detection, often requiring manual oversight, which is prone to human error. Crimes occurring at night are particularly challenging to monitor due to reduced visibility and alertness.
We address this critical gap by introducing an automated surveillance framework powered by Magnitude-Contrastive Glance-and-Focus Network (MGFN). This system leverages weakly-supervised learning to detect anomalies in real-time and assist law enforcement with actionable insights. Our approach combines spatial-temporal information extraction with feature amplification to enhance anomaly detection accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. By integrating predictive analytics and classification modules, our system not only detects anomalies but also predicts crime hotspots, trends, and offender characteristics.

Several methods for video anomaly detection have been proposed, including weakly-supervised learning approaches that utilize spatial-temporal features. Previous works like RTFM and MIL-based anomaly detection techniques focus on feature extraction but often fail to account for scene variations, resulting in suboptimal performance. The introduction of Feature Amplification Mechanism (FAM) and Magnitude-Contrastive Loss (MC Loss) in MGFN addresses these shortcomings by enhancing discriminative power and consistency of feature magnitudes.
Benchmarks such as UCF-Crime and XD-Violence have been widely used to evaluate anomaly detection methods. While existing techniques achieve reasonable performance, they lack the ability to provide real-time, context-aware analysis. Our proposed MGFN outperforms these models, setting a new standard in anomaly detection with its glance-and-focus architecture.
The proposed system consists of :
Glance Module: Captures global context from the entire video sequence using video clip-level transformers.
Focus Module: Refines local features in anomalous regions through self-attentional convolution.
Magnitude-Contrastive Loss: Ensures discriminative learning between normal and abnormal features while addressing scene variations.
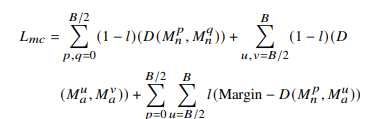
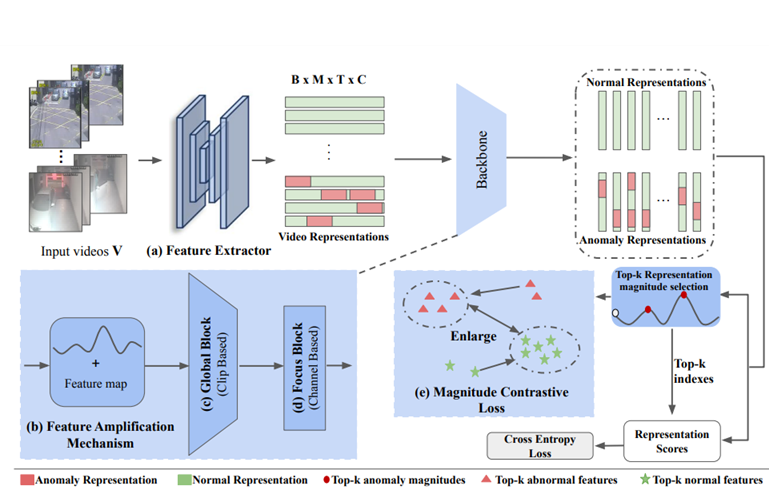
The cropped video of the anomaly is sent to a battery of classification models that finds the intricate details about the anomaly that has occurred (type of anomaly: assault, robbery, etc., instruments used: knife, gun, etc.) and finds the severity on a scale of 1-10.
Anomaly details, including time, location, and severity, are compiled into a report for law enforcement. Predictive analytics modules identify crime hotspots and trends, enabling proactive crime prevention strategies.
.png?Expires=1773507335&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=m0bqQ2yyjJ0LyJCNgqAEJJZJRDEj36asVfEAXGirSvI5uuiddj6Z4SUzCoQp~URTRhnWUpqwCGUVb8MqHlzvFgvsNqT5yZ6vrkWPq9Lq-~MDvC~XuEJHsGFxi04X6mExEx13Kw~YVjvpiIc~4aAiva5LvetBtZhdTdq-GP9K5yfLvfhiWehDP9biJg2E9yUCQb4PSjD2zbCX1NB42gll8D1FXB13BQmFE~JvWdQ7cVUoyvtaqwOof5YKtgtDxxxsazlvzA2gtuVs9qguWjlKP56cJOlOyo0Xhp9iAsAPPUFx-7EcBNq8bHMzOPFgFsk6S9~I4f7SYCFLJnCf5Fdnzg__)
Datasets
The model was trained and tested on two large-scale benchmarks:
UCF-Crime: Evaluated using AUC (Receiver Operating Characteristic curve).
XD-Violence: Evaluated using Average Precision (AP).
Evaluation Metrics
AUC: Measures the model's ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal videos.
AP: Assesses the precision-recall trade-off in anomaly classification.
CCTV Footage
https://drive.google.com/file/d/10lvjoqStG17RVE2wZ2M-CVV5ruVQy10V/view?usp=sharing
Result
https://drive.google.com/file/d/17GNMWxvo5juylXi4ceaE3K4tFTVhCT97/view?usp=sharing
Evaluation Metrics
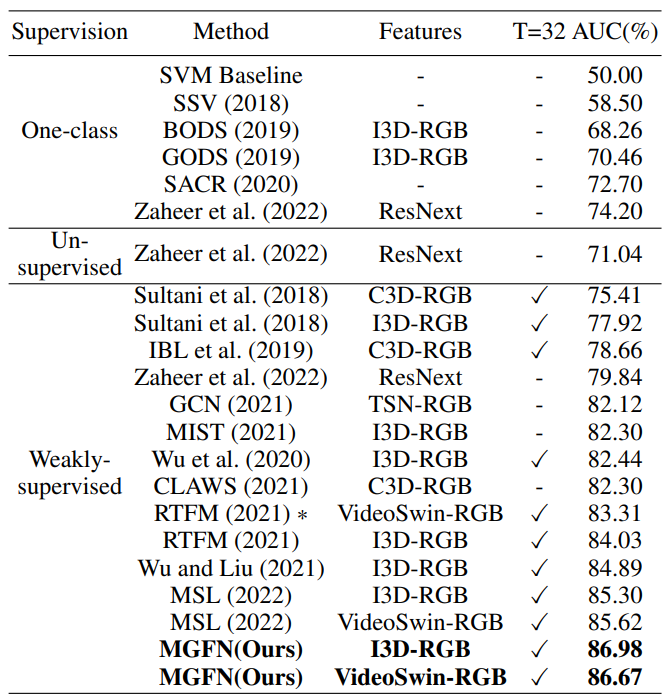
The MGFN model achieved state-of-the-art performance on both benchmarks:
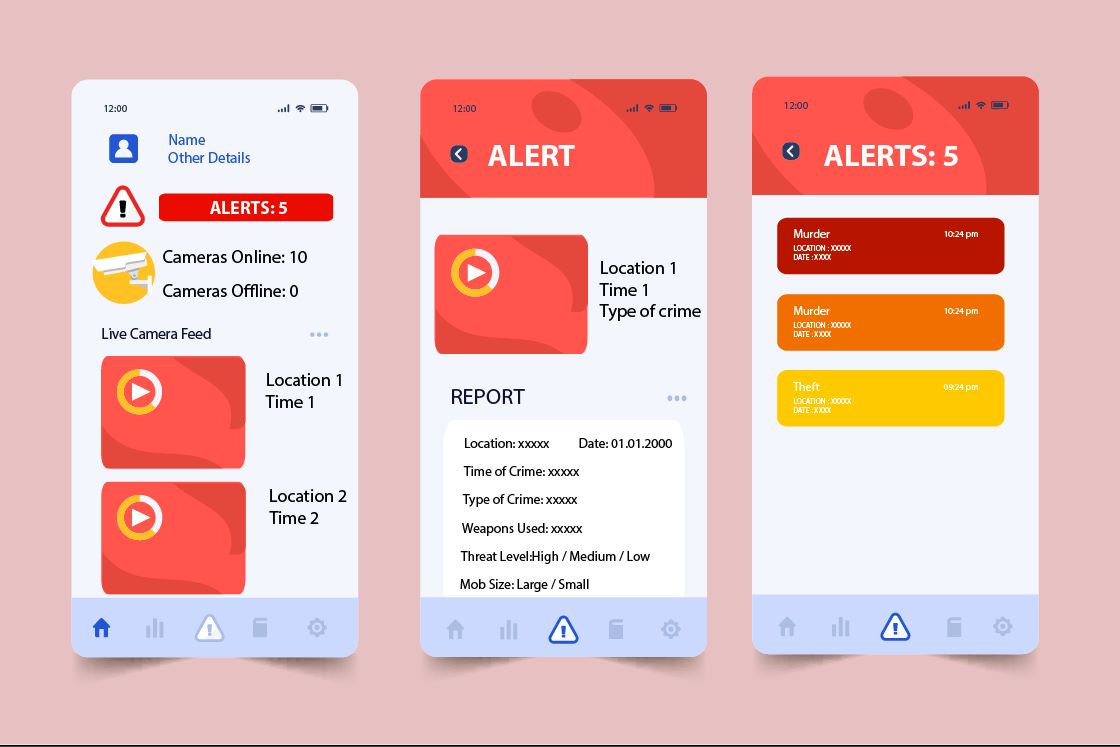
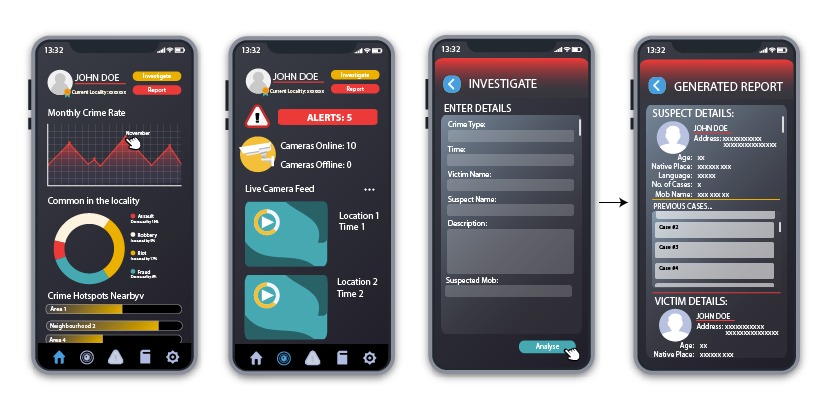
Here is a wireframe of the Android application.
The proposed system addresses key challenges in video anomaly detection and crime prevention. The glance-and-focus mechanism allows the model to balance global and local feature extraction, while the Magnitude-Contrastive loss enhances scene adaptability. The classification pipeline adds value by providing detailed insights into detected anomalies. Additionally, the integration of predictive analytics facilitates proactive policing, optimizing resource allocation and improving community safety.
Despite its success, the system has limitations, such as reliance on labeled training data and potential scalability challenges in dense urban areas. Future work will focus on unsupervised learning methods and edge-based deployment for large-scale implementations.
This paper introduced an advanced AI-powered surveillance system integrating MGFN for ultra-fast anomaly detection and predictive analytics for crime prevention. The system achieves state-of-the-art performance on established benchmarks, demonstrating its efficacy in real-world scenarios. By enabling real-time anomaly detection and proactive crime analysis, the system significantly enhances law enforcement's capabilities, paving the way for safer communities.
We thank the creators of UCF-Crime and XD-Violence datasets for providing valuable benchmarks. Special thanks to NVIDIA for GPU resources that enabled efficient model training.